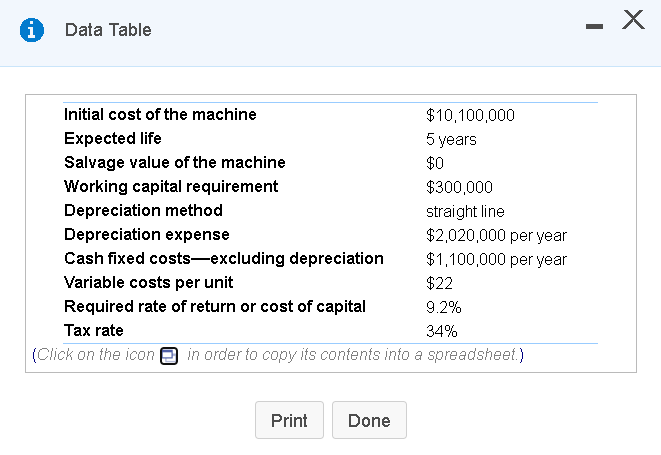
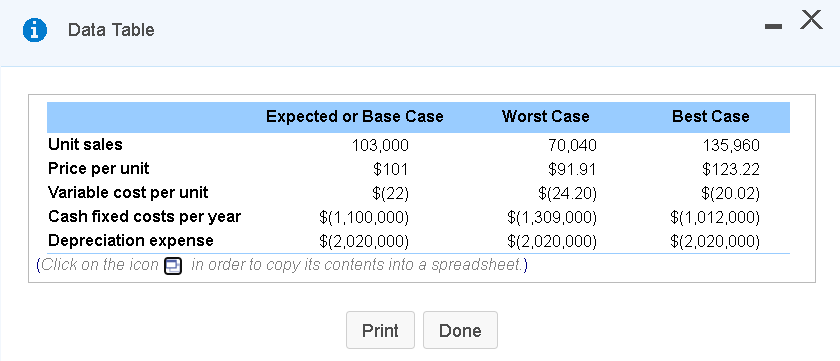
i Data Table - X Initial cost of the machine $10,100,000 Expected life 5 years Salvage value of the machine $0 Working capital requirement $300,000 Depreciation method straight line Depreciation expense $2,020,000 per year Cash fixed costsexcluding depreciation $1,100,000 per year Variable costs per unit $22 Required rate of return or cost of capital 9.2% Tax rate 34% (Click on the icon in order to copy its contents into a spreadsheet.) Print Done i Data Table - X Best Case Expected or Base Case Worst Case Unit sales 103,000 70,040 Price per unit $101 $91.91 Variable cost per unit $(22) $(24.20) Cash fixed costs per year $(1,100,000) $(1,309,000) Depreciation expense $(2,020,000) $(2,020,000) (Click on the icon in order to copy its contents into a spreadsheet.) 135,960 $123.22 $(20.02) $(1,012.000) $(2,020,000) Print Done (Related to Checkpoint 13.2 and Checkpoint 13.3) (Comprehensive risk analysis) Blinkeria is considering introducing a new line of hand scanners that can be used to copy material and then download it into a personal computer. These scanners are expected to sell for an average price of $101 each, and the company analysts performing the analysis expect that the firm can sell 103,000 units per year at this price for a period of five years, after which time they expect demand for the product to end as a result of new technology. In addition, variable costs are expected to be $22 per unit and fixed costs, not including depreciation, are forecast to be $1,100,000 per year. To manufacture this product, Blinkeria will need to buy a computerized production machine for $10.1 million that has no residual or salvage value, and will have an expected life of five years. In addition, the firm expects it will have to invest an additional $300,000 in working capital to support the new business. Other pertinent information concerning the business venture is provided here: a. Calculate the project's NPV. b. Determine the sensitivity of the project's NPV to a(n) 9 percent decrease in the number of units sold. c. Determine the sensitivity of the project's NPV to an) 9 percent decrease in the price per unit. d. Determine the sensitivity of the project's NPV to a(n) 9 percent increase in the variable cost per unit. e. Determine the sensitivity of the project's NPV to an) 9 percent increase in the annual fixed operating costs. f. Use scenario analysis to evaluate the project's NPV under worst- and best-case scenarios for the project's value drivers. The values for the expected or base-case along with the worst- and best-case scenarios are listed here: 5 a. The NPV for the base-case will be (Round to the nearest dollar.) Enter your answer in the answer box and then click Check Answer. ? 6 parts Clear All Check Answer remaining









