
Hi tutors can you guide and help me with this. The lesson is already in the picture use this as a guide thanks for helping
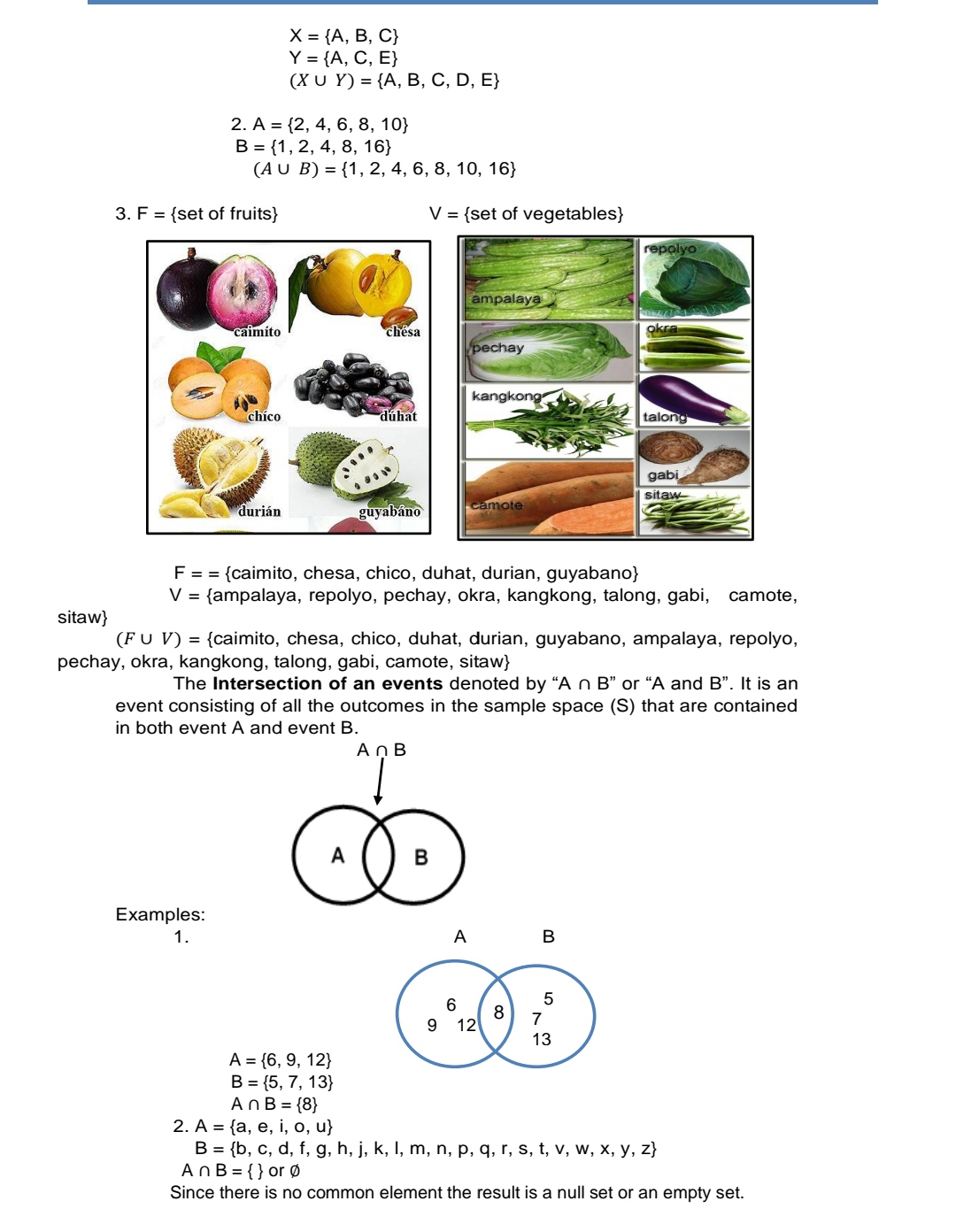
Events, and Union and Intersection of Events In this module, you are expected to illustrate events. and union and intersection Of events. The sample space of the random experiment is the collection of all possible outcomes. An event associated with a random experiment is the subset of the sample space. A probability of an event (n) can be defined as the set of outcomes of an experiment. In other words, an event (n) in the probability is the subset of the sample space (3). Examples of events: tossing a coin and it is landing on heads and tossing a coin and it is landing on tails. Here are the types of Events in Probability: Impossible event an event that cannot happen and is denoted by { } or ID. Example: In flipping a coin once, an impossible event would be getting both head and tail. 3 = {head, tail}. An event of getting both head and tail, A ={ } or 0. Sure event an event which occurs always whenever experiment performed. It consists of all possible outcomes in an event. Example: In throwing a die, the event of getting a natural number less than 7 is a sure event. S={1,2, 3, 4, 5,6} A={1,2, 3, 4, 5,6} Simple or elementary event an event where there be only one element of the same space in the set representing an event. Example: In throwing a die, 8 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}. The event of appearing 5 is given by A = {5}. Complementary event is the set of all elements of the sample space S which are not in the event A. It is denoted by A'. Example: 8 = {HH, TH, HT, TT} and A = {I-IT, TH}, then A\" = {HH, TT} The union of an events consist of all the outcomes in the sample space (8) that are contained either in event A or in event B or Both. It is denoted by \"A U B\" or A or B. AUB I. (03 Examples: 1. X = {A, B, C} Y = {A, C, E} (XU Y) = {A, B, C, D, E} 2. A = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10} B = {1, 2, 4, 8, 16} (A U B) = {1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 16} 3. F = {set of fruits} V = {set of vegetables} epolyo ampalaya caimito chesa pechay kangkong chico duhat talong gabi sitaw durian guyabano camote F = = {caimito, chesa, chico, duhat, durian, guyabano} V = fampalaya, repolyo, pechay, okra, kangkong, talong, gabi, camote, sitaw} (F U V) = {caimito, chesa, chico, duhat, durian, guyabano, ampalaya, repolyo, pechay, okra, kangkong, talong, gabi, camote, sitaw} The Intersection of an events denoted by "A n B" or "A and B". It is an event consisting of all the outcomes in the sample space (S) that are contained in both event A and event B. AnB B Examples: 1. A 8 9 12 13 A = {6, 9, 12} B = {5, 7, 13} An B = (8} 2. A = {a, e, i, o, u} B = {b, c, d, f, g, h, j, k, I, m, n, p, q, r, S, t, v, w, x, y, z} AnB = { } or Since there is no common element the result is a null set or an empty set.Assessmnet I. Illustrate the union and intersection of the following events. 1. A set of English alphabets. A (set of vowels) = B (set of consonants) = A U B = A n B = 2. A set of numbers between 1 to 20. A (odd numbers) = B (divisible by 3) = A U B = A n B = 3. A set of playing cards. A (spade) = B (ace) = A U B = A n B = 4. A set of plants in a song Bahay Kubo. A (plants start with s) = B (plant start with k) = A U B = A n B = 5. A set of letters in the word love and heart. A = B = AUB= AnB= ll. Answer the following questions below: 1. What have you learned lrom this module? 2. How do you illustrate the events, and union and intersection of an events? 3. Show your own example of union and intersection of an events











