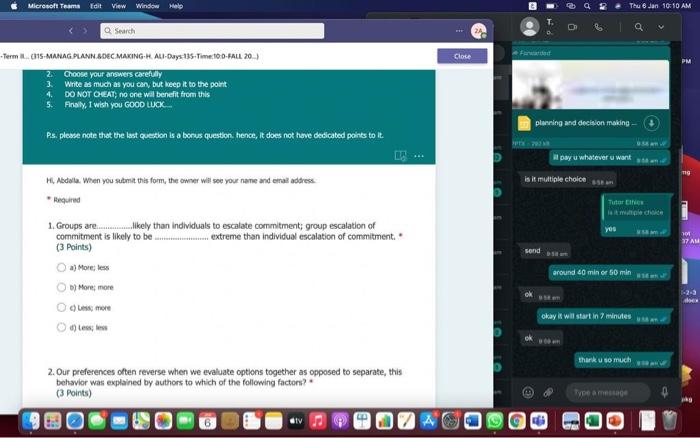
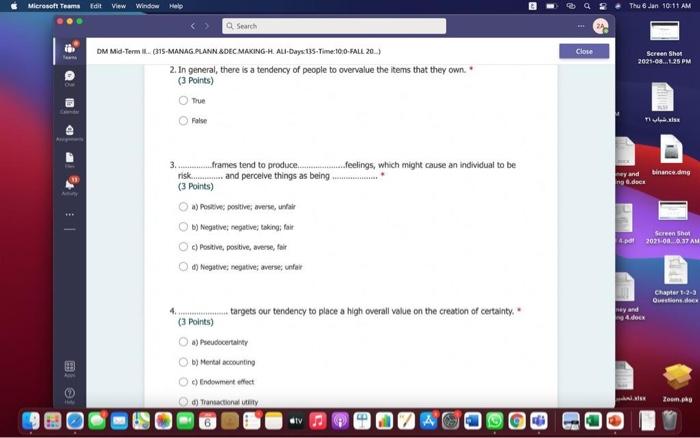
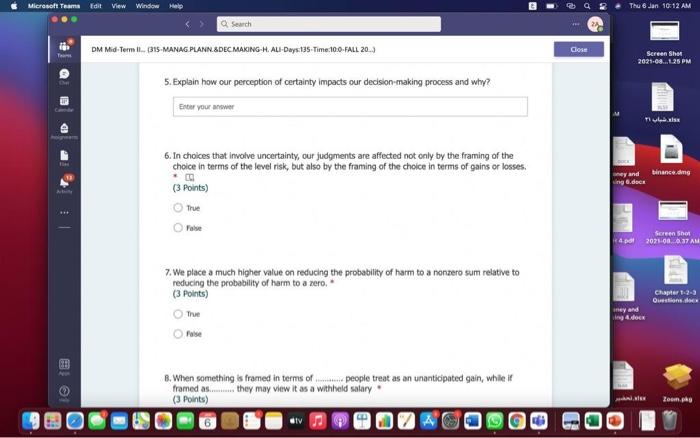
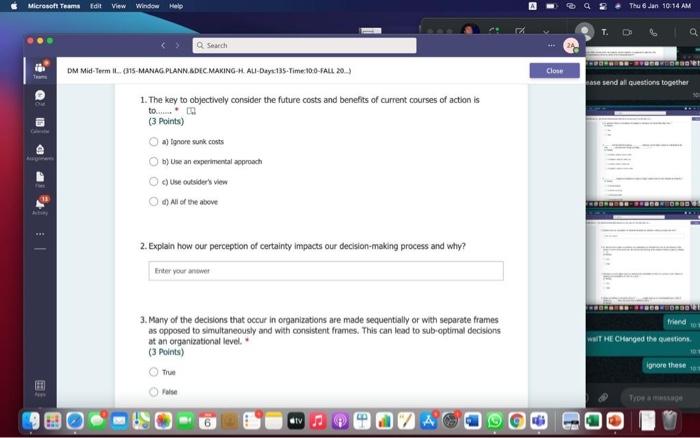
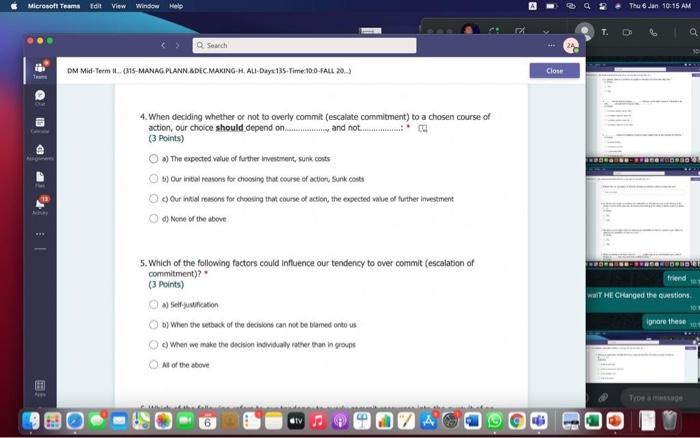
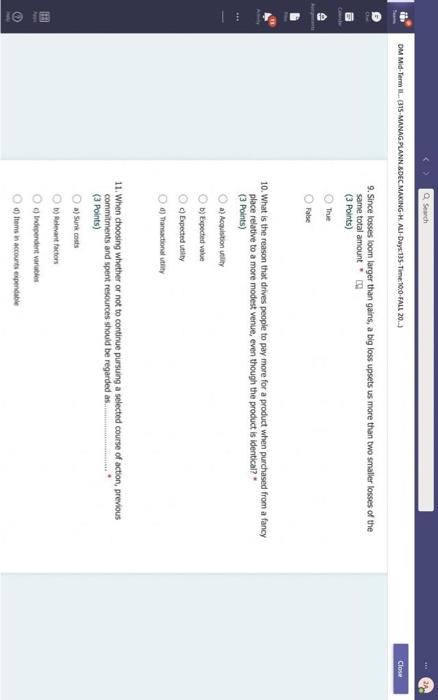
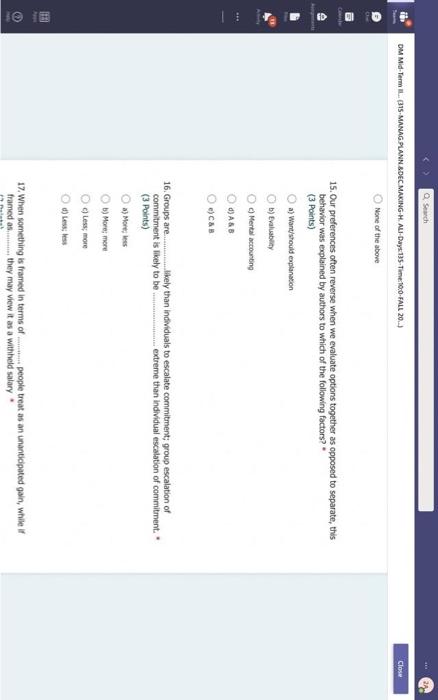
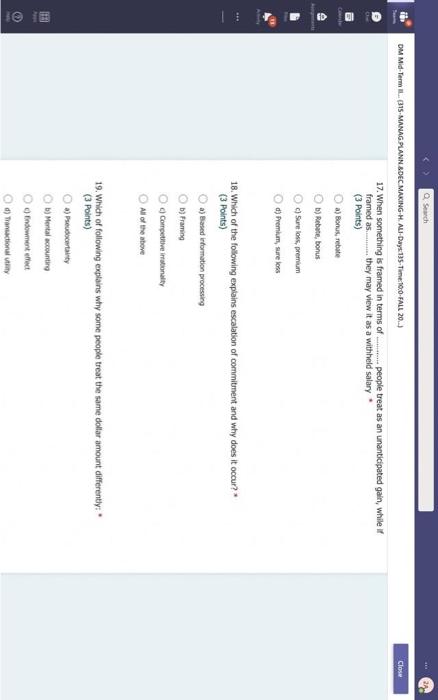
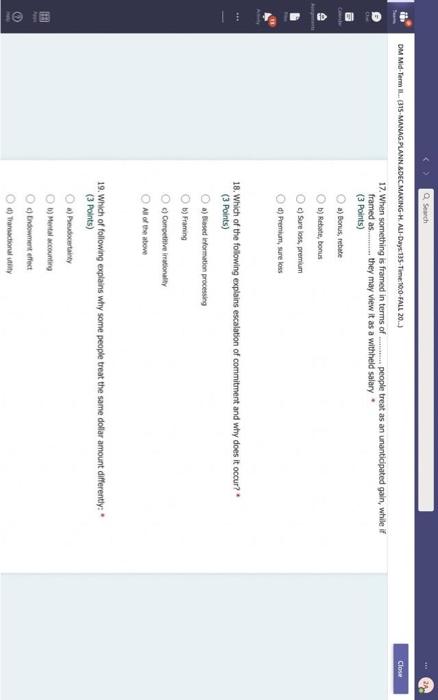
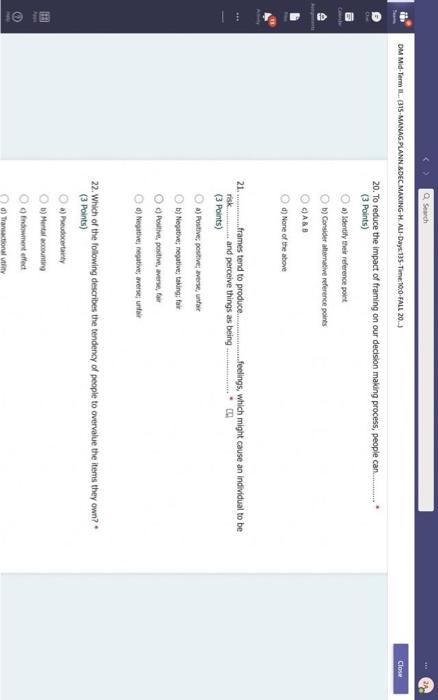
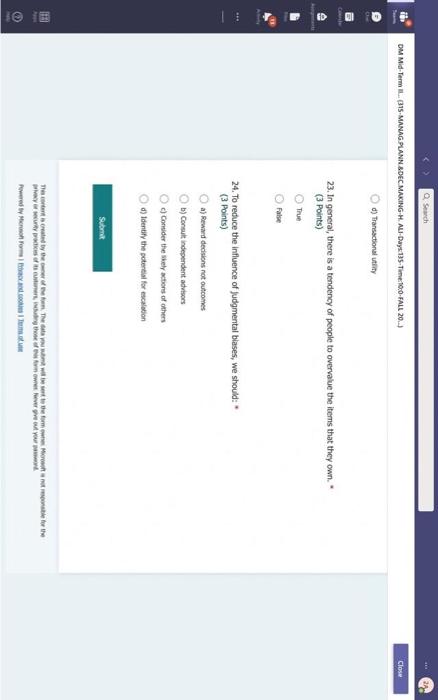
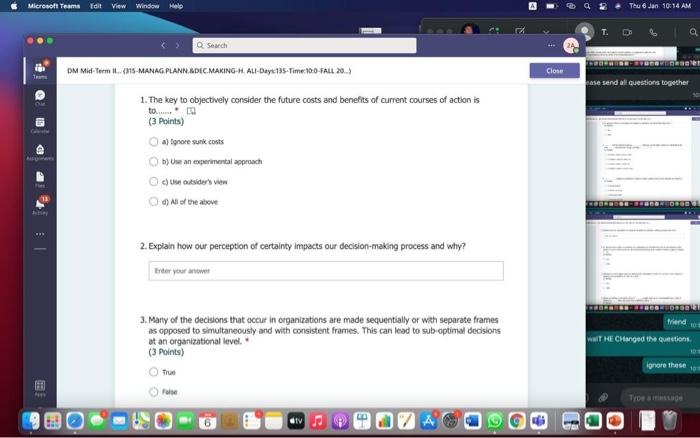
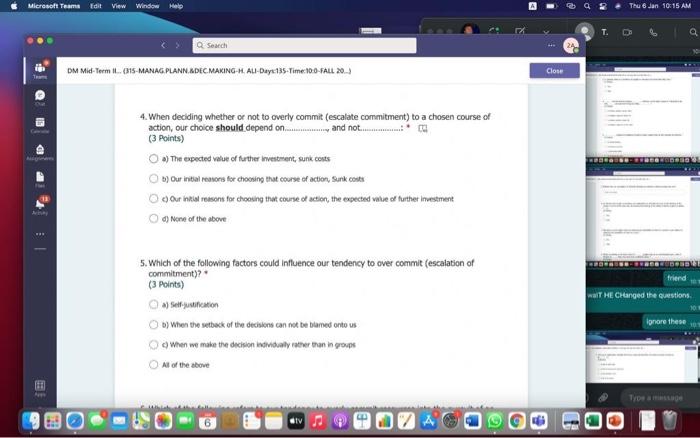
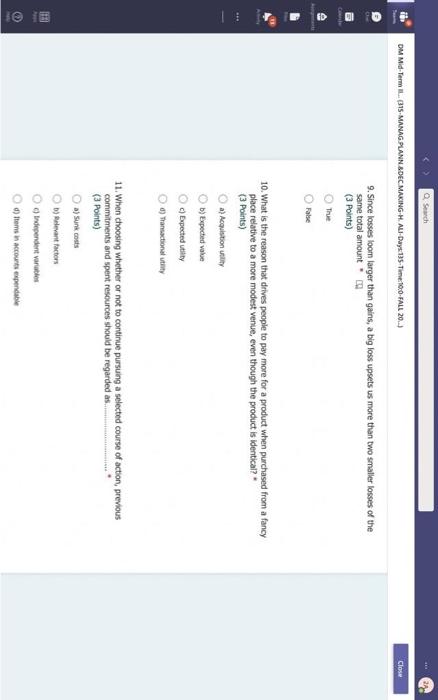
Hi, Abdala. When you sutmit this form, the owner will see your nane and enal address. Aeguired 1. Groups are Wikely than individuals to escalate cornmitment; group escalation of commitment is likely to be extreme than individual escalation of commitment. * (3 Points) a) More: less b) More; more 6) Lexs, more 6) Less; less 2. Our preferences often reverse when we evaluate options together as opposed to separate, this behavior was explained by authors to which of the following factors? * (3 Points) 2. In general, there is a tendency of people to overvalue the items that they own. * (3 Points) True Fatse 3. risk. frames tend to produce. feelings, which might cause an indwidual to be (3 Points) a) Posive; posthec; avere, wefair b) Negative; negative; laking; fair c) Postive, postive, avose, fair ) Negative; megative; averse; unfar 4. (3 Points) targets our tendency to place a high overall value on the creation of certainty, " a) Pseudocertainty b) Mental acooonting c) Endowmert effect d) Transactonal varity. 5. Explain how cur perception of certainty impacts our dedision-making process and why? 6. In choices that involve uncertainty, our judgments are affected not only by the framing of the choice in terms of the level risk, but also by the framing of the choice in terms of gains or losses. * Go (3 Points) True Falve 7. We place a much higher value on reducing the probability of harm to a nonzero sum relative to reducing the probability of harm to a zero. " (3 Polnts) The fase 8. When something is framed in terms of people treat as an unanticipated gain, whle if framed as. they may view it as a withheld salary " (3 Points) 1. The key to objectively consider the future costs and benefits of current courses of action is to [7 (3 Points) a) tgnore sunk costs b) Use an experimental approoch c) Use outuider's vitu d) Ai of the above 2. Explain how our perception of certainty impects our decision-making process and why? 3. Many of the decisions that occur in organizations are made sequentially or with separate frames as opposed to simultaneously and with consistent frames. This can lead to sub-optimal decisions at an organizational level. * (3 Points) True fase 4. When deciding whether or not to overly commit (escalate commitment) to a chosen course of action, our choice should depend on. (3 Points) a) The expected value of further investment, sunk costs b) Our inital reasons for chooning that course of action, Sunk costs c) Our intial reasons for chooing that course of action, the expected valie of further investment d) Nane of the above 5. Which of the following factors could influence our tendency to over commit fescalation of commitment)? " (3 Points) a) Serfyustifiation b) When the sebbock of the decisiens can not be blamed onte us c) When we make the decieion indidally moter tran in grous At of the atove 6. Which of the following refers to our tendency to overly commit resources into the pursuit of an initial goal or decision, irrespective of evidence suggesting otherwise? : (3 Points) a) Supply and demond b) Escalacion of comitment 4) Proeptual bissedrens d) Set.junzfication 7. We place a much higher value on reducing the probability of harm to a nanzero sum relative to reducing the probability of harm to a zero. " (3 Points) True False 8. In choices that involve uncertainty, our judgments are affected not only by the framing of the choice in terms of the level risk, but also by the framing of the choice in terms of gains or losses. (3 Polnts) True Falie 9. Since losses loom larger than gains, a big loss upsets us more than two smaller losses of the same total amount = \$ (3 Points) True Fabe 10. What is the reason that drives people to pay more for a product when purchased from a fancy place relative to a more modest venue, even though the product is identical? * (3 Points) a) Acquistion usility b) Expected value c) Expected utility d) Transactional unity 11. When choosing whether or not to continue pursung a selected course of action, previous commitments and spent resources should be regarded as. (3 Points) a) 5unk costs b) Relevant facters Q) Evependent varuatios d) frems in accounts expendable 12. (3 Points) targets our tendency to place a high overall value on the creation of certainty. * a) Preudocestainy b) Mental acoounting c) Endowmert effect d) Frarsectional velity 13. By merely considering choices framed as gains and losses separately, people have made suboptimal decisions, * (3 Points) True Fabe 14. Which of the following factors suggest that we have a strong preference for others who commit to a course of action and remain consistent in their opinions; as such, they face a high degree of pressure to appear consistent by continuing to support their prior conviction? " (3 Points) a) Imprewion mansgeewent b) Aeropeasi thaseines c) Correntibe irrabionalfy None of the above None of the above 15. Our preferences often reverse when we evaluate options together as opposed to separate, this behavior was explained by authors to which of the following factors? " (3 Points) a) Wantistould explanation b) Evaluabetity c) Mental actoonting d) A 5.B e) Ca B 16. Groups are.in.m.... Ilikely than individuals to escalate commitment; group escalation of commitment is likely to be extreme than individual escalation of commitment. * (3 Points) a) More: kes b) More; more c) Less, more d) Less; lest 17. When something is framed in terms of people treat as an unanticipated gain, while if framed as. they may view it as a withheld salary * 17. When something is feamed in terms of people treat as an unanticipated gain, while if framed as. (3 Points) they may view it as a withheld salary " a) sonus, rebate b) Rebete, bonus c) Sure loss, premum d) Premium, sure ioss 18. Which of the following explains escalation of commitment and why does it occur? : (3 Points) a) Elased irformation processing b) Framing c) Compether irrationality All of the above 19. Which of following explains why some people treat the same dollar amount differently: " (3 Points) a) Preudocertainty b) Mertal accountiry d) fidowment effect d) Transational varity 17. When something is fromed in terms of people treat as an unanticipated gain, while if framed as. they may view it as a withheld salary * (3 Points) a) Bonus, rebete b) Rebate, bonus c) Sure loss, premium d) Premium, sure ioss 18. Which of the following explains escalabon of commitment and why does it occur? * (3 Points) a) Eiosed ifformation processing b) Framing c) Corretinive irrosionalty All of the atowe 19. Which of following explains why some people treat the same dollar amount differently: " (3 Points) a) Peusocertainy b) Mental accounting c) Endowmers effect d) Transctional itaty 20. To reduce the impact of framing on our decision making process, people can. (3 Points) a) Identily theiv reference point b) Consider attemetive reference points c) A \& B d) None of the above 21. risk. and perceive things as being (3 Points) a) Postive; positive; avese, unfar b) Negative; negative; taking: far c) Positive, ponthe, avere, far d) Negntive; negative; wrene; unfar 22. Which of the following describes the tendency of people to overvalue the items they own? * (3 Points) a) hieusccertaiety b) Mental acoocuntion c) friowment affect d) Transectional vtiefy. d) Transactional utimy 23. In gencral, there is a tendency of people to overvalue the itcris that they own. (3 Polnts) True Falio 24. To reduce the influence of judgmental biases, we should: " (3 Points) a) Reward dedisions not oulcomes b) Consult independent advtsors c) Consider the skely actoons of others d) Identify the potereial for cucyiobion 1. The key to objectively consider the future costs and benefits of current courses of action is to [7 (3 Points) a) tgnore sunk costs b) Use an experimental approoch c) Use outuider's vitu d) Ai of the above 2. Explain how our perception of certainty impects our decision-making process and why? 3. Many of the decisions that occur in organizations are made sequentially or with separate frames as opposed to simultaneously and with consistent frames. This can lead to sub-optimal decisions at an organizational level. * (3 Points) True fase 4. When deciding whether or not to overly commit (escalate commitment) to a chosen course of action, our choice should depend on. (3 Points) a) The expected value of further investment, sunk costs b) Our inital reasons for chooning that course of action, Sunk costs c) Our intial reasons for chooing that course of action, the expected valie of further investment d) Nane of the above 5. Which of the following factors could influence our tendency to over commit fescalation of commitment)? " (3 Points) a) Serfyustifiation b) When the sebbock of the decisiens can not be blamed onte us c) When we make the decieion indidally moter tran in grous At of the atove 6. Which of the following refers to our tendency to overly commit resources into the pursuit of an initial goal or decision, irrespective of evidence suggesting otherwise? : (3 Points) a) Supply and demond b) Escalacion of comitment 4) Proeptual bissedrens d) Set.junzfication 7. We place a much higher value on reducing the probability of harm to a nanzero sum relative to reducing the probability of harm to a zero. " (3 Points) True False 8. In choices that involve uncertainty, our judgments are affected not only by the framing of the choice in terms of the level risk, but also by the framing of the choice in terms of gains or losses. (3 Polnts) True Falie 9. Since losses loom larger than gains, a big loss upsets us more than two smaller losses of the same total amount = \$ (3 Points) True Fabe 10. What is the reason that drives people to pay more for a product when purchased from a fancy place relative to a more modest venue, even though the product is identical? * (3 Points) a) Acquistion usility b) Expected value c) Expected utility d) Transactional unity 11. When choosing whether or not to continue pursung a selected course of action, previous commitments and spent resources should be regarded as. (3 Points) a) 5unk costs b) Relevant facters Q) Evependent varuatios d) frems in accounts expendable Hi, Abdala. When you sutmit this form, the owner will see your nane and enal address. Aeguired 1. Groups are Wikely than individuals to escalate cornmitment; group escalation of commitment is likely to be extreme than individual escalation of commitment. * (3 Points) a) More: less b) More; more 6) Lexs, more 6) Less; less 2. Our preferences often reverse when we evaluate options together as opposed to separate, this behavior was explained by authors to which of the following factors? * (3 Points) 2. In general, there is a tendency of people to overvalue the items that they own. * (3 Points) True Fatse 3. risk. frames tend to produce. feelings, which might cause an indwidual to be (3 Points) a) Posive; posthec; avere, wefair b) Negative; negative; laking; fair c) Postive, postive, avose, fair ) Negative; megative; averse; unfar 4. (3 Points) targets our tendency to place a high overall value on the creation of certainty, " a) Pseudocertainty b) Mental acooonting c) Endowmert effect d) Transactonal varity. 5. Explain how cur perception of certainty impacts our dedision-making process and why? 6. In choices that involve uncertainty, our judgments are affected not only by the framing of the choice in terms of the level risk, but also by the framing of the choice in terms of gains or losses. * Go (3 Points) True Falve 7. We place a much higher value on reducing the probability of harm to a nonzero sum relative to reducing the probability of harm to a zero. " (3 Polnts) The fase 8. When something is framed in terms of people treat as an unanticipated gain, whle if framed as. they may view it as a withheld salary " (3 Points) 1. The key to objectively consider the future costs and benefits of current courses of action is to [7 (3 Points) a) tgnore sunk costs b) Use an experimental approoch c) Use outuider's vitu d) Ai of the above 2. Explain how our perception of certainty impects our decision-making process and why? 3. Many of the decisions that occur in organizations are made sequentially or with separate frames as opposed to simultaneously and with consistent frames. This can lead to sub-optimal decisions at an organizational level. * (3 Points) True fase 4. When deciding whether or not to overly commit (escalate commitment) to a chosen course of action, our choice should depend on. (3 Points) a) The expected value of further investment, sunk costs b) Our inital reasons for chooning that course of action, Sunk costs c) Our intial reasons for chooing that course of action, the expected valie of further investment d) Nane of the above 5. Which of the following factors could influence our tendency to over commit fescalation of commitment)? " (3 Points) a) Serfyustifiation b) When the sebbock of the decisiens can not be blamed onte us c) When we make the decieion indidally moter tran in grous At of the atove 6. Which of the following refers to our tendency to overly commit resources into the pursuit of an initial goal or decision, irrespective of evidence suggesting otherwise? : (3 Points) a) Supply and demond b) Escalacion of comitment 4) Proeptual bissedrens d) Set.junzfication 7. We place a much higher value on reducing the probability of harm to a nanzero sum relative to reducing the probability of harm to a zero. " (3 Points) True False 8. In choices that involve uncertainty, our judgments are affected not only by the framing of the choice in terms of the level risk, but also by the framing of the choice in terms of gains or losses. (3 Polnts) True Falie 9. Since losses loom larger than gains, a big loss upsets us more than two smaller losses of the same total amount = \$ (3 Points) True Fabe 10. What is the reason that drives people to pay more for a product when purchased from a fancy place relative to a more modest venue, even though the product is identical? * (3 Points) a) Acquistion usility b) Expected value c) Expected utility d) Transactional unity 11. When choosing whether or not to continue pursung a selected course of action, previous commitments and spent resources should be regarded as. (3 Points) a) 5unk costs b) Relevant facters Q) Evependent varuatios d) frems in accounts expendable 12. (3 Points) targets our tendency to place a high overall value on the creation of certainty. * a) Preudocestainy b) Mental acoounting c) Endowmert effect d) Frarsectional velity 13. By merely considering choices framed as gains and losses separately, people have made suboptimal decisions, * (3 Points) True Fabe 14. Which of the following factors suggest that we have a strong preference for others who commit to a course of action and remain consistent in their opinions; as such, they face a high degree of pressure to appear consistent by continuing to support their prior conviction? " (3 Points) a) Imprewion mansgeewent b) Aeropeasi thaseines c) Correntibe irrabionalfy None of the above None of the above 15. Our preferences often reverse when we evaluate options together as opposed to separate, this behavior was explained by authors to which of the following factors? " (3 Points) a) Wantistould explanation b) Evaluabetity c) Mental actoonting d) A 5.B e) Ca B 16. Groups are.in.m.... Ilikely than individuals to escalate commitment; group escalation of commitment is likely to be extreme than individual escalation of commitment. * (3 Points) a) More: kes b) More; more c) Less, more d) Less; lest 17. When something is framed in terms of people treat as an unanticipated gain, while if framed as. they may view it as a withheld salary * 17. When something is feamed in terms of people treat as an unanticipated gain, while if framed as. (3 Points) they may view it as a withheld salary " a) sonus, rebate b) Rebete, bonus c) Sure loss, premum d) Premium, sure ioss 18. Which of the following explains escalation of commitment and why does it occur? : (3 Points) a) Elased irformation processing b) Framing c) Compether irrationality All of the above 19. Which of following explains why some people treat the same dollar amount differently: " (3 Points) a) Preudocertainty b) Mertal accountiry d) fidowment effect d) Transational varity 17. When something is fromed in terms of people treat as an unanticipated gain, while if framed as. they may view it as a withheld salary * (3 Points) a) Bonus, rebete b) Rebate, bonus c) Sure loss, premium d) Premium, sure ioss 18. Which of the following explains escalabon of commitment and why does it occur? * (3 Points) a) Eiosed ifformation processing b) Framing c) Corretinive irrosionalty All of the atowe 19. Which of following explains why some people treat the same dollar amount differently: " (3 Points) a) Peusocertainy b) Mental accounting c) Endowmers effect d) Transctional itaty 20. To reduce the impact of framing on our decision making process, people can. (3 Points) a) Identily theiv reference point b) Consider attemetive reference points c) A \& B d) None of the above 21. risk. and perceive things as being (3 Points) a) Postive; positive; avese, unfar b) Negative; negative; taking: far c) Positive, ponthe, avere, far d) Negntive; negative; wrene; unfar 22. Which of the following describes the tendency of people to overvalue the items they own? * (3 Points) a) hieusccertaiety b) Mental acoocuntion c) friowment affect d) Transectional vtiefy. d) Transactional utimy 23. In gencral, there is a tendency of people to overvalue the itcris that they own. (3 Polnts) True Falio 24. To reduce the influence of judgmental biases, we should: " (3 Points) a) Reward dedisions not oulcomes b) Consult independent advtsors c) Consider the skely actoons of others d) Identify the potereial for cucyiobion 1. The key to objectively consider the future costs and benefits of current courses of action is to [7 (3 Points) a) tgnore sunk costs b) Use an experimental approoch c) Use outuider's vitu d) Ai of the above 2. Explain how our perception of certainty impects our decision-making process and why? 3. Many of the decisions that occur in organizations are made sequentially or with separate frames as opposed to simultaneously and with consistent frames. This can lead to sub-optimal decisions at an organizational level. * (3 Points) True fase 4. When deciding whether or not to overly commit (escalate commitment) to a chosen course of action, our choice should depend on. (3 Points) a) The expected value of further investment, sunk costs b) Our inital reasons for chooning that course of action, Sunk costs c) Our intial reasons for chooing that course of action, the expected valie of further investment d) Nane of the above 5. Which of the following factors could influence our tendency to over commit fescalation of commitment)? " (3 Points) a) Serfyustifiation b) When the sebbock of the decisiens can not be blamed onte us c) When we make the decieion indidally moter tran in grous At of the atove 6. Which of the following refers to our tendency to overly commit resources into the pursuit of an initial goal or decision, irrespective of evidence suggesting otherwise? : (3 Points) a) Supply and demond b) Escalacion of comitment 4) Proeptual bissedrens d) Set.junzfication 7. We place a much higher value on reducing the probability of harm to a nanzero sum relative to reducing the probability of harm to a zero. " (3 Points) True False 8. In choices that involve uncertainty, our judgments are affected not only by the framing of the choice in terms of the level risk, but also by the framing of the choice in terms of gains or losses. (3 Polnts) True Falie 9. Since losses loom larger than gains, a big loss upsets us more than two smaller losses of the same total amount = \$ (3 Points) True Fabe 10. What is the reason that drives people to pay more for a product when purchased from a fancy place relative to a more modest venue, even though the product is identical? * (3 Points) a) Acquistion usility b) Expected value c) Expected utility d) Transactional unity 11. When choosing whether or not to continue pursung a selected course of action, previous commitments and spent resources should be regarded as. (3 Points) a) 5unk costs b) Relevant facters Q) Evependent varuatios d) frems in accounts expendable