Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Aspirin, an acetyl derivative of salicylic acid, is a white, crystalline, weakly acidic substance, with a melting point of 136 C (277 F), and

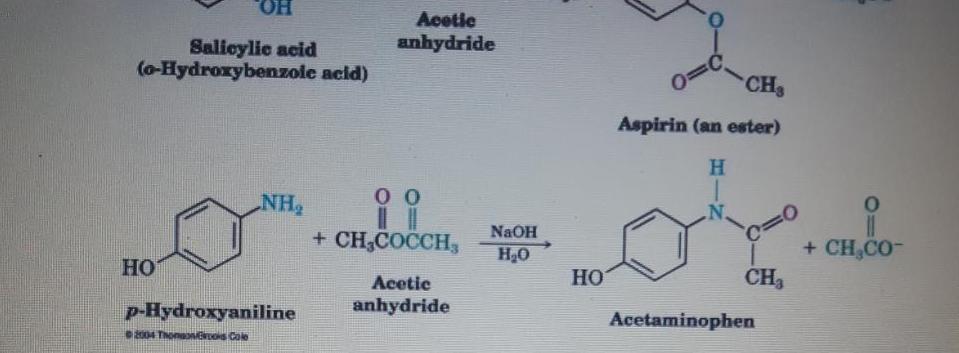
Aspirin, an acetyl derivative of salicylic acid, is a white, crystalline, weakly acidic substance, with a melting point of 136 "C (277 F), and a boiling point of 140 C (284 F).24 Its acid dissociation constant (pK.) is 3.5 at 25 C (77 F) (0) With reference to electron withdrawing and releasing group effects explain why Aspirin is stronger acid than Acetaminophen. (3marks) Acetaminophen undergoes reduction reaction to give product A. Illustrate the (I) complete reaction including the reagent and condition involved. (3marks) Aspirin reacts with Grignard reagent CH3M9B to give Structure 'B'. Show the (ii) formation of structure B. (3marks) Using chemical equation give the formation of product when p-Hudroxwaniline (2 marks) (iv) reacts with bromine. HO. Acetic anhydride Salicylic acid (o-Hydroxybenzole acid) CH Aspirin (an ester) H. NH + CH,COCCH, %3D + CH,CO- NAOH H20 Acetic HO CH3 p-Hydroxyaniline anhydride Acetaminophen 2004 ThonaNos Cole
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.38 Rating (151 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
See t...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


