Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Homework Assignment Problem 1 Problem description In the event of a loss-of-feedwater accident in a nuclear plant, a team of two operators needs to

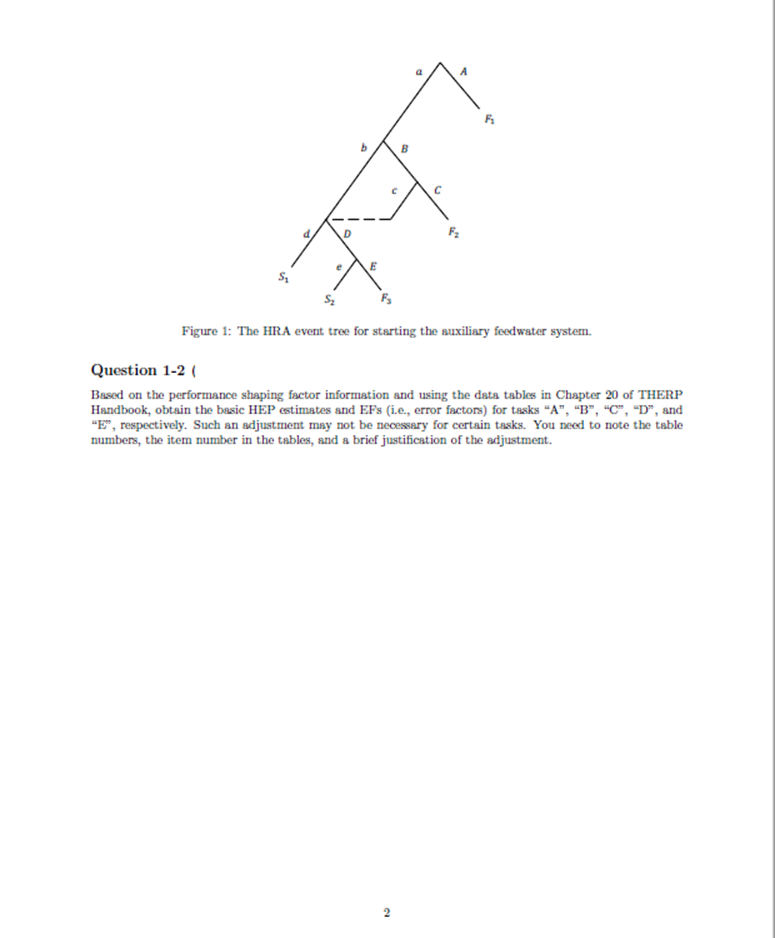
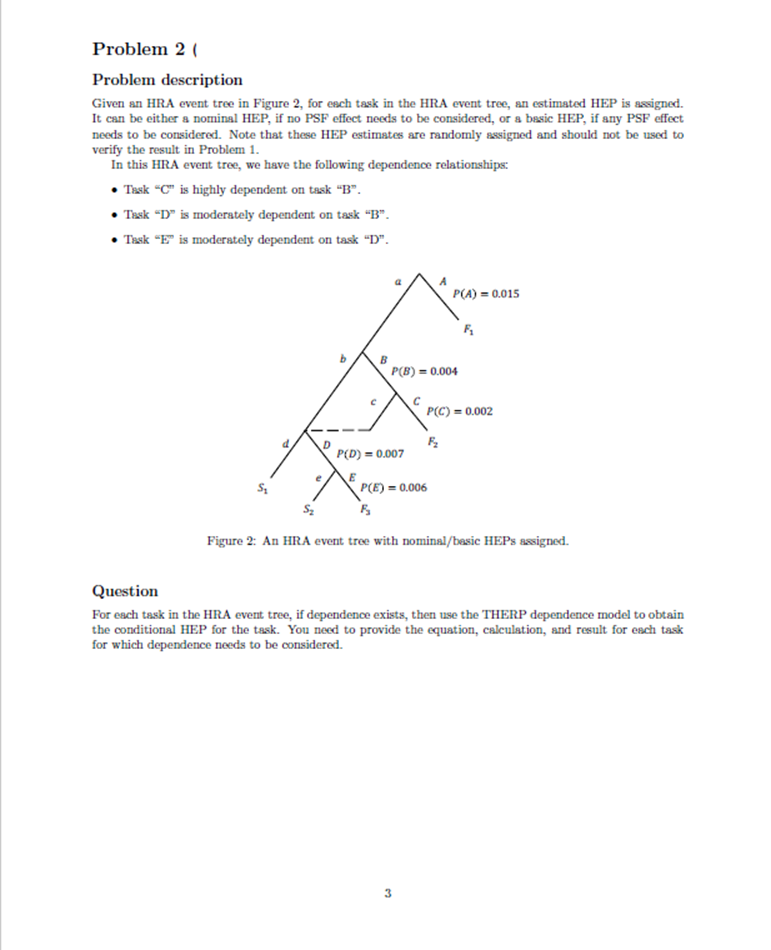

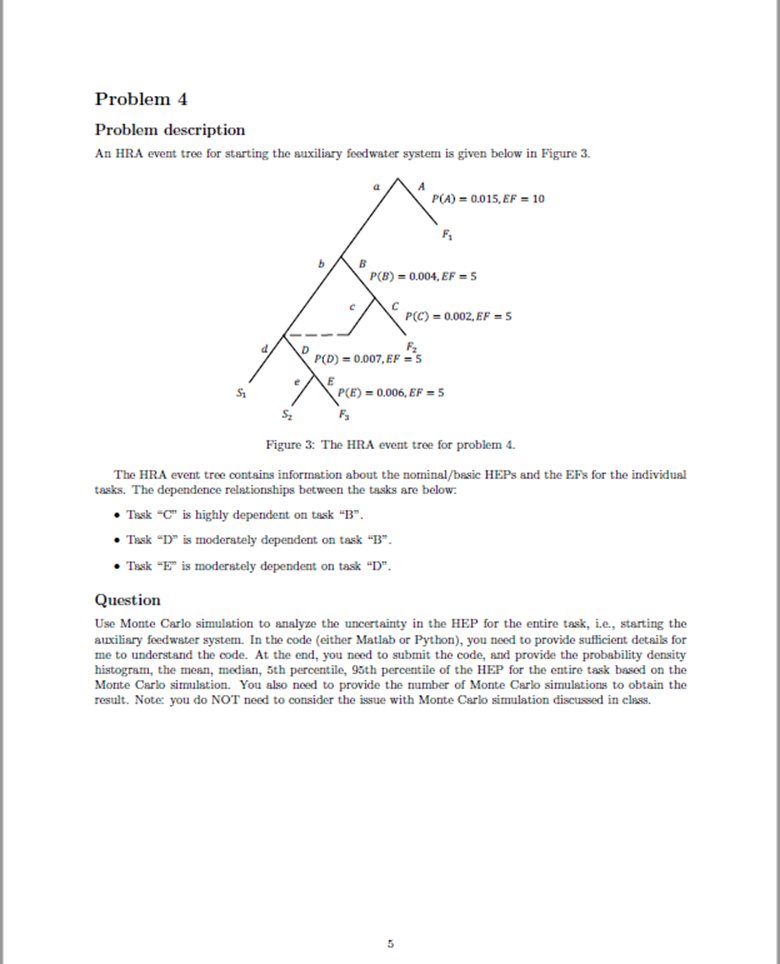
Homework Assignment Problem 1 Problem description In the event of a loss-of-feedwater accident in a nuclear plant, a team of two operators needs to start the auxiliary feedwater system to avoid damage to the plant. To successfully start the auxiliary feedwater system, the operators need to complete the following tasks: Task "A": The two operators need to successfully diagnose the loss-of-feedwater event within 20 min- utes. The loss-of-feedwater event is the first and the only event that needs to be diagnosed. This is a nominal diagnosis task. After the successful diagnosis of the event, the operators then need to complete two steps in the procedure for this type of event. Task "B": The first operator needs to successfully align the auxiliary feedwater pump to the available water source. The human error for this task is that the first operator may omit this step. Task "C": If task "B" is failed by the first operator, but as long as the second operator successfully aligns the auxiliary feedwater pump to the available water source, then the operators can still move to the next step in the procedure. The human error for this task is that the second operator may omit this step. Task "D": The first operator needs to successfully start the auxiliary feedwater pump. The human error for this task is that the first operator may omit this step. Task "E": If task "D" is failed by the first operator, but as long as the second operator successfully starts the auxiliary feedwater pump, then the operators are still successful in starting the auxiliary feedwater system (i.e., the entire task). The human error for this task is that the second operator may omit this step. Based on this task analysis, the HRA event tree for starting the auxiliary feedwater system is developed and shown in Figure 1. The performance shaping factors relevant to this problem are: both operators are skilled operators; both operators are under moderately high stress; there is no check-off provision in this procedure; the procedure is a short list procedure; the other performance shaping factors do not have either negative or positive effects on operator performance, and therefore do not need to be considered for this problem. Question 1-1 Using the data tables in Chapter 20 of THERP Handbook, obtain the nominal HEP estimates and EFs (ie., error factors) for tasks "A", "B", "C", "D", and "E", respectively. You need to note the table numbers, the item number in the tables, and a brief justification of your selection. d. 9 " D S Figure 1: The HRA event tree for starting the auxiliary feedwater system. Question 1-2 ( Based on the performance shaping factor information and using the data tables in Chapter 20 of THERP Handbook, obtain the basic HEP estimates and EFs (i.e., error factors) for tasks "A", "B", "C", "D", and "E", respectively. Such an adjustment may not be necessary for certain tasks. You need to note the table numbers, the item number in the tables, and a brief justification of the adjustment. 2 Problem 2 ( Problem description Given an HRA event tree in Figure 2, for each task in the HRA event tree, an estimated HEP is assigned. It can be either a nominal HEP, if no PSF effect needs to be considered, or a basic HEP, if any PSF effect needs to be considered. Note that these HEP estimates are randomly assigned and should not be used to verify the result in Problem 1. In this HRA event tree, we have the following dependence relationships: Task "C" is highly dependent on task "B". Task "D" is moderately dependent on task "B". Task "E" is moderately dependent on task "D". 49 P(A)=0.015 B P(B)=0.004 3 P(D)=0.007 P(C)=0.002 P(E)=0.006 S Figure 2: An HRA event tree with nominal/basic HEPs assigned. Question For each task in the HRA event tree, if dependence exists, then use the THERP dependence model to obtain the conditional HEP for the task. You need to provide the equation, calculation, and result for each task for which dependence needs to be considered. 02 Problem 3 Question 3-1 Given a lognormal probability distribution for a human error probability p: Inp~N(In= In 0.05, = 1), obtain the EF and uncertainty bounds for this distribution. Question 3-2 Given the median value = 0.02 and the EF-3 for a human error probability p, obtain the corresponding lognormal probability distribution. Problem 4 Problem description An HRA event tree for starting the auxiliary feedwater system is given below in Figure 3. P(A)=0.015, EF 10 b B P(B)=0.004, EF = 5 P(C)=0.002, EF = 5 Fz P(D)=0.007, EF = S S P(E)=0.006, EF = 5 S F Figure 3: The HRA event tree for problem 4. The HRA event tree contains information about the nominal/basic HEPs and the EFs for the individual tasks. The dependence relationships between the tasks are below. Task "C" is highly dependent on task "B". Task "D" is moderately dependent on task "B". Task "E" is moderately dependent on task "D". Question Use Monte Carlo simulation to analyze the uncertainty in the HEP for the entire task, i.e., starting the auxiliary feedwater system. In the code (either Matlab or Python), you need to provide sufficient details for me to understand the code. At the end, you need to submit the code, and provide the probability density histogram, the mean, median, 5th percentile, 95th percentile of the HEP for the entire task based on the Monte Carlo simulation. You also need to provide the number of Monte Carlo simulations to obtain the result. Note: you do NOT need to consider the issue with Monte Carlo simulation discussed in class.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


