Hi, I am reposting this. The instructions for creating the program is given below however, I have done most of the programming. I want help adding the yellow things to my program and checking my work to see if it matches the instructions. Please comment explaining the additions. Thanks.

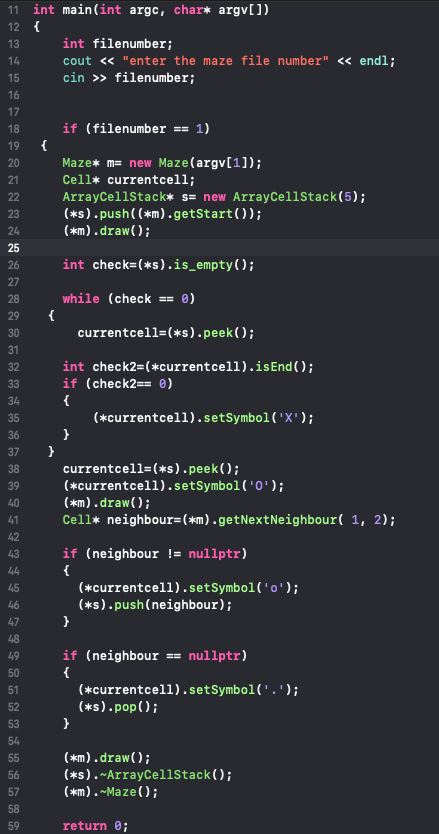
Create the maze Get a pointer to the start Make another pointer for a Cell Make a stack Push the start on the stack Draw the maze Start the two counters (total steps, steps in path) While the stack is not empty Get a pointer to the cell on top of the stack (current cell) If it's the end, were done Update counters Update symbol to X Break out of loop Update the current cell's symbol to o Draw the maze Get a pointer to a neighbouring cell If the neighbour exists Update counters Update current cell's symbol to o Push the new cell on the stack If there are no valid neighbours, we backtrack Update counters Set symbol to . Pop the cell off the stack Make the program sleep a so it prints nicely (I did 250ms) Print out the counters Draw the maze one final tie Delete things 11 int main(int argc, char* argv]) 13 14 15 int filenumber; cout filenumber; 18 if (filenumber1) Maze* m new Maze(argv[1]); Cell* currentcell; ArrayCellStack* snew ArrayCellStack (5); (#5) .push( (*m).getStart ( )) ; (xm).draw) 23 25 int check (*s).is_empty); while (check0) currentcella(#5). peek ( ) ; 30 31 int check2-(currentce11).isEnd ); if (check2= 0) 35 (*currentcell).setSymbol('X' currentcella(#5), peek ( ) ; (*currentcell).setSymbol('0') (xm).draw) Cell* neighbour-(m).getNextNeighbour( 1, 2); 38 if (neighbour ! nullptr) (*currentcell).setSymbol('o') (*s).push (neighbour); if (neighbour- nullptr) (*currentcell).setSymbol('.'); (*s).pop); 52 (#m).draw(); (*s).ArrayCellStack ) (*m). Maze); 57 return 0 Create the maze Get a pointer to the start Make another pointer for a Cell Make a stack Push the start on the stack Draw the maze Start the two counters (total steps, steps in path) While the stack is not empty Get a pointer to the cell on top of the stack (current cell) If it's the end, were done Update counters Update symbol to X Break out of loop Update the current cell's symbol to o Draw the maze Get a pointer to a neighbouring cell If the neighbour exists Update counters Update current cell's symbol to o Push the new cell on the stack If there are no valid neighbours, we backtrack Update counters Set symbol to . Pop the cell off the stack Make the program sleep a so it prints nicely (I did 250ms) Print out the counters Draw the maze one final tie Delete things 11 int main(int argc, char* argv]) 13 14 15 int filenumber; cout filenumber; 18 if (filenumber1) Maze* m new Maze(argv[1]); Cell* currentcell; ArrayCellStack* snew ArrayCellStack (5); (#5) .push( (*m).getStart ( )) ; (xm).draw) 23 25 int check (*s).is_empty); while (check0) currentcella(#5). peek ( ) ; 30 31 int check2-(currentce11).isEnd ); if (check2= 0) 35 (*currentcell).setSymbol('X' currentcella(#5), peek ( ) ; (*currentcell).setSymbol('0') (xm).draw) Cell* neighbour-(m).getNextNeighbour( 1, 2); 38 if (neighbour ! nullptr) (*currentcell).setSymbol('o') (*s).push (neighbour); if (neighbour- nullptr) (*currentcell).setSymbol('.'); (*s).pop); 52 (#m).draw(); (*s).ArrayCellStack ) (*m). Maze); 57 return 0








