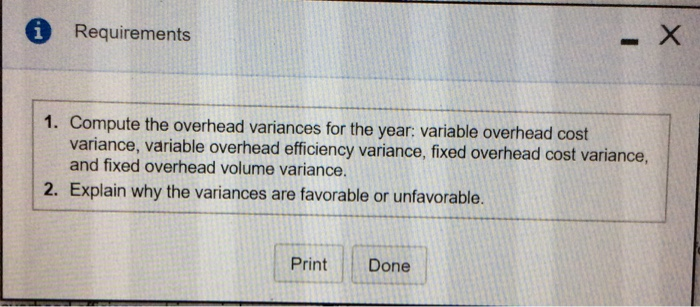
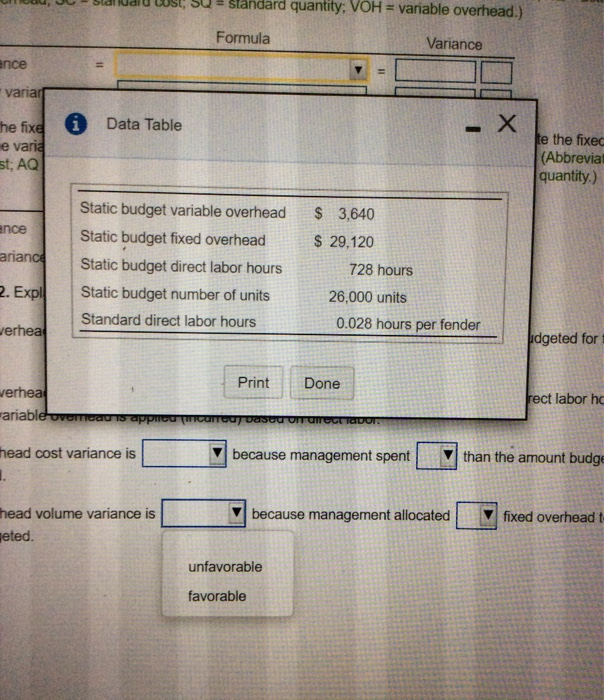
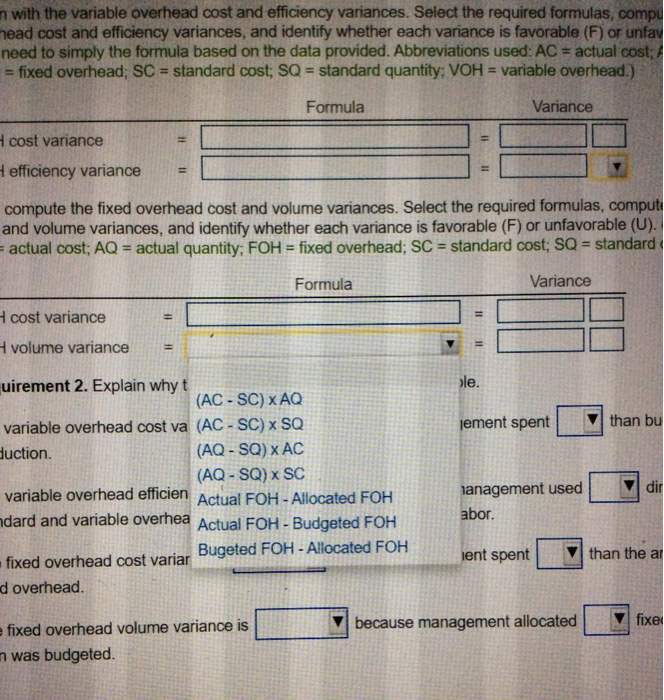
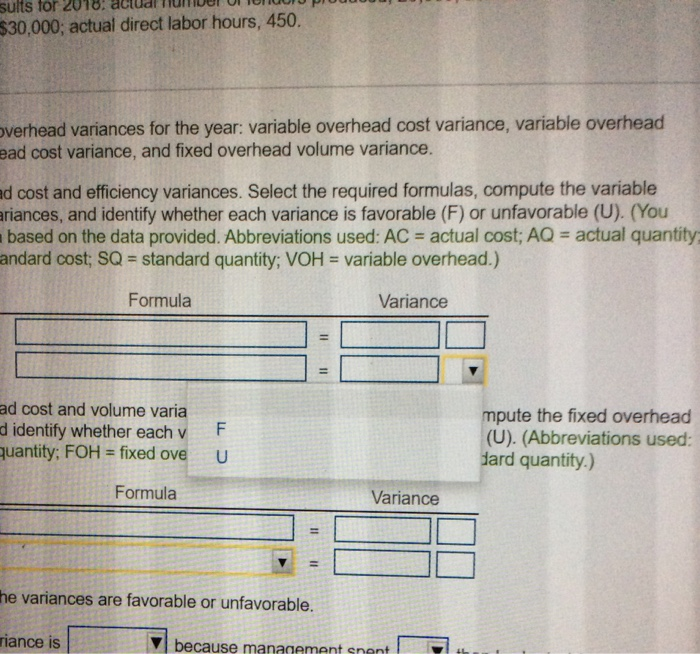
A Requirements 1. Compute the overhead variances for the year: variable overhead cost variance, variable overhead efficiency variance, fixed overhead cost variance, and fixed overhead volume variance. 2. Explain why the variances are favorable or unfavorable. Print Done Standard quantity: VOH = variable overhead.) Formula Variance ance variari i Data Table the fixe e varia st; AQ te the fixec (Abbrevia quantity.) ance arianca Static budget variable overhead Static budget fixed overhead Static budget direct labor hours Static budget number of units Standard direct labor hours $ 3,640 $ 29,120 728 hours 26,000 units 0.028 hours per fender 2. Expl verhead \dgeted for Print Done verhea ariable ovomeau is apprica (COTCU) DISOU on unreclador. rect labor hd because management spent head cost variance is 1. than the amount budge because management allocated head volume variance is Heted. fixed overheadt unfavorable favorable Grand Fender uses a standard cost system and provide the following information: (Click the icon to view the information.) Grand Fender allocates manufacturing overhead to production based on standard direct labor hours. Grand Fender reported the following actual results for 2018: actual number of fenders produced, 20,000; actual variable overhead, $5,800; actual fixed overhead, $30,000; actual direct labor hours, 450. Read the requirements Requirement 1. Compute the overhead variances for the year: variable overhead cost variance, variable overhead efficiency variance, fixed overhead cost variance, and fixed overhead volume variance. Begin with the variable overhead cost and efficiency variances. Select the required formulas, compute the variable overhead cost and efficiency variances, and identify whether each variance is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). (You may need to simply the formula based on the data provided. Abbreviations used: AC = actual cost; AQ = actual quantity, FOH = fixed overhead; SC - standard cost; SQ - standard quantity, VOH = variable overhead.) Formula Variance VOH cost variance VOH efficiency variance Now compute the fixed overhead cost and volume variances. Select the required formulas, compute the fixed overhead cost and volume variances, and identify whether each variance is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). (Abbreviations used: AC = actual cost; AQ = actual quantity: FOH = fixed overhead; SC = standard cost; SQ - standard quantity.) Formula Variance FOH cost variance FOH volume variance Requirement 2. Explain why the variances are favorable or unfavorable. The variable overhead cost variance is because management spent production than budgeted for the actual The variable overhead efficiency variance is because management used direct labor hours than standard and variable overhead is applied (incurred) based on direct labor. The fixed overhead cost variance is because management spent than the amount budgeted for fixed overhead because management allocated fixed overhead to jobs The fixed overhead volume variance is than was budgeted less more sults for 201 $30,000; actual direct labor hours, 450. overhead variances for the year: variable overhead cost variance, variable overhead ead cost variance, and fixed overhead volume variance. ad cost and efficiency variances. Select the required formulas, compute the variable ariances, and identify whether each variance is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). (You based on the data provided. Abbreviations used: AC = actual cost; AQ = actual quantity andard cost; SQ = standard quantity; VOH = variable overhead.) Formula Variance ad cost and volume varia d identify whether each v quantity; FOH = fixed ove F U mpute the fixed overhead (U). (Abbreviations used: dard quantity.) Formula Variance II v 11 the variances are favorable or unfavorable. riance is because management sont