Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Here is the Heap class code: #include #include using namespace std; // This class implements a heap (heap-tree). class Heap { public: Heap(); // Constructs
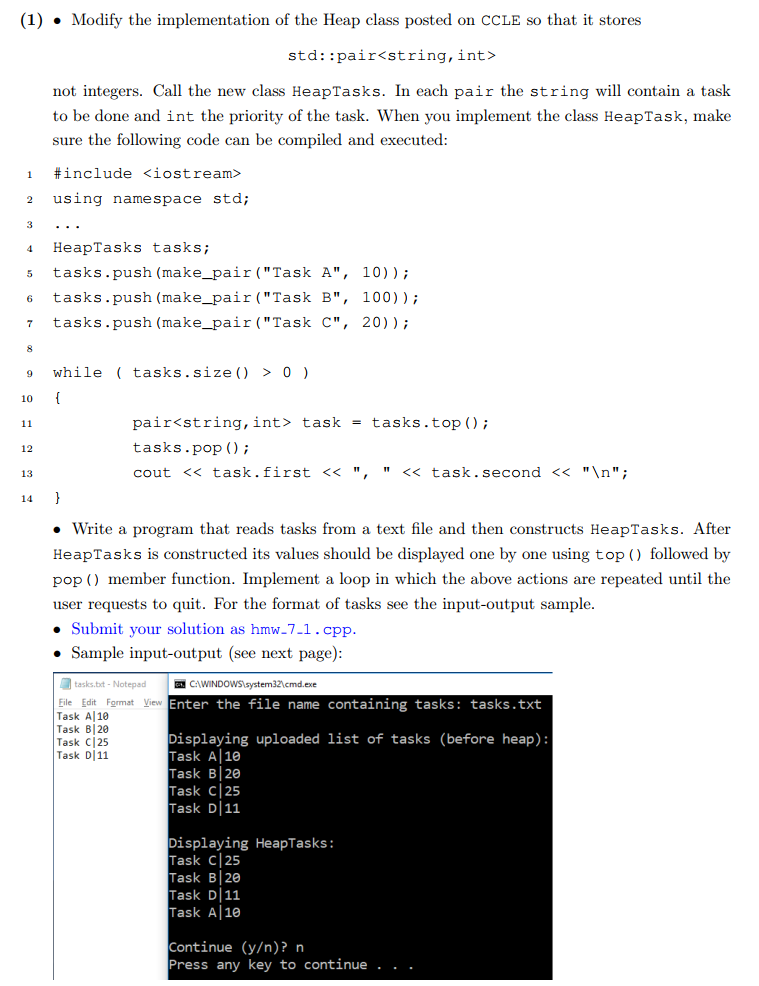
Here is the Heap class code:
#include#include using namespace std; // This class implements a heap (heap-tree). class Heap { public: Heap(); // Constructs an empty heap. void push(int new_element); // Adds a new element to this heap. int top() const; //Gets the maximum element stored in this heap. void pop(); //Removes the maximum element from this heap. int size() const; // Returns the number of elements in this heap. public: /** Turns the tree back into a heap, provided only the root node violates the heap condition. */ void fix_heap(); //Heapify is the process of converting a binary tree into a Heap data structure. /** Returns the index of the left child. @param index the index of a node in this heap @param index the index of a node in this heap @return the index of the left child of the given node */ int get_left_child_index(int index); /** Returns the index of the right child. @param index the index of a node in this heap @return the index of the right child of the given node */ int get_right_child_index(int index); /** Returns the index of the parent. @param index the index of a node in this heap @return the index of the parent of the given node */ int get_parent_index(int index); /** Returns the value of the left child. @param index the index of a node in this heap @return the value of the left child of the given node */ int get_left_child(int index); /** Returns the value of the right child. @param index the index of a node in this heap @return the value of the right child of the given node */ int get_right_child(int index); /** Returns the value of the parent. @param index the index of a node in this heap @return the value of the parent of the given node */ int get_parent(int index); vector elements; }; Heap::Heap() { elements.push_back(0); } void Heap::push(int new_element) { // Add a new leaf elements.push_back(0); int index = elements.size() - 1; // Demote parents that are smaller than the new element while (index > 1 && get_parent(index) 1) { elements[1] = last; fix_heap(); } } int Heap::size() const { return elements.size() - 1; } void Heap::fix_heap() { int root = elements[1]; int last_index = elements.size() - 1; // Promote children of removed root while they are larger than last int index = 1; bool more = true; while (more) { int child_index = get_left_child_index(index); if (child_index child) { child_index = get_right_child_index(index); child = get_right_child(index); } // Check if smaller child is larger than root if (child > root) { // Promote child elements[index] = child; index = child_index; } else { // Root is larger than both children more = false; } } else { // No children more = false; } } // Store root element in vacant slot elements[index] = root; } int Heap::get_left_child_index(int index) { return 2 * index; } int Heap::get_right_child_index(int index) { return 2 * index + 1; } int Heap::get_parent_index(int index) { return index / 2; } int Heap::get_left_child(int index) { return elements[2 * index]; } int Heap::get_right_child(int index) { return elements[2 * index + 1]; } int Heap::get_parent(int index) { return elements[index / 2]; } int main() { Heap tasks; tasks.push(1); tasks.push(3); tasks.push(-2); tasks.push(1); tasks.push(4); tasks.push(-9); tasks.push(1); tasks.push(5); while (tasks.size() > 0) { int task = tasks.top(); tasks.pop(); cout (1) Modify the implementation of the Heap class posted on CCLE so that it stores std: :pair not integers. Call the new class HeapTasks. In each pair the string will contain a task to be done and int the priority of the task. When you implement the class HeapTask, make sure the following code can be compiled and executed #include 2 using namespace std; 4 HeapTasks tasks s tasks.push (make_pair ("Task A", 10)); 6 tasks.push (make_pair ("Task B", 100)) 7 tasks.push (make_pair ("Task C", 20)) while tasks.size) > 0) 10 pairstring, int> task = tasks.top ( ); tasks.pop ) cout not integers. Call the new class HeapTasks. In each pair the string will contain a task to be done and int the priority of the task. When you implement the class HeapTask, make sure the following code can be compiled and executed #include 2 using namespace std; 4 HeapTasks tasks s tasks.push (make_pair ("Task A", 10)); 6 tasks.push (make_pair ("Task B", 100)) 7 tasks.push (make_pair ("Task C", 20)) while tasks.size) > 0) 10 pairstring, int> task = tasks.top ( ); tasks.pop ) cout
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


