














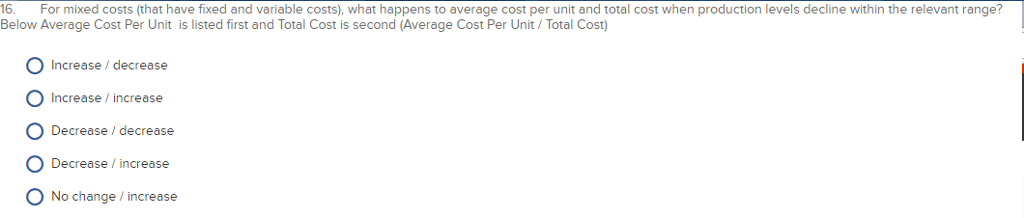


 Historically, overhead costs have declined as a percent of total manufacturing costs
Historically, overhead costs have declined as a percent of total manufacturing costs
Historically, overhead costs have declined as a percent of total manufacturing costs. True False GAAP requires period costs to be allocated to products. True False Cost of goods manufactured is the sum of manufacturing costs added to production and beginning work-in-process inventory, less ending work-in-process inventory. True False Compared to job costing, a properly designed activity-based system more accurately traces costs to products. O True O False Activities cause cost drivers to consume resources. True False The conference method can be a useful method for forecasting costs outside the relevant range. True False Cost-volume profit analysis and break-even analysis are based on the assumption that inventories are constant. True False Which of the following is not an ethical standard of managerial accounting? Competence Confidentiality Fairness Integrity Credibility Which of the following statements regarding Work-in-Process is not correct? Work-in-Process is partially completed inventory. Work-in-Process consists of direct labor, direct material, and manufacturing overhead. Work-in-Process Inventory is debited (left-hand-side of T-account) to record direct material used and direct labor incurred. O Work-in-Process Inventory appears on the year-end balance sheet. Work-in-Process Inventory is credited to account for actual overhead costs. Why do companies use normal costing? to measure variable and fixed costs separately to smooth out seasonal variations in overhead costs to support pricing and decision making before actual costs are incurred All of the above B and C but not A. What is the most accurate method for accounting for under- or over-applied manufacturing overhead at year-end? charging it to Work-in-Process Inventory. charging it to Cost of Goods Sold. charging it to a special loss account. prorating it among Raw Materials Inventory. Finished-Goods Inventory, and Cost of Goods Sold. carrying the over or under-applied balance forward to the next year by applying it to the accrued overhead account. The following tasks are associated with an activity-based costing system: Calculation of cost application rates Identification of cost drivers Assignment of cost to products Identification of cost pools Which of the following choices correctly expresses the proper order of the preceding tasks in creating an activity-based costing system? 1. 2, 3, 4. 2. 4.1.3. 3, 4. 2, 1. 4. 2.1.3. 4. 2. 3, 1. The percent of total activity cost that activity-based costing charges to a product is the: overhead ratio consumption ratio activity rate overhead rate predetermined rate How is ABC similar to a job-cost system with a single plant-wide rate? Both approaches assume that unit-level costs are variable and non-unit-level costs are fixed. Both approaches first accumulate overhead costs and then assign costs to cost objects, Both approaches recognize the distinction between batch-, product-, and facility- level costs, Both approaches develop rates using actual overhead costs and the actual number of cost drivers. Compared to job costing, ABC tends to Reduce cross-subsidization Simplify the accounting system Reduce costing accuracy Provide information that is less relevant for cost management Use more unit-level cost drivers and less non-unit level drivers For mixed costs (that have fixed and variable costs), what happens to average cost per unit and total cost when production levels decline within the relevant range? Below Average Cost Per Unit is listed first and Total Cost is second (Average Cost Per Unit/Total Cost) Increase/decrease Increase/increase Decrease/decrease Decrease/increase No change/increase A company observed a decrease in the cost per unit. All other things being equal, which of the following is probably true? The company is studying a variable cost, and total volume has increased. The company is studying a variable cost, and total volume has decreased. The company is studying a fixed cost, and total volume has increased. The company is studying a fixed cost, and total volume has decreased. The company is studying a fixed cost, and total volume has remained constant. Which of the follow statements about a high R-squared measure in a regression is not true? It indicates a good fit of the regression line through the data points It shows that a large amount of the change in the cost object (y) is explained by changes in the cost driver (x). It means that there is a causal relation between the cost driver (x) and the cost object (y). It means that, if the assumptions of the regression model are met. one can be relatively confident when using the regression information to predict future costs, It indicates that there is a correlation between the cost driver (x) and the cost object (y). Which of the following statements is true? Compared to the income statement you learned about in Mgmt 200. the contribution margin income statement simplifies costs by categorizing them as either fixed or variable, Both the income statement used in Mgmt 200 and the contribution margin income statement separately report product versus period costs. Cost of goods sold reported on the income statement used in Mgmt 200 is limited to only variable costs, Creating a contribution margin income statement is not necessary to do break-even analysis. The Mgmt 200 income statement is used primarily for internal reporting purposes, while the contribution margin income statement is used primarily for external reporting purposes















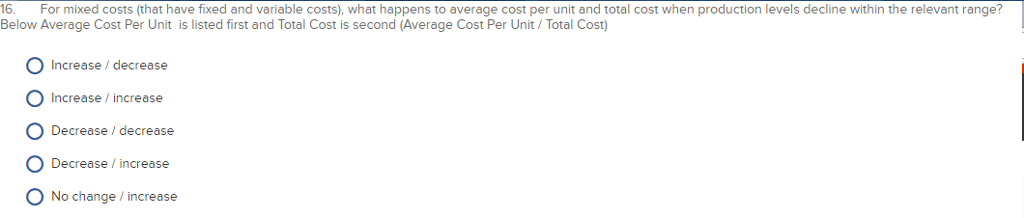


 Historically, overhead costs have declined as a percent of total manufacturing costs
Historically, overhead costs have declined as a percent of total manufacturing costs





