How do I solve for this using linear programming in Excel? Per the text below, the task is to develop an alternative methodology for splitting the daily shipments of spare parts among three strategic freight forwarders (FF1, FF2, FF3).


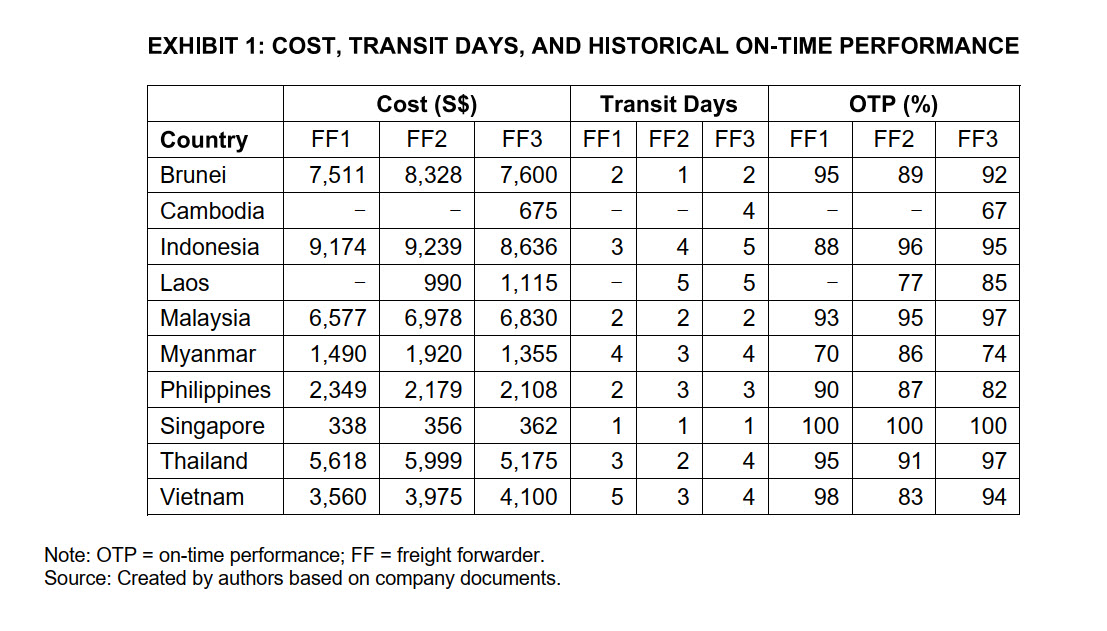
Caterpillar believed in dividing business among the three FFs rather than relying too much on any one FF, and this helped the company to mitigate risk. To that end, it was decided that no FF would get more than 60 per cent of Caterpillar's total shipping expenditures on any given day. This meant, for example, that if Caterpillar were to spend S$40,000 for shipments on a given day, no FF would receive more than S$24,000. While there was a maximum on the amount to be paid to an FF, there was no minimum, for obvious competitive reasons. The procurement team used an experience-based heuristic for selecting an FF for each country, while taking into account the costs, the number of transit days, the OTP statistics, and the 60 per cent expenditure ceiling. As it was being pressed by the internal audit team, which was promoting continuous process improvements, the procurement team wondered if Tan, during his month-long internship, could develop a more rigorous, analytical method for making the FF selection for each country. DAILY FREIGHT FORWARDING DECISION The ADC operations team was responsible for meeting the key performance indicator of shipping spare parts ordered by dealers. Urgent orders of spare parts flowed through Caterpillar dealers' order system. For destinations without contracted rates, such as for the 10 countries in the Southeast Asia region, the operations team would consolidate all shipments daily by country. By late afternoon, it would then raise a freight spot quote inquiry to the procurement team and request that it appoint a freight forwarder (FF) for each country. Caterpillar had discovered through experience that it could gain from spot as opposed to contracted rates, as many FFs often had excess capacity to these 10 countries. The procurement team would forward information on the weight, volume, and delivery locations of each spare-parts shipment to three strategic FFs (FF1, FF2, and FF3) appointed for the Southeast Asia region. The FFs would submit a quotation indicating the cost and the number of transit days they would require to make all the deliveries in each country. The procurement team would then evaluate the submissions and proceed to select an FF for each country based on the data for the shipments required that day (see Exhibit 1). Finally, the consolidated shipment for each country would be picked up by the selected FF before the end of the business day. On July 5, 2017, for deliveries to Brunei, FF1 quoted S$7,51114 and estimated that it would require two transit days to get all the spare parts delivered, while FF2 quoted S$8,328 for one transit day and FF3 quoted S$7,600 for two transit days. Caterpillar privileged prompt aftermarket service to its customers. Accordingly, it tracked the delivery performance of each shipment as it had a "committed delivery lead time" in servicing its dealers. If an FF quoted to deliver all the shipments in a country within two days but failed to do so, it would have negative implications for all parties. Caterpillar only worked with FFs that had on-time-performance (OTP) statistics near the top in the industry. For the Brunei market, FF1 had historically delivered 95 per cent of shipments on time when it had quoted two day deliveries, while FF2 and FF3 had achieved historical OTP rates of 89 per cent and 92 per cent, respectively, when they had quoted one and two day deliveries in the past. Caterpillar had many customers in Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand (see Exhibit 1). There were not many shipments to be made within Singapore, as most dealers there came directly to the ADC to pick up the required parts. For those who did not, the three FFs delivered all shipments to them by the next business day. New markets were also opening up in Cambodia and Laos. The current low volumes of orders coming from these countries had not yet enticed all three FFs to serve them. Thus, FF1 did not provide service to either Cambodia or Laos; FF2 was not servicing Laos; and FF3 was the only FF serving both countries. EXHIBIT 1: COST, TRANSIT DAYS, AND HISTORICAL ON-TIME PERFORMANCE Note: OTP= on-time performance; FF= freight forwarder. Source: Created by authors based on company documents









