Hi can you please help me with some economics solutions. I am practising my work on an old exam. I am answering the questions however have nothing to reference to to determine if my answers are correct. Can you please help me. Thank you
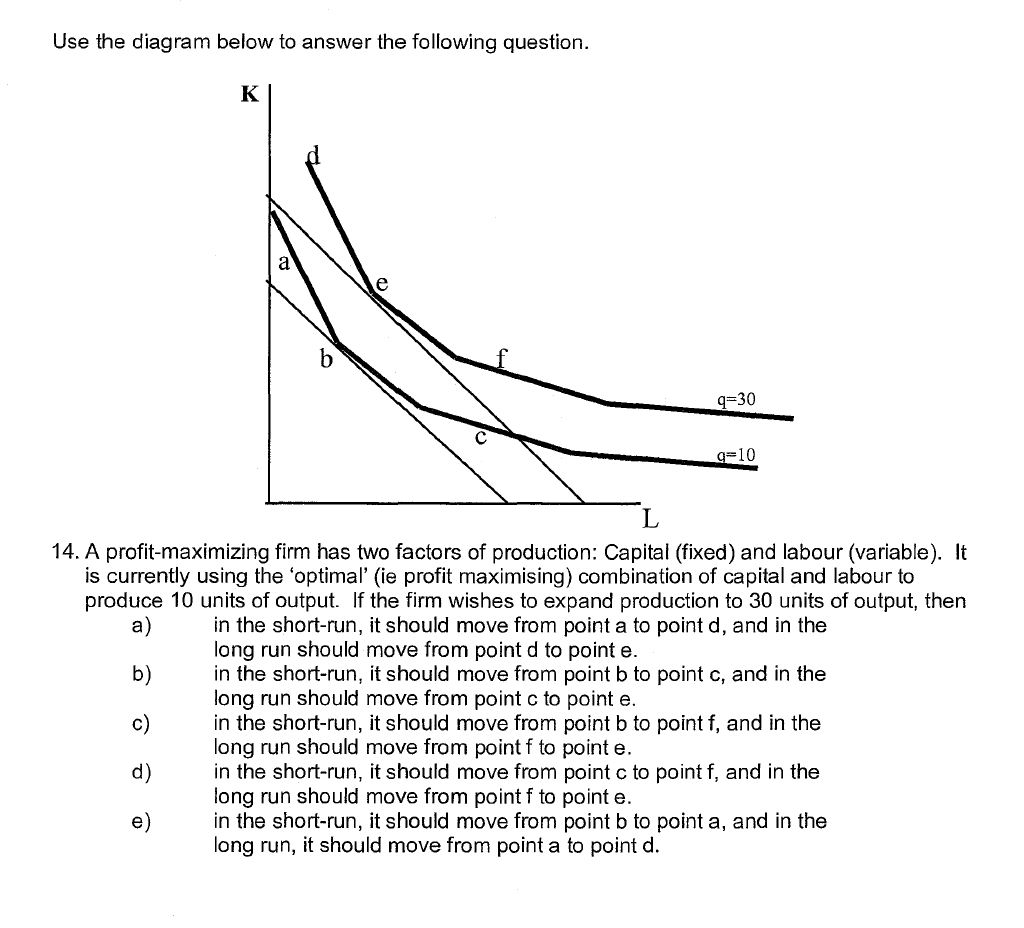
1. Which of the following would be included as an economic cost but not as an accounting cost? a) b) C) d) 8) The lease payments on business premises . The interest component of the business's mortgage repayments _ The electricity used in the production process Business overheads (such as insurance). _ The time a business owner spends doing the books each night. 2. Ceteris paribus, which of the following would be likely to shift the demand curve for new home-builders to the right? a) b) C) *3} Et) A fall in the price of new homes. . An increase in the price of new homes An economic 'boom' (is period of growth). 'An economic recession. A fall in the price of old homes 3. Assume that the market for coffee Is in equilibrium. Ceferis paribus, an unexpected frost that wipes out half the wo'rld' s crop is likely to? a) b) 0) d) 6) shift the demand curve for coffee to the right, increasing equilibrium price and quantity. shift the supply curve for coffee to the right, increasing equilibrium price and quantity. shift the simply curve for coffee to the left. increasing equilibrium price and quantity. shift the supply curve for coffee to the right, increasing equilibrium price and decreasing equilibrium quantity. shift the supply curve for coffee to the left. increasing equilibrium price and decreasing equilibrium quantity. 4. If the price elasticity of demand is equal to 2. then a) b) C) d) e) A 1% increase in price will lead to a 2% fall in the quantity demanded, and an increase in total revenue. A 1% increase in price will lead to a 12% fall in the quantity demanded, and an increase in total revenue. A 1% increase in price will lead to a 2% felt in the quantity demanded, and a decrease in total revenue. A 1% increase in price will lead to a 1.2% fall in the quantity demanded. and a decrease in total revenue. A 1% increase in price will lead to a 2% fall in the quantity demanded. We cannot tell what will happen to revenue without Knowing what marginal costs are. 5. Which of the following is true of monopolistic competition? a) There are few firms in the industry b) Market entry and exit is difficult 0) Products are homogenous d) Long-run prots are zero e) All of the above 6. All of the follOwing describe or affect the behaviour of long-run costs except: a) When the firm is encountering increasing returns to scale. long-run ' average cost (LRAC) is decreasing ' b) The long-run is considered to be a part of a manager's planning horizon. o) Relatively high fixed costs in the long-run determine the shape of the LRAC curve. . - d) if the firm is encountering constant returns to scale, LRAC is constant over that range of plant sizes. e) All of these describe or affect lo ng-run costs 7. If the Marginalcosts are equal to 30 and the price elasticity of demand is 2, then What price maximizes profits? - a) 30 b) 40 c) 50 d) 60 e) - 70 12. You are comparing two potential. mutually exclusive projects. Both have an expected net present value of 2000, but project A has a standard deviation of 2000. while project B has a standard deviation of 3000. - a) A risk-averse manager would be indifferent between the two projects, while a risk-neutral manager would prefer project A. b) A risk-averse manager would prefer project A to project B, while a risk-neutral manager would prefer project B. c) A riskaverse manager Would prefer project B to project A while a riskneutral manager would prefer project A. d) A risk-averse manager would-prefer projectA, while a risk-neutral manager would be indifferent between the two projects. e) A riskaverse manager would prefer project B, while a riskneutral manager would be indifferent between the two projects. 13. You are evaluating a potentlul project which has uncertain future cash flows. The project will require an immediate outlay of $500. In year 1, cash flow will be $200 with probability .5, and $700 with probability .5. In year 2, cash ows will be $200 with probability .2, $400 with probability .6 and $700 with probability .2. In year three cash flows will be either $200. $300. 2? a) b) 0) '2') Et) $400, $600 or $700 each with probability .2. What is the expected-value of cash flows in year $400 $450 $420 $433 None of the above Use the diagram below to answer the following question. 14. A profit-maximizing firm has Mo factors of production: Capital (xed) and labour (variable). It is currently using the 'optimal' (ie prot maximising) combination of capital and labour to produce 10 units of output. If the firm wishes to expand production to 30 units of output, then a) in the short-run, itshould move from point a to point d, and in the long run should move from point d to point e. b) in the short-run, it should move from point b to point c, and in the long run should move from point e to point e. c) in the short-run, it should move from point b to point t, and in the long run should move from pointfto point e. d) in the short-run, it should move from point e to point f, and in the long run should move from pointfto pointe. e) in the short-run, it should move from point b to point a. and in the long run, it should move from point a to point d