I don't understand the graphs
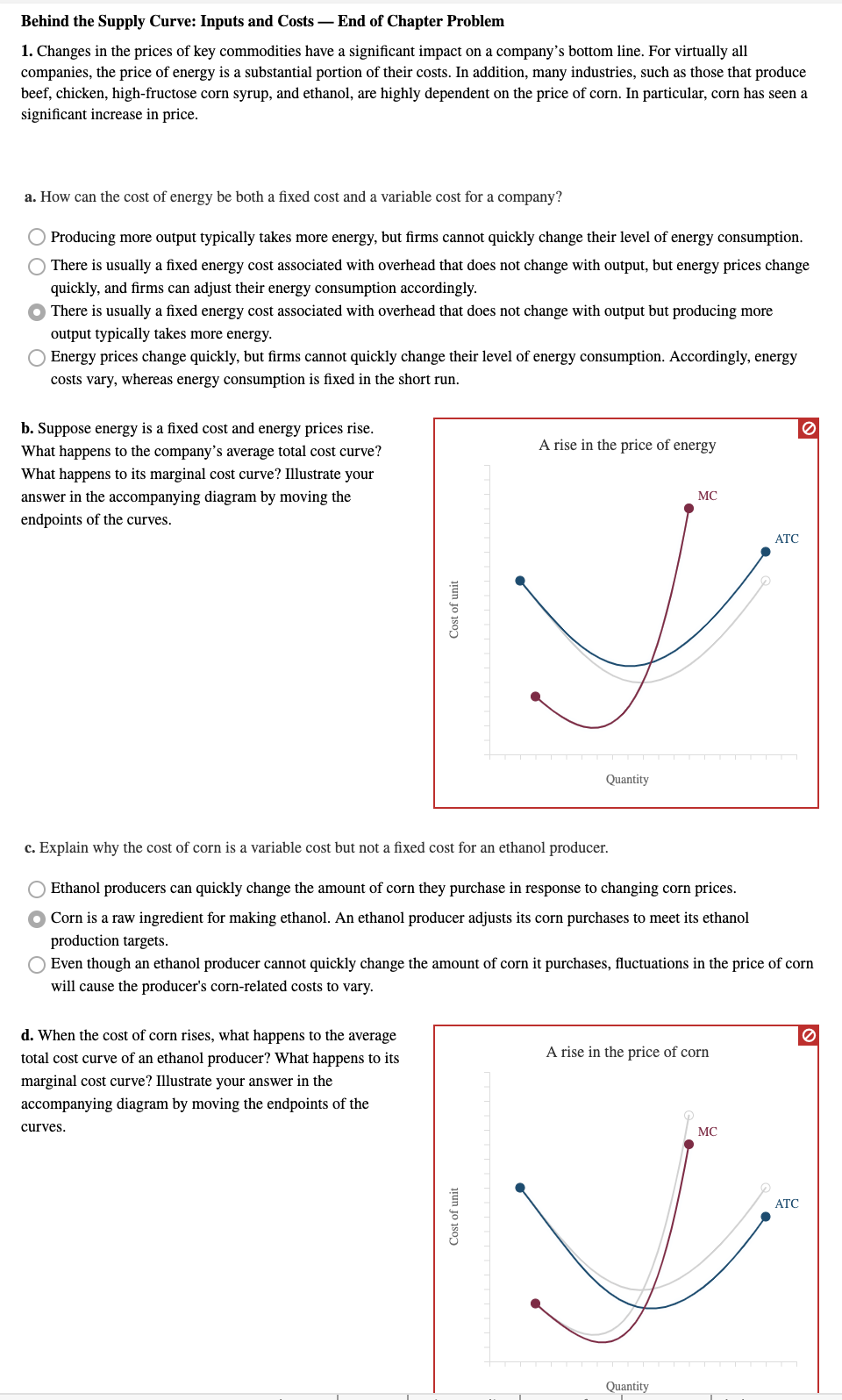
Behind the Supply Curve: Inputs and Costs - End of Chapter Problem 1. Changes in the prices of key commodities have a significant impact on a company's bottom line. For virtually all companies, the price of energy is a substantial portion of their costs. In addition, many industries, such as those that produce beef, chicken, high-fructose corn syrup, and ethanol, are highly dependent on the price of corn. In particular, corn has seen a significant increase in price. a. How can the cost of energy be both a fixed cost and a variable cost for a company? Producing more output typically takes more energy, but firms cannot quickly change their level of energy consumption. There is usually a fixed energy cost associated with overhead that does not change with output, but energy prices change quickly, and firms can adjust their energy consumption accordingly. . There is usually a fixed energy cost associated with overhead that does not change with output but producing more output typically takes more energy. Energy prices change quickly, but firms cannot quickly change their level of energy consumption. Accordingly, energy costs vary, whereas energy consumption is fixed in the short run. b. Suppose energy is a fixed cost and energy prices rise. What happens to the company's average total cost curve? A rise in the price of energy What happens to its marginal cost curve? Illustrate your answer in the accompanying diagram by moving the MC endpoints of the curves. ATC Cost of unit Quantity c. Explain why the cost of corn is a variable cost but not a fixed cost for an ethanol producer. Ethanol producers can quickly change the amount of corn they purchase in response to changing corn prices. . Corn is a raw ingredient for making ethanol. An ethanol producer adjusts its corn purchases to meet its ethanol production targets. Even though an ethanol producer cannot quickly change the amount of corn it purchases, fluctuations in the price of corn will cause the producer's corn-related costs to vary. d. When the cost of corn rises, what happens to the average total cost curve of an ethanol producer? What happens to its A rise in the price of corn marginal cost curve? Illustrate your answer in the accompanying diagram by moving the endpoints of the curves. MC Cost of unit ATC Quantity