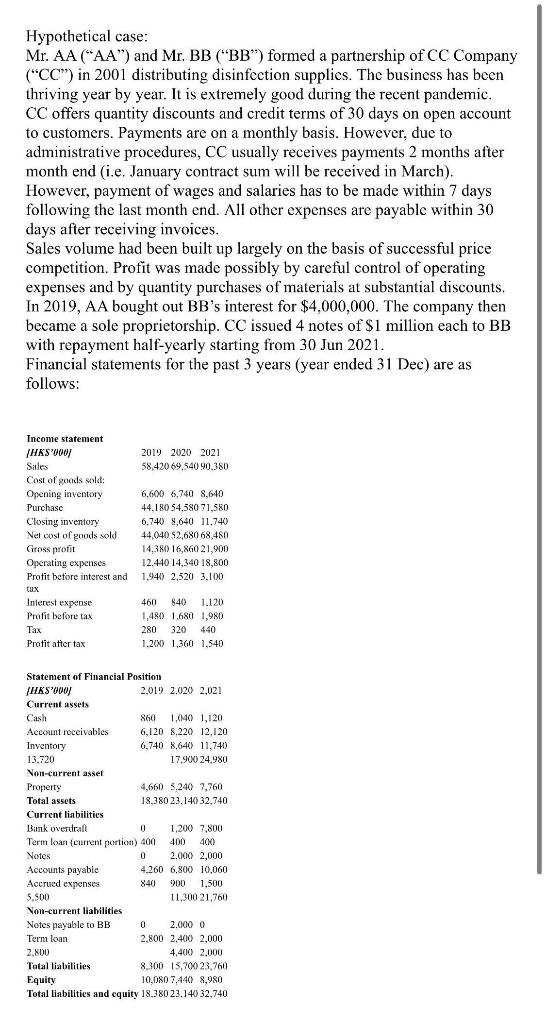

Hypothetical case: Mr. AA ("AA") and Mr. BB ("BB") formed a partnership of CC Company ("CC") in 2001 distributing disinfection supplies. The business has been thriving year by year. It is extremely good during the recent pandemic. CC offers quantity discounts and credit terms of 30 days on open account to customers. Payments are on a monthly basis. However, due to administrative procedures, CC usually receives payments 2 months after month end (i.e. January contract sum will be received in March). However, payment of wages and salaries has to be made within 7 days following the last month end. All other expenses are payable within 30 days after receiving invoices. Sales volume had been built up largely on the basis of successful price competition. Profit was made possibly by careful control of operating expenses and by quantity purchases of materials at substantial discounts. In 2019, AA bought out BB's interest for $4,000,000. The company then became a sole proprietorship. CC issued 4 notes of $1 million each to BB with repayment half-yearly starting from 30 Jun 2021. Financial statements for the past 3 years (year ended 31 Dec) are as follows: Income statement [HKS'000] Sales Cost of goods sold: Opening inventory Purchase Closing inventory Net cost of goods sold. Gross profit Operating expenses Profit before interest and tax Interest expense Profit before tax Tax Profit after tax Non-current asset Property Total assets Current liabilities 2019 2020 2021 58,420 69,540 90,3801 Statement of Financial Position [HKS'000] Current assets Cash Account receivables Inventory 13.720 Accounts payable Accrued expenses 5,500 Non-current liabilities. Notes payable to BB Term loan 6.600 6,740 8,640 44,180 54,580 71.580 6,740 8,640 11.740 44,040 $2,680 68,480 14,380 16,860 21,900 12.440 14,340 18,800. 1,940 2,520 3,100 2.800 Total liabilities 460 840 1.120 1,480 1,680 1,980 280 320 440 1,200 1,360 1,540 2.019 2.020 2,021 860 1,040 1,120 6,120 8,220 12,120 6,740 8,640 11,740. 17,900 24,980 Bank overdraft 0 Term loan (current portion) 400. Notes 0 4,660 5,240 7,760 18,380 23,140 32,740 1,200 7,800 400 400 2,000 2,000 4,260 6,800 10,060 840 900 1,500 11,300 21,760 0 2,000 0 2,800 2,400 2.000 4,400 2,000 8,300 15,700 23,760 Equity 10,080 7,440 8,980 Total liabilities and equity 18.380 23,140 32,740 Questions: (2) What problems are CC facing with? (3) How does CC manage with the problems? - End - Hypothetical case: Mr. AA ("AA") and Mr. BB ("BB") formed a partnership of CC Company ("CC") in 2001 distributing disinfection supplies. The business has been thriving year by year. It is extremely good during the recent pandemic. CC offers quantity discounts and credit terms of 30 days on open account to customers. Payments are on a monthly basis. However, due to administrative procedures, CC usually receives payments 2 months after month end (i.e. January contract sum will be received in March). However, payment of wages and salaries has to be made within 7 days following the last month end. All other expenses are payable within 30 days after receiving invoices. Sales volume had been built up largely on the basis of successful price competition. Profit was made possibly by careful control of operating expenses and by quantity purchases of materials at substantial discounts. In 2019, AA bought out BB's interest for $4,000,000. The company then became a sole proprietorship. CC issued 4 notes of $1 million each to BB with repayment half-yearly starting from 30 Jun 2021. Financial statements for the past 3 years (year ended 31 Dec) are as follows: Income statement [HKS'000] Sales Cost of goods sold: Opening inventory Purchase Closing inventory Net cost of goods sold. Gross profit Operating expenses Profit before interest and tax Interest expense Profit before tax Tax Profit after tax Non-current asset Property Total assets Current liabilities 2019 2020 2021 58,420 69,540 90,3801 Statement of Financial Position [HKS'000] Current assets Cash Account receivables Inventory 13.720 Accounts payable Accrued expenses 5,500 Non-current liabilities. Notes payable to BB Term loan 6.600 6,740 8,640 44,180 54,580 71.580 6,740 8,640 11.740 44,040 $2,680 68,480 14,380 16,860 21,900 12.440 14,340 18,800. 1,940 2,520 3,100 2.800 Total liabilities 460 840 1.120 1,480 1,680 1,980 280 320 440 1,200 1,360 1,540 2.019 2.020 2,021 860 1,040 1,120 6,120 8,220 12,120 6,740 8,640 11,740. 17,900 24,980 Bank overdraft 0 Term loan (current portion) 400. Notes 0 4,660 5,240 7,760 18,380 23,140 32,740 1,200 7,800 400 400 2,000 2,000 4,260 6,800 10,060 840 900 1,500 11,300 21,760 0 2,000 0 2,800 2,400 2.000 4,400 2,000 8,300 15,700 23,760 Equity 10,080 7,440 8,980 Total liabilities and equity 18.380 23,140 32,740 Questions: (2) What problems are CC facing with? (3) How does CC manage with the problems? - End








