Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
how to write the body of the functions? from typing import List import csv import math ################################################################################ # Begin constants ################################################################################ COLUMN_ID = 0 COLUMN_NAME
how to write the body of the functions? 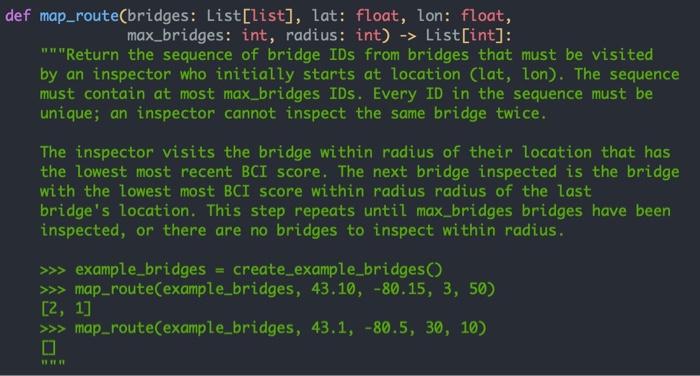
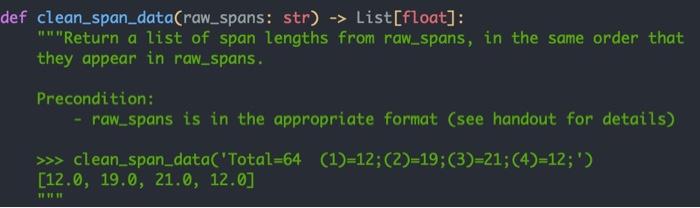
def map_route(bridges: List[list], lat: float, lon: float, max_bridges: int, radius: int) -> List[int]: "Return the sequence of bridge IDs from bridges that must be visited by an inspector who initially starts at location (lat, lon). The sequence must contain at most max_bridges IDs. Every ID in the sequence must be unique; an inspector cannot inspect the same bridge twice. The inspector visits the bridge within radius of their location that has the lowest most recent BCI score. The next bridge inspected is the bridge with the lowest most BCI score within radius radius of the last bridge's location. This step repeats until max_bridges bridges have been inspected, or there are no bridges to inspect within radius. >>> example_bridges = create_example_bridges() >>> map_route(example_bridges, 43.10, -80.15, 3, 50) [2, 1] >>> map_route(example_bridges, 43.1, -80.5, 30, 10) HR def clean_span_data(raw_spans: str) -> List[float]: "Return a list of span lengths from raw_spans, in the same order that they appear in raw_spans. Precondition: - raw_spans is in the appropriate format (see handout for details) >>> clean_span_data('Total=64 (1)=12;(2)=19;(3)=21;(4)=12;') [12.0, 19.0, 21.0, 12.0] TIT from typing import List
import csv
import math
################################################################################
# Begin constants
################################################################################
COLUMN_ID = 0
COLUMN_NAME = 1
COLUMN_HIGHWAY = 2
COLUMN_LAT = 3
COLUMN_LON = 4
COLUMN_YEAR_BUILT = 5
COLUMN_LAST_MAJOR_REHAB = 6
COLUMN_LAST_MINOR_REHAB = 7
COLUMN_NUM_SPANS = 8
COLUMN_SPAN_DETAILS = 9
COLUMN_DECK_LENGTH = 10
COLUMN_LAST_INSPECTED = 11
COLUMN_BCI = 12
INDEX_BCI_YEARS = 0
INDEX_BCI_SCORES = 1
MISSING_BCI = -1.0
EARTH_RADIUS = 6371
################################################################################
# Sample data for docstring examples
################################################################################
def create_example_bridge_1() -> list:
"""Return a bridge in our list-format to use for doctest examples.
This bridge is the same as the bridge from row 3 of the dataset.
"""
return [
1, 'Highway 24 Underpass at Highway 403',
'403', 43.167233, -80.275567, '1965', '2014', '2009', 4,
[12.0, 19.0, 21.0, 12.0], 65.0, '04/13/2012',
[['2013', '2012', '2011', '2010', '2009', '2008', '2007',
'2006', '2005', '2004', '2003', '2002', '2001', '2000'],
[MISSING_BCI, 72.3, MISSING_BCI, 69.5, MISSING_BCI, 70.0, MISSING_BCI,
70.3, MISSING_BCI, 70.5, MISSING_BCI, 70.7, 72.9, MISSING_BCI]]
]
def create_example_bridge_2() -> list:
"""Return a bridge in our list-format to use for doctest examples.
This bridge is the same as the bridge from row 4 of the dataset.
"""
return [
2, 'WEST STREET UNDERPASS',
'403', 43.164531, -80.251582, '1963', '2014', '2007', 4,
[12.2, 18.0, 18.0, 12.2], 61.0, '04/13/2012',
[['2013', '2012', '2011', '2010', '2009', '2008', '2007',
'2006', '2005', '2004', '2003', '2002', '2001', '2000'],
[MISSING_BCI, 71.5, MISSING_BCI, 68.1, MISSING_BCI, 69.0, MISSING_BCI,
69.4, MISSING_BCI, 69.4, MISSING_BCI, 70.3, 73.3, MISSING_BCI]]
]
def create_example_bridge_3() -> list:
"""Return a bridge in our list-format to use for doctest examples.
This bridge is the same as the bridge from row 33 of the dataset.
"""
return [
3, 'STOKES RIVER BRIDGE', '6',
45.036739, -81.33579, '1958', '2013', '', 1,
[16.0], 18.4, '08/28/2013',
[['2013', '2012', '2011', '2010', '2009', '2008', '2007',
'2006', '2005', '2004', '2003', '2002', '2001', '2000'],
[85.1, MISSING_BCI, 67.8, MISSING_BCI, 67.4, MISSING_BCI, 69.2,
70.0, 70.5, MISSING_BCI, 75.1, MISSING_BCI, 90.1, MISSING_BCI]]
]
def create_example_bridges() -> List[list]:
"""Return a list containing three unique example bridges.
The bridges contained in the list are from row 3, 4, and 33 of the dataset
(in that order).
"""
return [
create_example_bridge_1(),
create_example_bridge_2(),
create_example_bridge_3()
]
################################################################################
# Helper function
################################################################################
def calculate_distance(lat1: float, lon1: float,
lat2: float, lon2: float) -> float:
"""Return the distance in kilometers between the two locations defined by
(lat1, lon1) and (lat2, lon2), rounded to the nearest meter.
>>> calculate_distance(43.659777, -79.397383, 43.657129, -79.399439)
0.338
>>> calculate_distance(43.42, -79.24, 53.32, -113.30)
2713.226
"""
# This function uses the haversine function to find the
# distance between two locations. You do NOT need to understand why it
# works. You will just need to call on the function and work with what it
# returns.
# Based on code at goo.gl/JrPG4j
# convert decimal degrees to radians
lon1, lat1, lon2, lat2 = (math.radians(lon1), math.radians(lat1),
math.radians(lon2), math.radians(lat2))
# haversine formula t
lon_diff = lon2 - lon1
lat_diff = lat2 - lat1
a = (math.sin(lat_diff / 2) ** 2
+ math.cos(lat1) * math.cos(lat2) * math.sin(lon_diff / 2) ** 2)
c = 2 * math.asin(math.sqrt(a))
return round(c * EARTH_RADIUS, 3)


Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


