Hi there, I already solved most of this problem, but I need help with this last part:
 Already solved portion:
Already solved portion:

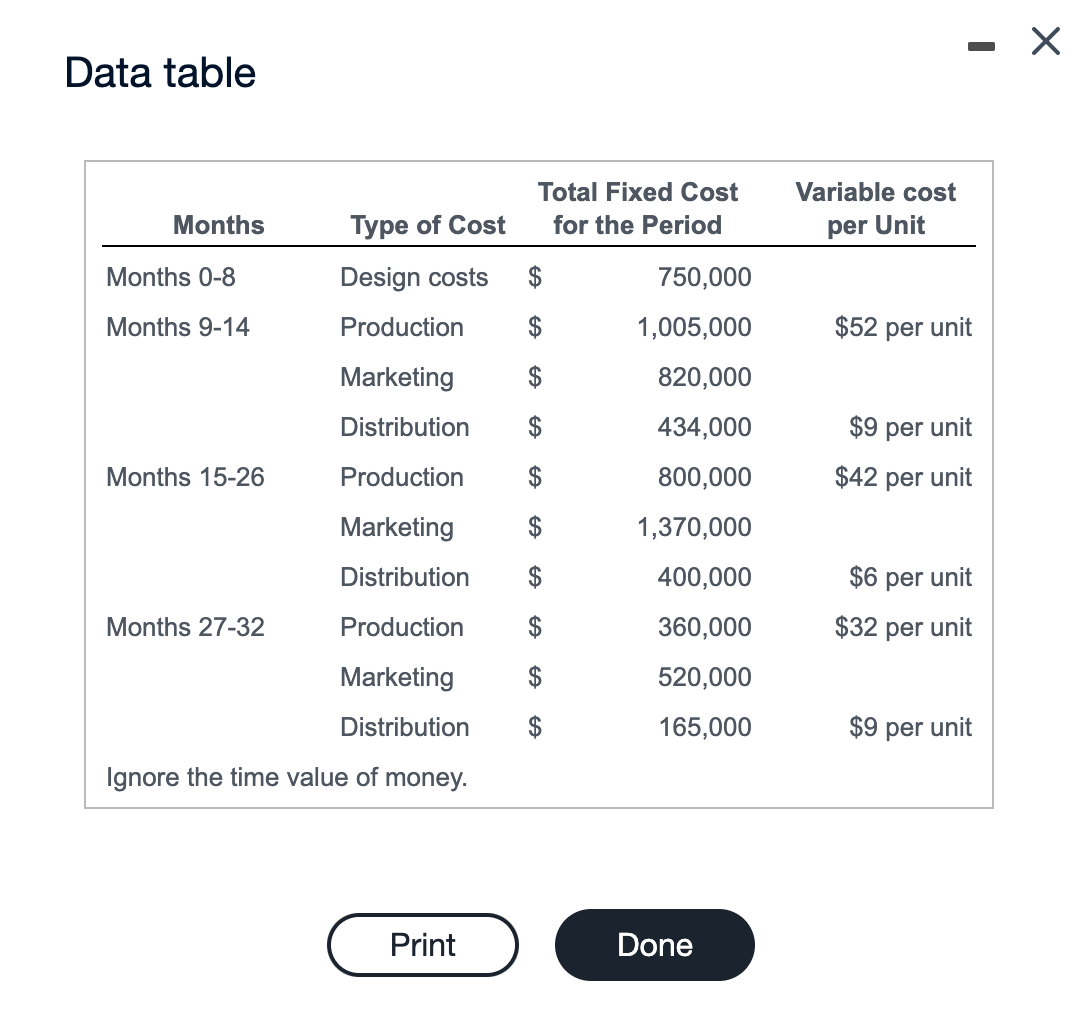




If Ideatronics were to decrease the price in the initial growth phase from $450 to $410, with the result that sales would increase to 35,000 units: Sales dollars for that period would Variable costs would increase by v decrease by increase by Operating income would Ideatronics is going to introduce a combination phone/tablet product. Design and testing will take 8 months. Ideatronics expects to sell 32,000 units during the first 6 months of sales. Sales over the next 12 months are expected to be less robust at 26,000. And, sales in the final 6 months of the expected life cycle are expected to be 13,000. Ideatronics is budgeting for this product as follows: (Click the icon to view the cost information.) Read the requirements. Data table Variable cost Total Fixed Cost for the Period Months per Unit Months 0-8 Type of Cost Design costs Production $ 750,000 Months 9-14 $ $52 per unit 1,005,000 820,000 Marketing Distribution $ 434,000 $9 per unit $42 per unit Months 15-26 Production $ 800,000 $ 1,370,000 Marketing Distribution $ 400,000 $6 per unit $32 per unit Months 27-32 Production $ $ $ 360,000 520,000 Marketing Distribution Ignore the time value of money. 165,000 $9 per unit Print Done Requirement 1. If Ideatronics prices the phone/tablets at $450 each, how much operating income will the company make over the product's life cycle? What is the operating income per unit? Begin by preparing the life cycle income statement in order to determine how much operating income the company will make over the product's life cycle. Projected Life Cycle Income Statement Revenues $ 31,950,000 Variable costs: Months 9-14 1,952,000 Months 15-26 1,248,000 Months 27-32 533,000 Total variable costs 3,733,000 Fixed costs: Design costs 750,000 2,165,000 Production Marketing 2,710,000 Distribution 999,000 Total fixed costs 6,624,000 $ 21,593,000 Life cycle operating income What is the operating income per unit? (Round your answer to the nearest cent.) The operating income per unit is $ 304.13 Requirement 2. Excluding the initial product design costs, what is the operating income in each of the three sales phases of the product's life cycle, assuming the price stays at $450? Projected Life Cycle Income Statement Months 9-14 Months 15-26 Months 27-32 Revenues $ 14,400,000 $ 11,700,000 $ 5,850,000 Variable costs 1,952,000 1,248,000 533,000 Fixed costs: Distribution 434,000 400,000 165,000 Marketing 820,000 1,005,000 1,370,000 800,000 520,000 360,000 Production Total fixed costs 2,259,000 2,570,000 1,045,000 $ 10,189,000 $ 7,882,000 $ 4,272,000 Life cycle operating income Requirement 3. How would you explain the change in budgeted operating income over the product's life cycle? What other factors does the company need to consider before developing the new combination phone/tablet product? . 1 In analyzing the relative profitability of the product during the three sales phases of its life cycle, the results are as expected . During the initial growth phase, sales and profits are highest . In the maturity phase of the life-cycle, fixed costs increase slightly overall due to higher marketing costs This helps keep the product in the public eye and supports the anticipated sales of 26,000 units. Finally, in the decline phase, fixed costs are significantly reduced while the selling price stays the same. Variable costs also decrease a bit in this phase. Though unit sales are significantly reduced operating income as a percentage of sales is much higher than the maturity phase and is approaching the percentage experienced in the initial growth phase. Requirement 4. Ideatronics is concerned about the number of units it expects to sell in the first sales phase. The company is considering pricing the phone/tablet at $410 for the first 6 months and then increasing the price to $450 thereafter. With this pricing strategy, Ideatronics expects to sell 35,000 units instead of the originally forecast 32,000 units in the first sales phase, and the same number of units for the remaining life cycle. Assuming the same cost structure as given in the problem, which pricing strategy would you recommend? Explain. Begin by preparing the life cycle income statement in order to determine how much operating income the company will make over the product's life cycle, under the new assumptions. Projected Life Cycle Income Statement Revenues $ 31,900,000 Variable costs: Months 9-14 2,135,000 Months 15-26 1,248,000 Months 27-32 533,000 Total variable costs 3,916,000 Fixed costs: Design costs 750,000 Production 2,165,000 Marketing 2,710,000 Distribution 999,000 Total fixed costs 6,624,000 $ 21,360,000 Life cycle operating income
 Already solved portion:
Already solved portion: 











