 Hint: For part e. You need to estimate how much of the overhead is fixed and how much is variable using the high low method (you have two observations - Year 1 and Year 2)
Hint: For part e. You need to estimate how much of the overhead is fixed and how much is variable using the high low method (you have two observations - Year 1 and Year 2)
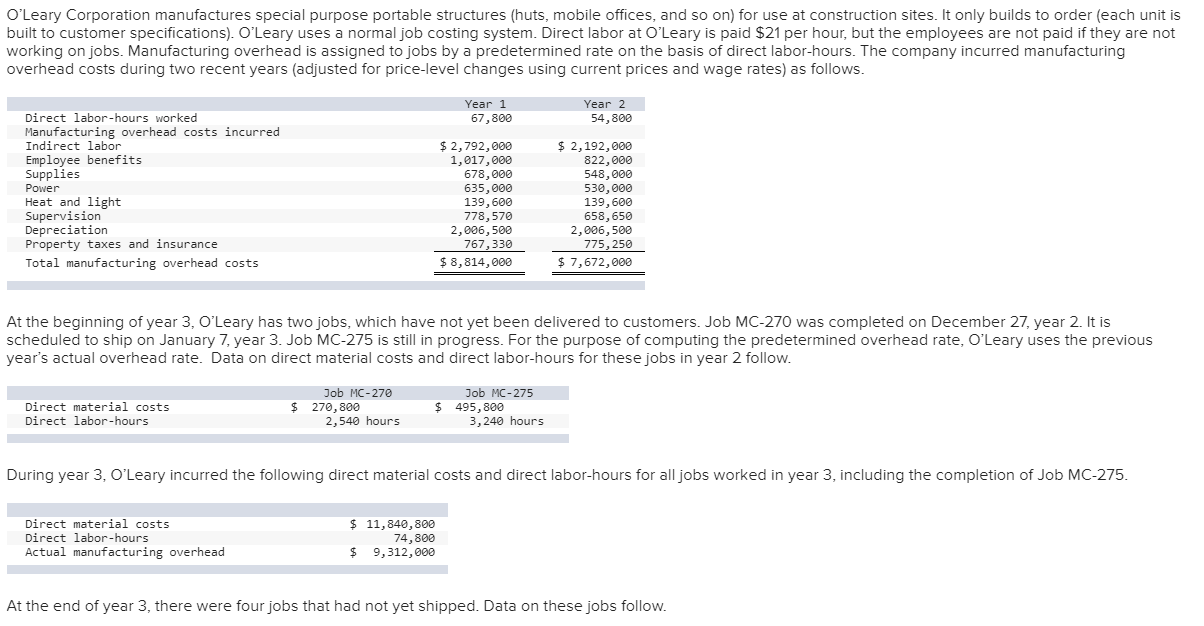
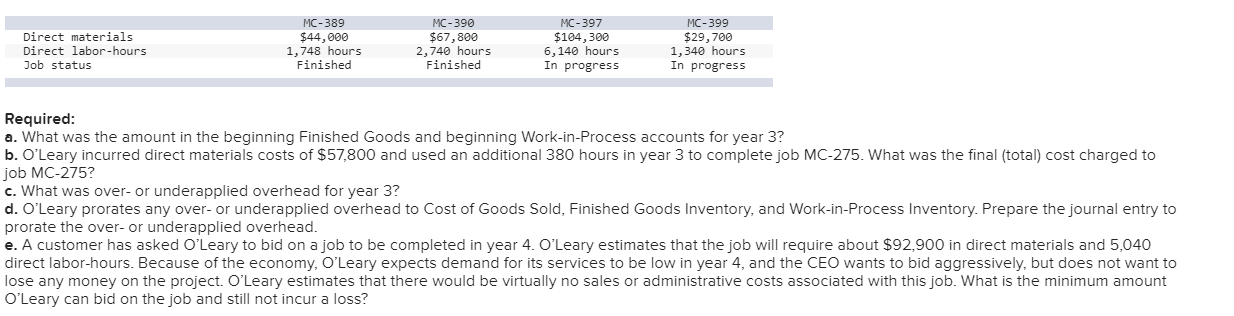
O'Leary Corporation manufactures special purpose portable structures (huts, mobile offices, and so on) for use at construction sites. It only builds to order (each unit is built to customer specifications). O'Leary uses a normal job costing system. Direct labor at O'Leary is paid $21 per hour, but the employees are not paid if they are not working on jobs. Manufacturing overhead is assigned to jobs by a predetermined rate on the basis of direct labor-hours. The company incurred manufacturing overhead costs during two recent years (adjusted for price-level changes using current prices and wage rates) as follows. Year 1 67,800 Year 2 54,800 Direct labor-hours worked Manufacturing overhead costs incurred Indirect labor Employee benefits Supplies Power Heat and light Supervision Depreciation Property taxes and insurance Total manufacturing overhead costs $ 2,792,000 1,017,000 678,000 635,000 139,600 778,570 2,006,500 767,330 $ 8,814,000 $ 2,192,000 822,000 548,000 530,000 139,600 658,650 2,006,500 775,250 $ 7,672,000 At the beginning of year 3, O'Leary has two jobs, which have not yet been delivered to customers. Job MC-270 was completed on December 27, year 2. It is scheduled to ship on January 7, year 3. Job MC-275 is still in progress. For the purpose of computing the predetermined overhead rate, O'Leary uses the previous year's actual overhead rate. Data on direct material costs and direct labor-hours for these jobs in year 2 follow. Direct material costs Direct labor-hours $ Job MC-270 270,800 2,540 hours $ Job MC-275 495,800 3,240 hours During year 3, O'Leary incurred the following direct material costs and direct labor-hours for all jobs worked in year 3, including the completion of Job MC-275. Direct material costs Direct labor-hours Actual manufacturing overhead $ 11,840, 800 74,800 $ 9,312,000 At the end of year 3, there were four jobs that had not yet shipped. Data on these jobs follow. Direct materials Direct labor-hours Job status MC-389 $44,000 1,748 hours Finished MC-390 $67,800 2,740 hours Finished MC-397 $104,300 6, 140 hours In progress MC-399 $29,700 1,340 hours In progress Required: a. What was the amount in the beginning Finished Goods and beginning Work-in-Process accounts for year 3? b. O'Leary incurred direct materials costs of $57,800 and used an additional 380 hours in year 3 to complete job MC-275. What was the final (total) cost charged to job MC-275? c. What was over- or underapplied overhead for year 3? d. O'Leary prorates any over- or underapplied overhead to Cost of Goods Sold, Finished Goods Inventory, and Work-in-Process Inventory. Prepare the journal entry to prorate the over- or underapplied overhead. e. A customer has asked O'Leary to bid on a job to be completed in year 4. O'Leary estimates that the job will require about $92,900 in direct materials and 5,040 direct labor-hours. Because of the economy, O'Leary expects demand for its services to be low in year 4, and the CEO wants to bid aggressively, but does not want to lose any money on the project. O'Leary estimates that there would be virtually no sales or administrative costs associated with this job. What is the minimum amount O'Leary can bid on the job and still not incur a loss? O'Leary Corporation manufactures special purpose portable structures (huts, mobile offices, and so on) for use at construction sites. It only builds to order (each unit is built to customer specifications). O'Leary uses a normal job costing system. Direct labor at O'Leary is paid $21 per hour, but the employees are not paid if they are not working on jobs. Manufacturing overhead is assigned to jobs by a predetermined rate on the basis of direct labor-hours. The company incurred manufacturing overhead costs during two recent years (adjusted for price-level changes using current prices and wage rates) as follows. Year 1 67,800 Year 2 54,800 Direct labor-hours worked Manufacturing overhead costs incurred Indirect labor Employee benefits Supplies Power Heat and light Supervision Depreciation Property taxes and insurance Total manufacturing overhead costs $ 2,792,000 1,017,000 678,000 635,000 139,600 778,570 2,006,500 767,330 $ 8,814,000 $ 2,192,000 822,000 548,000 530,000 139,600 658,650 2,006,500 775,250 $ 7,672,000 At the beginning of year 3, O'Leary has two jobs, which have not yet been delivered to customers. Job MC-270 was completed on December 27, year 2. It is scheduled to ship on January 7, year 3. Job MC-275 is still in progress. For the purpose of computing the predetermined overhead rate, O'Leary uses the previous year's actual overhead rate. Data on direct material costs and direct labor-hours for these jobs in year 2 follow. Direct material costs Direct labor-hours $ Job MC-270 270,800 2,540 hours $ Job MC-275 495,800 3,240 hours During year 3, O'Leary incurred the following direct material costs and direct labor-hours for all jobs worked in year 3, including the completion of Job MC-275. Direct material costs Direct labor-hours Actual manufacturing overhead $ 11,840, 800 74,800 $ 9,312,000 At the end of year 3, there were four jobs that had not yet shipped. Data on these jobs follow. Direct materials Direct labor-hours Job status MC-389 $44,000 1,748 hours Finished MC-390 $67,800 2,740 hours Finished MC-397 $104,300 6, 140 hours In progress MC-399 $29,700 1,340 hours In progress Required: a. What was the amount in the beginning Finished Goods and beginning Work-in-Process accounts for year 3? b. O'Leary incurred direct materials costs of $57,800 and used an additional 380 hours in year 3 to complete job MC-275. What was the final (total) cost charged to job MC-275? c. What was over- or underapplied overhead for year 3? d. O'Leary prorates any over- or underapplied overhead to Cost of Goods Sold, Finished Goods Inventory, and Work-in-Process Inventory. Prepare the journal entry to prorate the over- or underapplied overhead. e. A customer has asked O'Leary to bid on a job to be completed in year 4. O'Leary estimates that the job will require about $92,900 in direct materials and 5,040 direct labor-hours. Because of the economy, O'Leary expects demand for its services to be low in year 4, and the CEO wants to bid aggressively, but does not want to lose any money on the project. O'Leary estimates that there would be virtually no sales or administrative costs associated with this job. What is the minimum amount O'Leary can bid on the job and still not incur a loss

 Hint: For part e. You need to estimate how much of the overhead is fixed and how much is variable using the high low method (you have two observations - Year 1 and Year 2)
Hint: For part e. You need to estimate how much of the overhead is fixed and how much is variable using the high low method (you have two observations - Year 1 and Year 2)





