homework help needed thanks
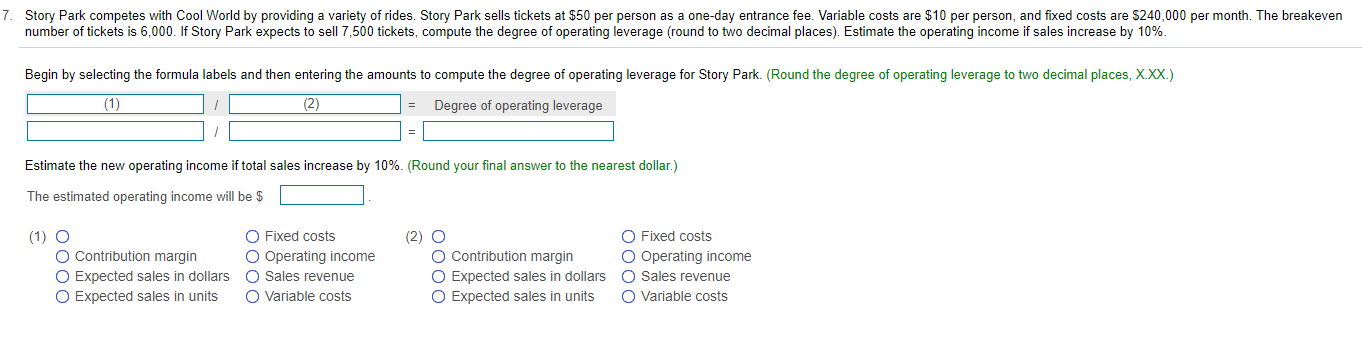
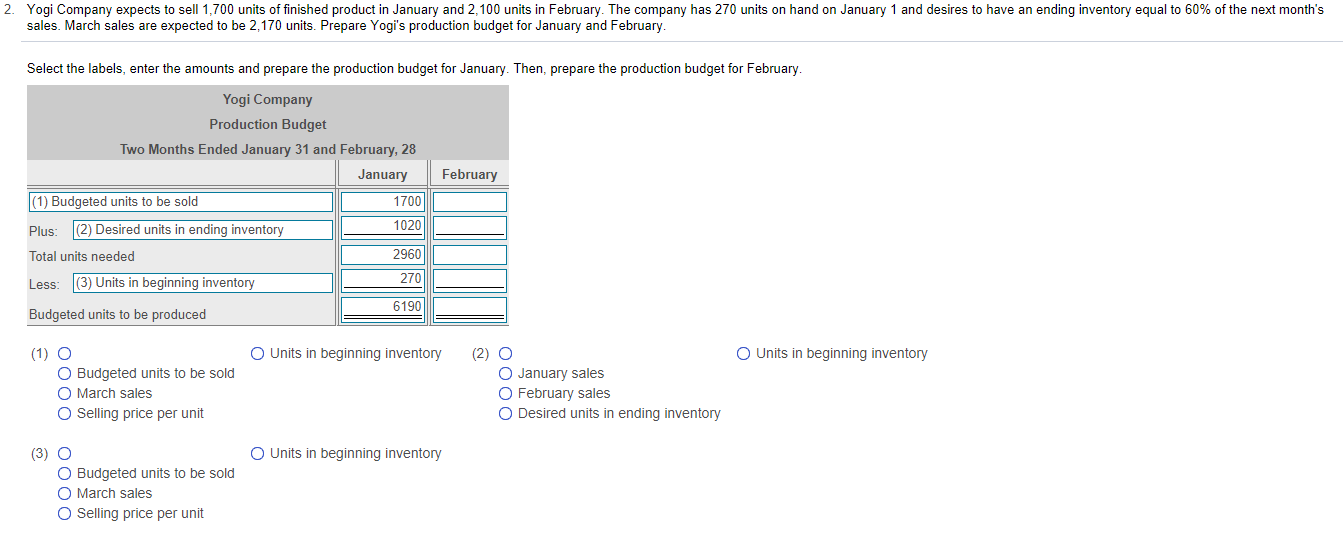
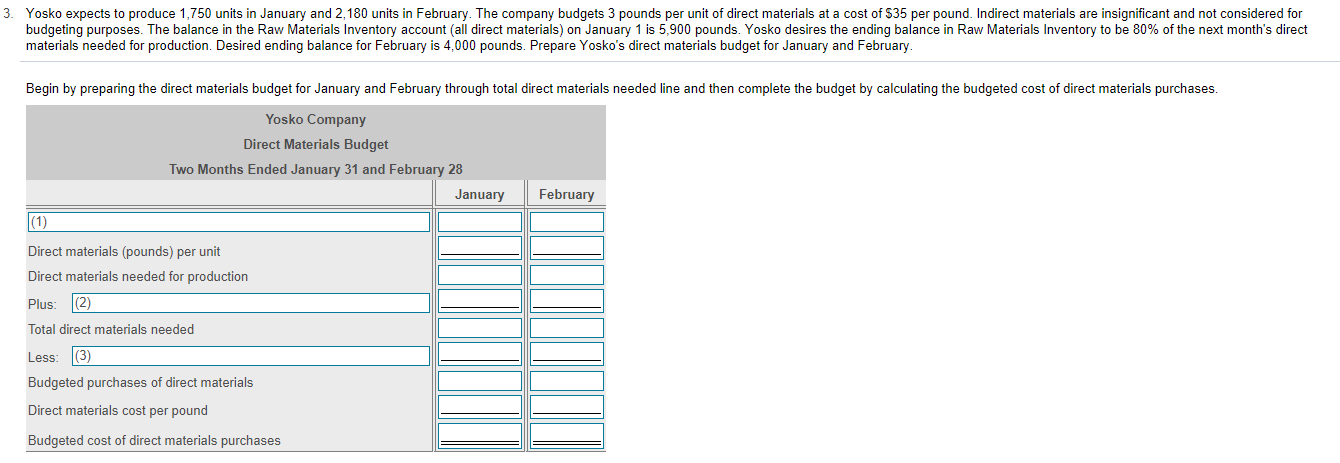
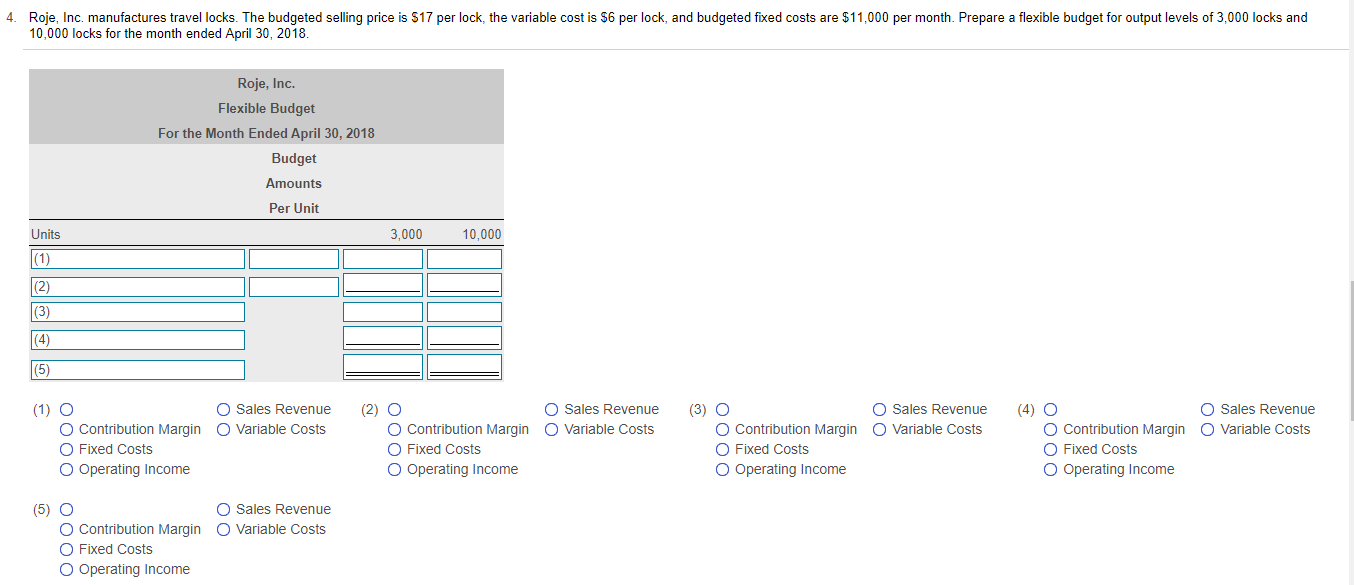
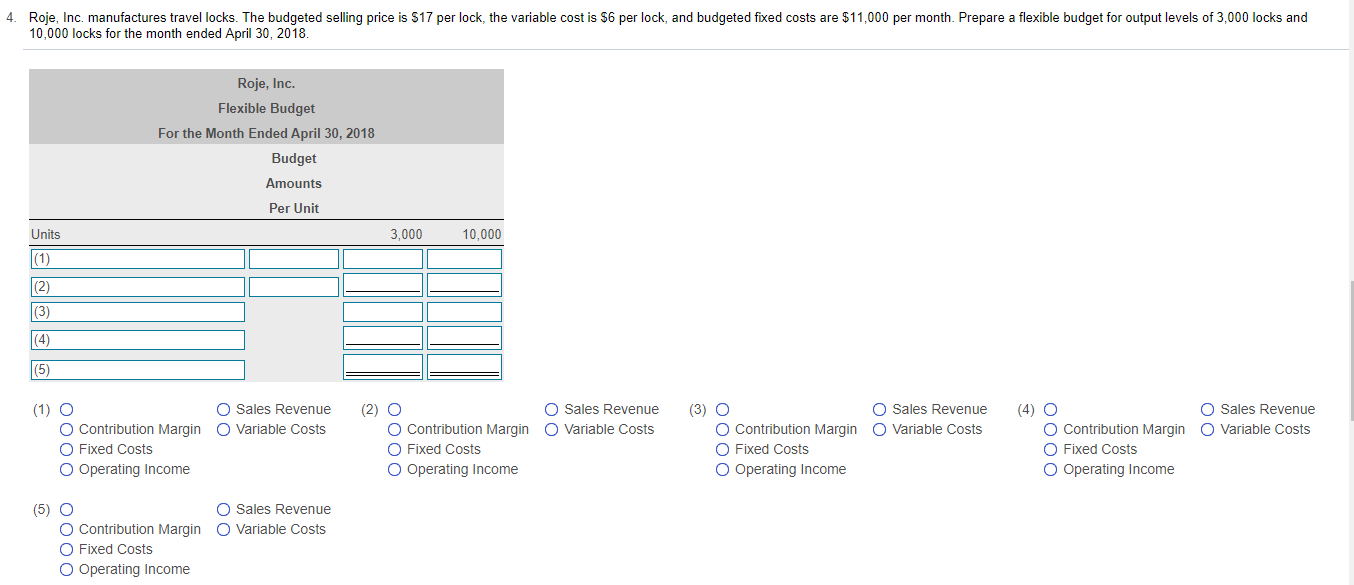

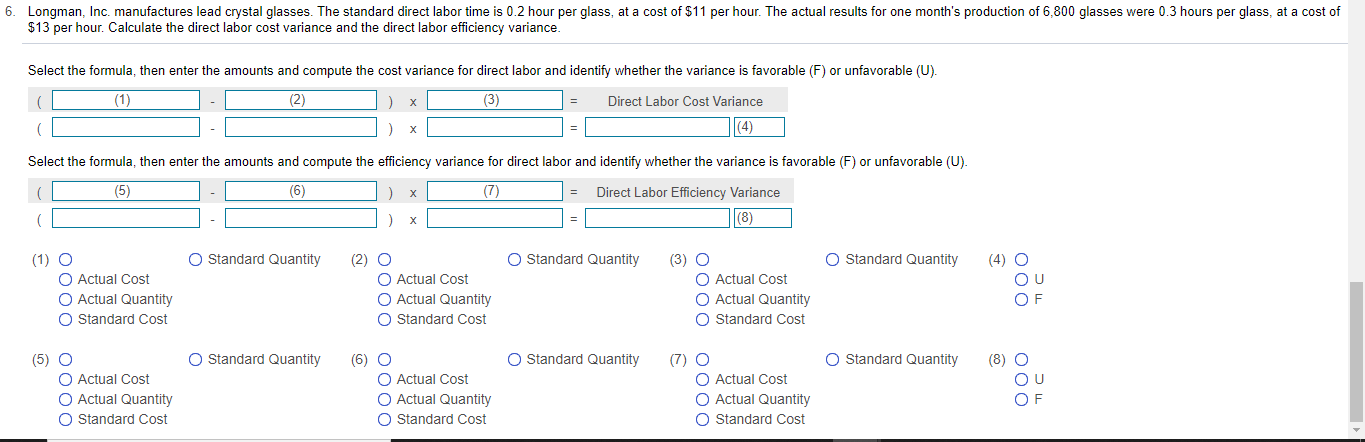
7. Story Park competes with Cool World by providing a variety of rides. Story Park sells tickets at $50 per person as a one-day entrance fee. Variable costs are $10 per person, and fixed costs are $240,000 per month. The breakeven number of tickets is 6,000. If Story Park expects to sell 7,500 tickets, compute the degree of operating leverage (round to two decimal places). Estimate the operating income if sales increase by 10%. Begin by selecting the formula labels and then entering the amounts to compute the degree of operating leverage for Story Park. (Round the degree of operating leverage to two decimal places, X.XX.) (1) ID (2) - Degree of operating leverage Estimate the new operating income if total sales increase by 10% (Round your final answer to the nearest dollar.) The estimated operating income will be $ . (1) O O Contribution margin O Expected sales in dollars O Expected sales in units O Fixed costs Operating income Sales revenue O Variable costs (2) O Contribution margin Expected sales in dollars O Expected sales in units Fixed costs Operating income Sales revenue O Variable costs 3. Yosko expects to produce 1,750 units in January and 2,180 units in February. The company budgets 3 pounds per unit of direct materials at a cost of $35 per pound. Indirect materials are insignificant and not considered for budgeting purposes. The balance in the Raw Materials Inventory account (all direct materials) on January 1 is 5,900 pounds. Yosko desires the ending balance in Raw Materials Inventory to be 80% of the next month's direct materials needed for production. Desired ending balance for February is 4,000 pounds. Prepare Yosko's direct materials budget for January and February Begin by preparing the direct materials budget for January and February through total direct materials needed line and then complete the budget by calculating the budgeted cost of direct materials purchases. Yosko Company Direct Materials Budget Two Months Ended January 31 and February 28 January February (1) Direct materials (pounds) per unit Direct materials needed for production Plus (2) Total direct materials needed Less: (3) Budgeted purchases of direct materials Direct materials cost per pound Budgeted cost of direct materials purchases 4. Roje, Inc. manufactures travel locks. The budgeted selling price is $17 per lock, the variable cost is $6 per lock, and budgeted fixed costs are $11,000 per month. Prepare a flexible budget for output levels of 3,000 locks and 10,000 locks for the month ended April 30, 2018. Roje, Inc. Flexible Budget For the Month Ended April 30, 2018 Budget Amounts Per Unit 3,000 10,000 Units (1) (2) O O Sales Revenue O Variable Costs Sales Revenue O Variable Costs O Sales Revenue O Variable Costs O Sales Revenue O Variable Costs (1) O O Contribution Margin O Fixed Costs Operating Income Contribution Margin Fixed Costs Operating Income (3) O Contribution Margin O Fixed Costs Operating Income (4) O O Contribution Margin Fixed Costs Operating Income (5) O Sales Revenue O Variable Costs O Contribution Margin O Fixed Costs Operating Income 7. Story Park competes with Cool World by providing a variety of rides. Story Park sells tickets at $50 per person as a one-day entrance fee. Variable costs are $10 per person, and fixed costs are $240,000 per month. The breakeven number of tickets is 6,000. If Story Park expects to sell 7,500 tickets, compute the degree of operating leverage (round to two decimal places). Estimate the operating income if sales increase by 10%. Begin by selecting the formula labels and then entering the amounts to compute the degree of operating leverage for Story Park. (Round the degree of operating leverage to two decimal places, X.XX.) (1) ID (2) - Degree of operating leverage Estimate the new operating income if total sales increase by 10% (Round your final answer to the nearest dollar.) The estimated operating income will be $ . (1) O O Contribution margin O Expected sales in dollars O Expected sales in units O Fixed costs Operating income Sales revenue O Variable costs (2) O Contribution margin Expected sales in dollars O Expected sales in units Fixed costs Operating income Sales revenue O Variable costs 3. Yosko expects to produce 1,750 units in January and 2,180 units in February. The company budgets 3 pounds per unit of direct materials at a cost of $35 per pound. Indirect materials are insignificant and not considered for budgeting purposes. The balance in the Raw Materials Inventory account (all direct materials) on January 1 is 5,900 pounds. Yosko desires the ending balance in Raw Materials Inventory to be 80% of the next month's direct materials needed for production. Desired ending balance for February is 4,000 pounds. Prepare Yosko's direct materials budget for January and February Begin by preparing the direct materials budget for January and February through total direct materials needed line and then complete the budget by calculating the budgeted cost of direct materials purchases. Yosko Company Direct Materials Budget Two Months Ended January 31 and February 28 January February (1) Direct materials (pounds) per unit Direct materials needed for production Plus (2) Total direct materials needed Less: (3) Budgeted purchases of direct materials Direct materials cost per pound Budgeted cost of direct materials purchases 4. Roje, Inc. manufactures travel locks. The budgeted selling price is $17 per lock, the variable cost is $6 per lock, and budgeted fixed costs are $11,000 per month. Prepare a flexible budget for output levels of 3,000 locks and 10,000 locks for the month ended April 30, 2018. Roje, Inc. Flexible Budget For the Month Ended April 30, 2018 Budget Amounts Per Unit 3,000 10,000 Units (1) (2) O O Sales Revenue O Variable Costs Sales Revenue O Variable Costs O Sales Revenue O Variable Costs O Sales Revenue O Variable Costs (1) O O Contribution Margin O Fixed Costs Operating Income Contribution Margin Fixed Costs Operating Income (3) O Contribution Margin O Fixed Costs Operating Income (4) O O Contribution Margin Fixed Costs Operating Income (5) O Sales Revenue O Variable Costs O Contribution Margin O Fixed Costs Operating Income













