How do you calculate the external funds required?
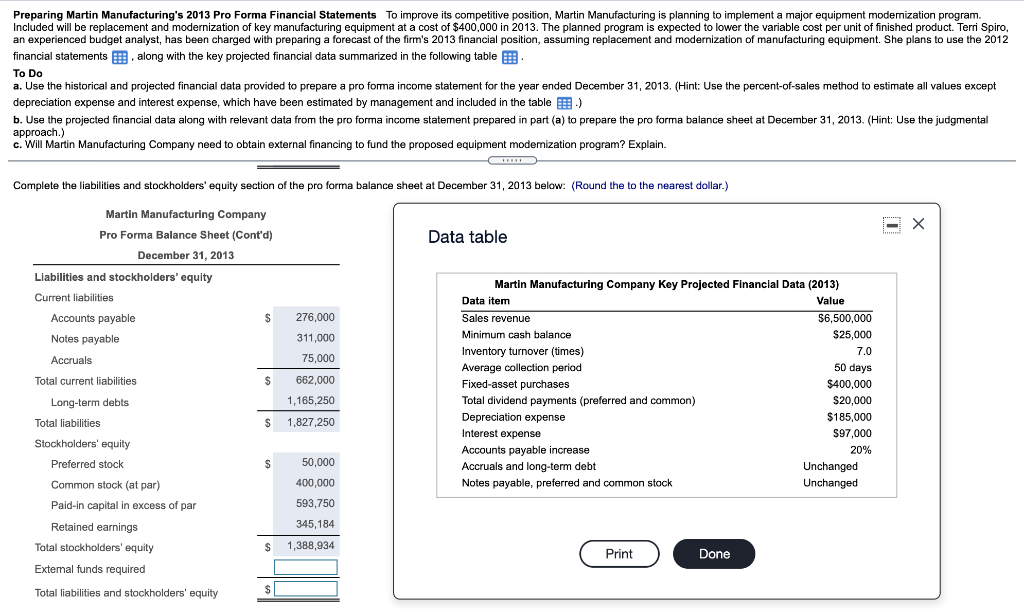
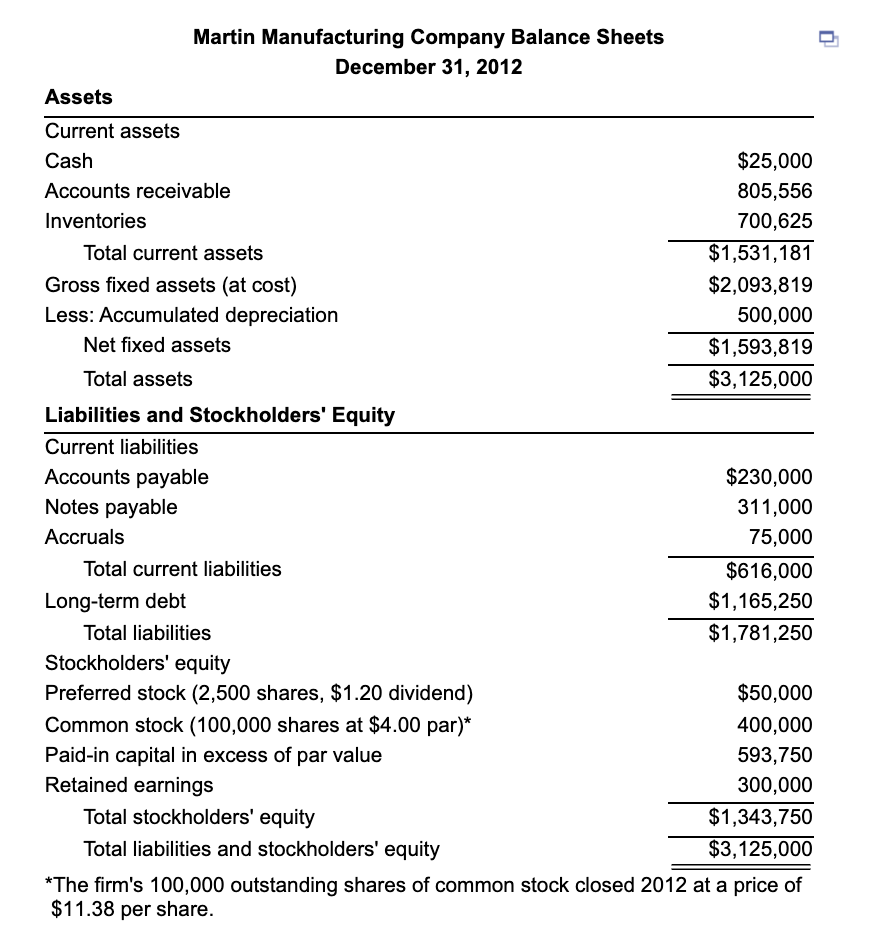
Preparing Martin Manufacturing's 2013 Pro Forma Financial Statements To improve its competitive position, Martin Manufacturing is planning to implement a major equipment modernization program Included will be replacement and modernization of key manufacturing equipment at a cost of $400,000 in 2013. The planned program is expected to lower the variable cost per unit of finished product. Terri Spiro, an experienced budget analyst, has been charged with preparing a forecast of the firm's 2013 financial position, assuming replacement and modernization of manufacturing equipment. She plans to use the 2012 financial statements along with the key projected financial data summarized in the following table 1 To Do a. Use the historical and projected financial data provided to prepare a pro forma income statement for the year ended December 31, 2013. (Hint: Use the percent-of-sales method to estimate all values except depreciation expense and interest expense, which have been estimated by management and included in the table.) b. Use the projected financial data along with relevant data from the pro forma income statement prepared in part (a) to prepare the pro forma balance sheet at December 31, 2013. (Hint: Use the judgmental approach.) c. Will Martin Manufacturing Company need to obtain external financing to fund the proposed equipment modemization program? Explain. Complete the liabilities and stockholders' equity section of the pro forma balance sheet at December 31, 2013 below: (Round the to the nearest dollar.) Data table Martin Manufacturing Company Pro Forma Balance Sheet (Cont'd) December 31, 2013 Liabilities and stockholders' equity Current liabilities $ 276,000 Accounts payable Notes payable Accruals Total current liabilities 311,000 75,000 $ 662,000 Martin Manufacturing Company Key Projected Financial Data (2013) Data item Value Sales revenue $6,500,000 Minimum cash balance $25,000 $ Inventory turnover (times) 7.0 Average collection period 50 days Fixed-asset purchases $400,000 Total dividend payments (preferred and common) $20,000 Depreciation expense $185,000 $97,000 Accounts payable increase 20% Accruals and long-term debt Unchanged Notes payable, preferred and common stock Unchanged 1,165,250 $ 1,827,250 Interest expense $ 50,000 Long-term debts Total liabilities Stockholders' equity ' Preferred stock Common stock (at par) Paid-in capital in excess of par Retained earnings Total stockholders' equity External funds required Total liabilities and stockholders' equity ' 400,000 593,750 345,184 1,388,934 S Print Done $ Martin Manufacturing Company Balance Sheets December 31, 2012 Assets Current assets Cash $25,000 Accounts receivable 805,556 Inventories 700,625 Total current assets $1,531,181 Gross fixed assets (at cost) $2,093,819 Less: Accumulated depreciation 500,000 Net fixed assets $1,593,819 Total assets $3,125,000 Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Current liabilities Accounts payable $230,000 Notes payable 311,000 Accruals 75,000 Total current liabilities $616,000 Long-term debt $1,165,250 Total liabilities $1,781,250 Stockholders' equity Preferred stock (2,500 shares, $1.20 dividend) $50,000 Common stock (100,000 shares at $4.00 par)* 400,000 Paid-in capital in excess of par value 593,750 Retained earnings 300,000 Total stockholders' equity $1,343,750 Total liabilities and stockholders' equity $3,125,000 *The firm's 100,000 outstanding shares of common stock closed 2012 at a price of $11.38 per share. Preparing Martin Manufacturing's 2013 Pro Forma Financial Statements To improve its competitive position, Martin Manufacturing is planning to implement a major equipment modernization program Included will be replacement and modernization of key manufacturing equipment at a cost of $400,000 in 2013. The planned program is expected to lower the variable cost per unit of finished product. Terri Spiro, an experienced budget analyst, has been charged with preparing a forecast of the firm's 2013 financial position, assuming replacement and modernization of manufacturing equipment. She plans to use the 2012 financial statements along with the key projected financial data summarized in the following table 1 To Do a. Use the historical and projected financial data provided to prepare a pro forma income statement for the year ended December 31, 2013. (Hint: Use the percent-of-sales method to estimate all values except depreciation expense and interest expense, which have been estimated by management and included in the table.) b. Use the projected financial data along with relevant data from the pro forma income statement prepared in part (a) to prepare the pro forma balance sheet at December 31, 2013. (Hint: Use the judgmental approach.) c. Will Martin Manufacturing Company need to obtain external financing to fund the proposed equipment modemization program? Explain. Complete the liabilities and stockholders' equity section of the pro forma balance sheet at December 31, 2013 below: (Round the to the nearest dollar.) Data table Martin Manufacturing Company Pro Forma Balance Sheet (Cont'd) December 31, 2013 Liabilities and stockholders' equity Current liabilities $ 276,000 Accounts payable Notes payable Accruals Total current liabilities 311,000 75,000 $ 662,000 Martin Manufacturing Company Key Projected Financial Data (2013) Data item Value Sales revenue $6,500,000 Minimum cash balance $25,000 $ Inventory turnover (times) 7.0 Average collection period 50 days Fixed-asset purchases $400,000 Total dividend payments (preferred and common) $20,000 Depreciation expense $185,000 $97,000 Accounts payable increase 20% Accruals and long-term debt Unchanged Notes payable, preferred and common stock Unchanged 1,165,250 $ 1,827,250 Interest expense $ 50,000 Long-term debts Total liabilities Stockholders' equity ' Preferred stock Common stock (at par) Paid-in capital in excess of par Retained earnings Total stockholders' equity External funds required Total liabilities and stockholders' equity ' 400,000 593,750 345,184 1,388,934 S Print Done $ Martin Manufacturing Company Balance Sheets December 31, 2012 Assets Current assets Cash $25,000 Accounts receivable 805,556 Inventories 700,625 Total current assets $1,531,181 Gross fixed assets (at cost) $2,093,819 Less: Accumulated depreciation 500,000 Net fixed assets $1,593,819 Total assets $3,125,000 Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Current liabilities Accounts payable $230,000 Notes payable 311,000 Accruals 75,000 Total current liabilities $616,000 Long-term debt $1,165,250 Total liabilities $1,781,250 Stockholders' equity Preferred stock (2,500 shares, $1.20 dividend) $50,000 Common stock (100,000 shares at $4.00 par)* 400,000 Paid-in capital in excess of par value 593,750 Retained earnings 300,000 Total stockholders' equity $1,343,750 Total liabilities and stockholders' equity $3,125,000 *The firm's 100,000 outstanding shares of common stock closed 2012 at a price of $11.38 per share








