Question
How can you express the following constraint using the decision variables defined previously? A. If project 3 is selected, project 4 cannot be selected. P
How can you express the following constraint using the decision variables defined previously?
A. If project 3 is selected, project 4 cannot be selected.
P3 + P4 1
P3 P4
1 - P4 P3
1 - P3 P4
P4 1 + P3
B. How can you express the following constraint using the decision variables defined previously? Additional decision variables can be defined if necessary.
At most two of the investments 1, 2, 3 are chosen, or at least three of the investments 3, 4, 5, 6 are chosen.
2 - (P1 + P2 + P3) M * Y, (P3 + P4 + P5 + P6) - 3 M * (1 - Y),
Y is binary, M is a large number
(P1 + P2 + P3) - 2 M * Y, 3 - (P3 + P4 + P5 + P6) M * (1 - Y),
Y is binary, M is a large number
(P1 + P2 + P3) 2Y, (P3 + P4 + P5 + P6) 3(1 - Y),
Y is binary
(P1 + P2 + P3) 2Y, (P3 + P4 + P5 + P6) 3(1 - Y),
Y is binary
(P1 + P2 + P3) 2Y, (P3 + P4 + P5 + P6) 3Y,
Y is binary
C. How can you express the following constraint using the decision variables defined previously? You may define additional decision variables if needed.
Either both investments 1 and 2 are chosen, or neither investment 5 nor 6 is chosen.
(P1 + P2) = M * Y, (P5 + P6) = M * (1 - Y),
Y is binary, M is a large number
2 - (P1 + P2) M * Y, (P5 + P6) M * (1 - Y),
Y is binary, M is a large number
2 - (P1 + P2) M * Y, (P5 + P6) M * (1 - Y),
Y is binary, M is a large number
2 - (P1 + P2) M * Y, (P5 + P6) M * (1 - Y),
Y is binary, M is a large number
(P1 + P2) 2Y, (P5 + P6) 0,
Y is binary
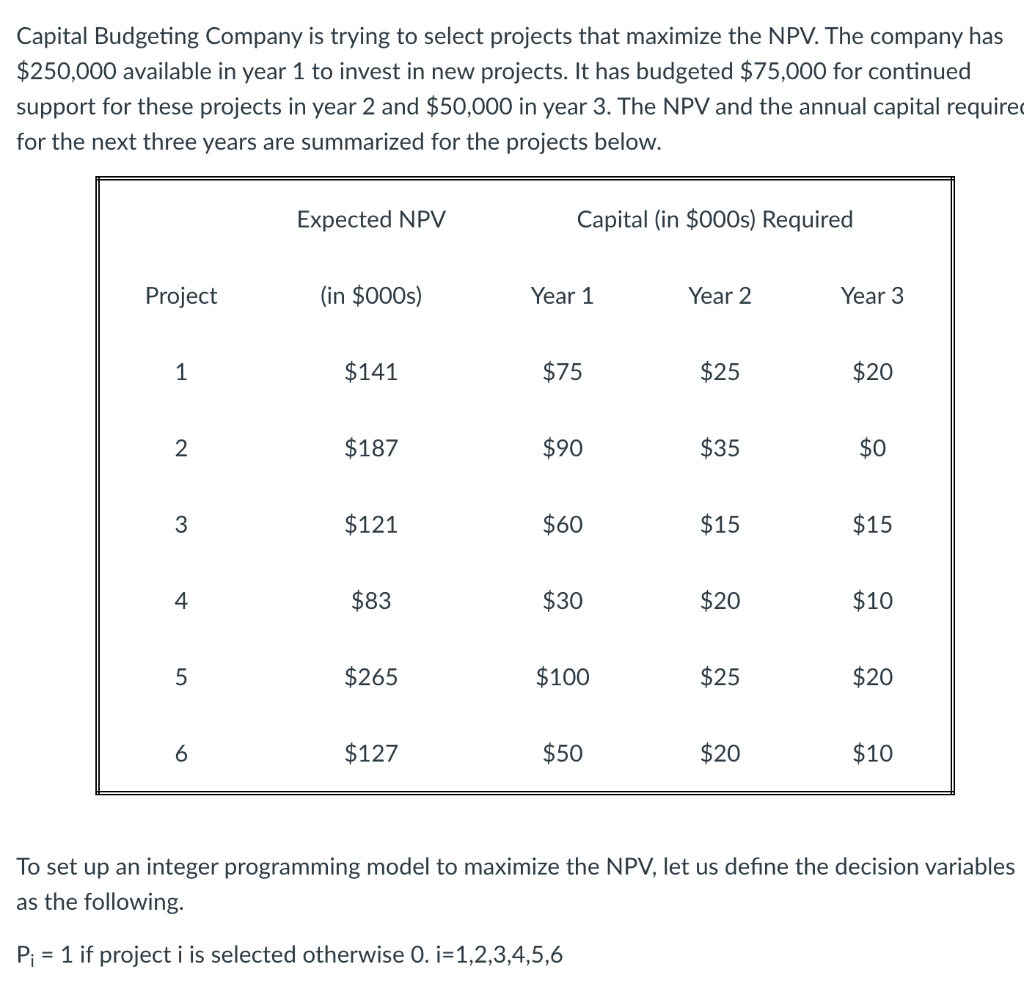
Capital Budgeting Company is trying to select projects that maximize the NPV. The company has $250,000 available in year 1 to invest in new projects. It has budgeted $75,000 for continued support for these projects in year 2 and $50,000 in year 3. The NPV and the annual capital required for the next three years are summarized for the projects below. Expected NPV Capital (in $000s) Required Project (in $000s) Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 1 $141 $75 $25 $20 2 $187 $90 $35 $0 3 $121 $60 $15 $15 4 $83 $30 $20 $10 5 $265 $100 $25 $20 6 $127 $50 $20 $10 To set up an integer programming model to maximize the NPV, let us define the decision variables as the following P; = 1 if project i is selected otherwise 0. i=1,2,3,4,5,6 Capital Budgeting Company is trying to select projects that maximize the NPV. The company has $250,000 available in year 1 to invest in new projects. It has budgeted $75,000 for continued support for these projects in year 2 and $50,000 in year 3. The NPV and the annual capital required for the next three years are summarized for the projects below. Expected NPV Capital (in $000s) Required Project (in $000s) Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 1 $141 $75 $25 $20 2 $187 $90 $35 $0 3 $121 $60 $15 $15 4 $83 $30 $20 $10 5 $265 $100 $25 $20 6 $127 $50 $20 $10 To set up an integer programming model to maximize the NPV, let us define the decision variables as the following P; = 1 if project i is selected otherwise 0. i=1,2,3,4,5,6Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


