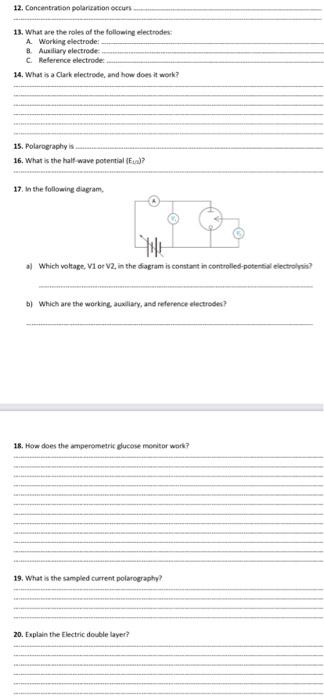
Homework \# 2 Student's Name: NCVM 322-tlectro-Chemitery 1. th the Electrolysis experiment, the potentiometer measures and the ammeter measures a) votuge; current. b) Botertiat cathoibe x) Charges; innt d) Hone 2. Dverpotential, ohmic potential, and concentration polariation make electrolysis more difficult. They a) drive the reaction forward mone uafavorable b) drive the indl roleage more necative. requiring mote vohage from the power wpply c) evercome the concertraton of ions to deposiend at electrode surface di) Bant 3. Cocolometry in a) a dheruical analyis based en countirethe electrons used in a reaction b) an cxidation ef some organic compounds in the solution c) a tedhnigue that meature the goteatil requited for the electrolvit di Norn 4, In anperometry. a) We caculate the electric current between the analve and the concentration b) We medsure the curent that in proportional to the electrens of the analple. if we measure the electric curient between a puir of electrodet that are driving an electrolvis. reactich. d) None. 5. Voltammetry is a) a collection of technicues in which the relation between corent and voltage is observed during. electrochemical procertsei b) a technigut in whith the relation between cursest and electrens is transfeured bebwes two zlectubies. c) a collection of electrens and charges that mabe nedex reactions daring electrochemical peotesues. di) None, 6. Meicury is not useful for studying exidations. Why? a) becaute ite in reduced in noncemplexing mhidia new no 25 V foerwas s.C. E.t. b] becauie Higa complesed with ioni near +0.25 V (veruss 5.6.t. c) because Hgar a llevid not solid. d) becaute of it exidued in noncomplexing meda near to. 25 V foerbos S.C. ..). 7. Charging cutrent arises from a) sxdation or teductien reactiost. b) thaving or discharging of the electric double layer at the electrode-polution interiace. c) decars more rapidly than faradic cument. d) None 8. Faradaic curent arives frem a) eeduction of oxidation of analyte at the working electrosle b) electrostatic attraction or repulion of ions in solstion and electrons in the electrode c) decays of mitreury dropi durite the process. d) None 9. When underpotential deposition occurs? 10. What is the diffecence between amperemetry and colometry? 13. What are the roles of the following electrodes: A. Working telectrode: 8. Aunitiary electrode: C. Reference electrode: 14. What is a Clark electrede, and how does it work? 15. Polarography is 16. What is the half wave potential {E1a) ? 17. In the following dugam. a) Which voltage, V1 or V2, in the diagram is constant in controlles-potertial electrolvis? b) Which are the working auxlliary, and reference electredes? 18. How does the anperometric glucole monitor wark? 19. What is the sampled current polarography? 20. Explain the Electric double layer? 21. Whar is the souate wove votammetry? 22. Explain the stroing malysir? 24. How we test for completion of the depostion in evctyacharimetric mabins? 61+217.13ki the reactont are Cathol- 2H2O+2e=H(w)+20H Asude: H,O21D,(s)+H+2c the word alardart men in this fuention? tree enerwichatge for the leaction 22. For bis Aractor. If redaction of Mri? eccorn rapidx. Jur't raud be becwas whin theie of (b) and (ic)? at the cathede? Find the weige percent ef lead bictate in the inkrown Pb(lactate)2+2H2OPbO2(x)+2lactate+4H+2e 34. in the following electrochamirat nut: indicate the ilectrodms? It we wart to cenerate tir2 from B. what is the relectride far geceratien the fi? 33. The senifity of a couloneter as governed by the dellyery af as minemum cuntert for ins minimum sne Shppene that 3ma can be delivered for 0.1s. (a) How many molin of electrons ane delivered by 5ml inr 0.1s ? same mumber of elections? 32. Explain the Electroeravenetre arayis and drow the cell. Kedicate the chectrode