Question
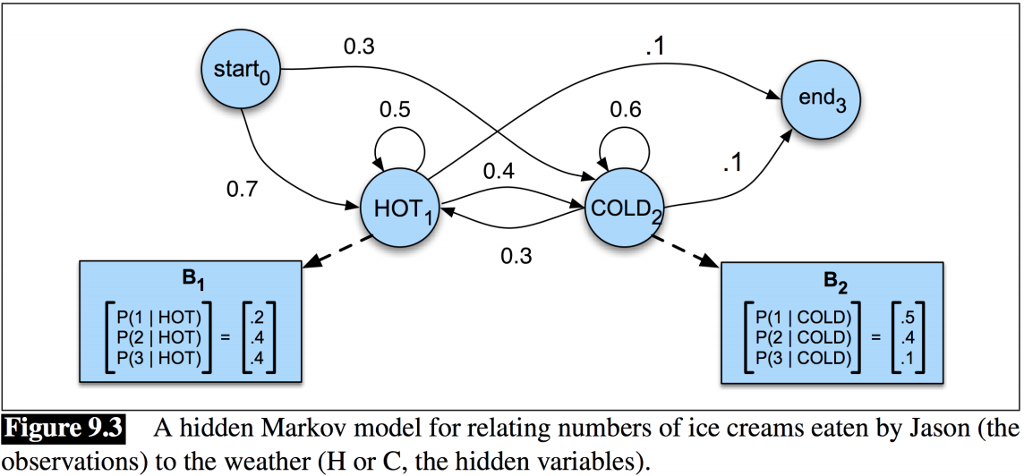
Here is an HMM diagram, adapted from Speech and Language Processing (Jurafsky & Martin, 3rd ed. draft). The temperature of day (hidden state HOT or
Here is an HMM diagram, adapted from Speech and Language Processing (Jurafsky & Martin, 3rd ed. draft). The temperature of day (hidden state HOT or COLD) changes the number of ice cream cones Dan Jurafsky eats (1, 2, or 3). Since the days temperature impacts the number of ice creams eaten, we can infer the hidden states from just the observed ice cream consumption.
A) Give an observation sequence with a most probable hidden state sequence that starts with a HOT day and ends with a COLD day. Show your probability calculations.
B) Give an observation sequence with a most probable hidden state sequence that starts with COLD day and ends with a HOT day. Show your probability calculations
0.3 starto 0.5 0.6 end 3 0.4 0.7 HOT COLD 0.3 2 P(1 | HOT) .2 P(2 | HOT)4 P(3 | HOT)4 P(1 COLD) P(2 COLD).4 P(3 | COLD) Figure 9.3 observations) to the weather (H or C, the hidden variables). A hidden Markov model for relating numbers of ice creams eaten by Jason (the 0.3 starto 0.5 0.6 end 3 0.4 0.7 HOT COLD 0.3 2 P(1 | HOT) .2 P(2 | HOT)4 P(3 | HOT)4 P(1 COLD) P(2 COLD).4 P(3 | COLD) Figure 9.3 observations) to the weather (H or C, the hidden variables). A hidden Markov model for relating numbers of ice creams eaten by Jason (theStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


