Question
(i) Equipment which had cost 30,000 during the year to 31 July 2017 was sold in February 2020 for 10,000. The company depreciates equipment at
(i) Equipment which had cost 30,000 during the year to 31 July 2017 was sold in February 2020 for 10,000. The company depreciates equipment at 20% per annum on cost with a full charge in the year of acquisition and none in the year of disposal. (Some of the equipment was over five years old on 31 July 2020). (ii) Non-current asset investments which had cost 25,000 some years previously were sold during the year for 21,000. (iii) Dividends received during the year were 5,000. Dividends totalling 100,000 were paid during the year. (iv) The 14% debentures were issued many years ago and are due to be redeemed on 1 January 2021. A fresh issue of 12% debentures was made on 31 July 2020. (v) Interest paid during the year (including debenture interest) was 8,000. All interest was paid on the due date and no interest was accrued at either the start or the end of the year.
No interest was received during the year. (vi) Taxation shown as a liability on 31 July 2019 was paid during the year to 31 July 2020 at the amount stated. (vii) In January 2020, the company issued 50,000 1 ordinary shares at a premium of 60p per share. Required: (a) Calculate the company's profit before tax for the year to 31 July 2020. (b) Prepare a statement of cash flows for the year to 31 July 2020 in accordance with the requirements of IAS7 (using the indirect method). (c) Reconcile the total cash and cash equivalents shown by the statement of cash flows to the equivalent figures shown in the opening and closing statements of financial position. Part 2: Impairment Roland Company uses special strapping equipment in its packaging business. The equipment was purchased in January 2019 for $10,000,000 and had an estimated useful life of 8 years with no salvage value. At December 31, 2020, new technology was introduced that would accelerate the obsolescence of Rolands equipment. Rolands controller estimates that expected future net cash flows on the equipment will be $6,300,000 and that the fair value of the equipment is $5,600,000. Roland intends to continue using the equipment, but it is estimated that the remaining useful life is 4 years. Roland uses straight-line depreciation. Instructions a. Prepare the journal entry (if any) to record the impairment at December 31, 2020. b. Prepare any journal entries for the equipment at December 31, 2021. The fair value of the equipment at December 31, 2021, is estimated to be $5,900,000. c. Repeat the requirements for (a) and (b), assuming that Roland intends to dispose of the equipment and that it has not been disposed of as of December 31, 2021.
Part 3: Decommissioning costs Oil Products Company purchases an oil tanker depot on January 1, 2020, at a cost of $6,000,000. Oil Products expects to operate the depot for 10 years, at which time it is legally required to dismantle the depot and remove the underground storage tanks. It is estimated that it will cost $750,000 to dismantle the depot and remove the tanks at the end of the depots useful life. Required: a. Prepare the journal entries to record the depot and decommissioning costs for the depot on January 1, 2020. Use interest rate of interest rate of 6%. b. Prepare any journal entries required for the depot and the decommissioning costs at December 31, 2020. Oil Products uses straight-line depreciation; the estimated salvage value for the depot is zero. c. On December 31, 2029, Oil Products pays a demolition firm to dismantle the depot and remove the tanks at a price of $870,000. Prepare the journal entry for the settlement of the decommissioning costs.
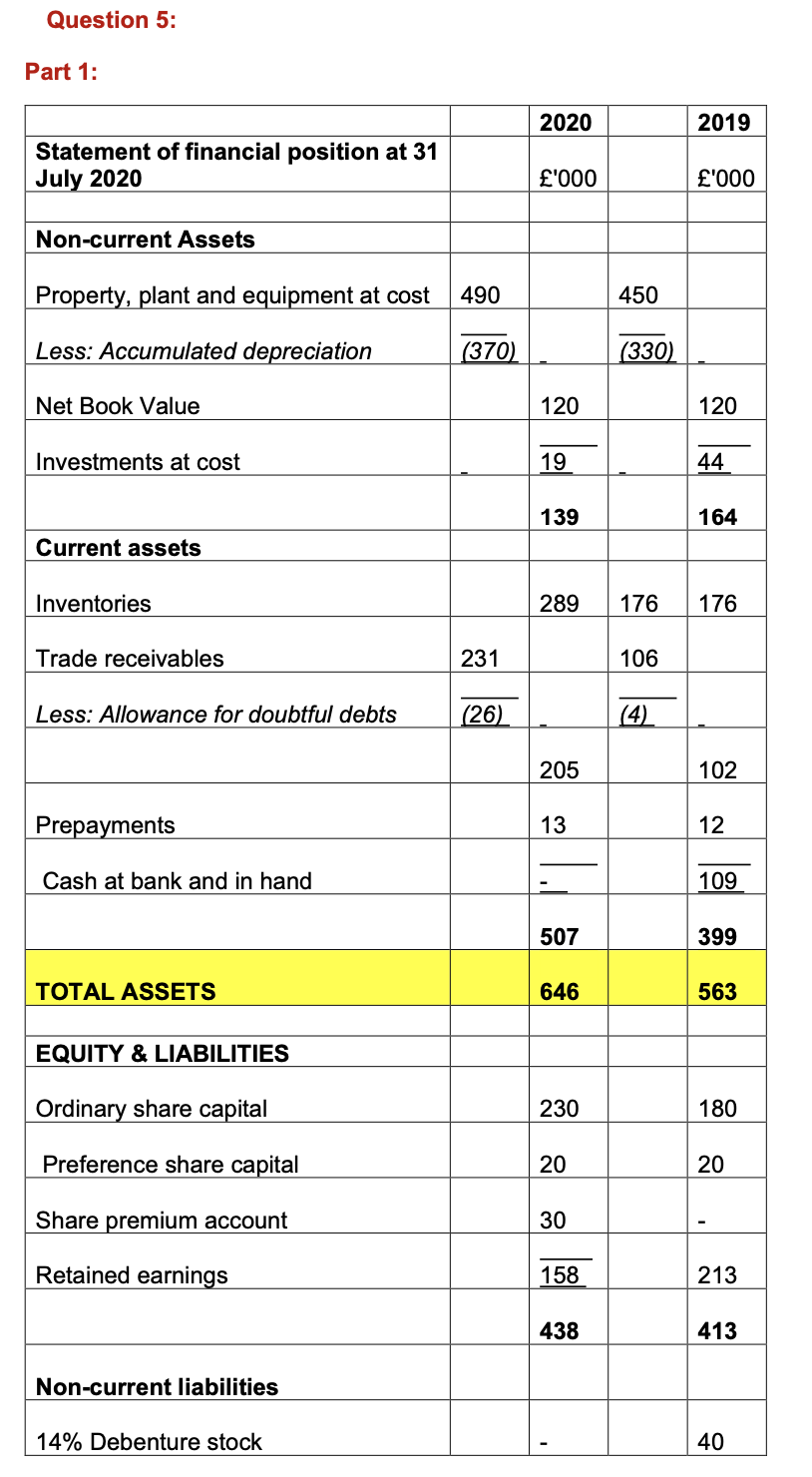
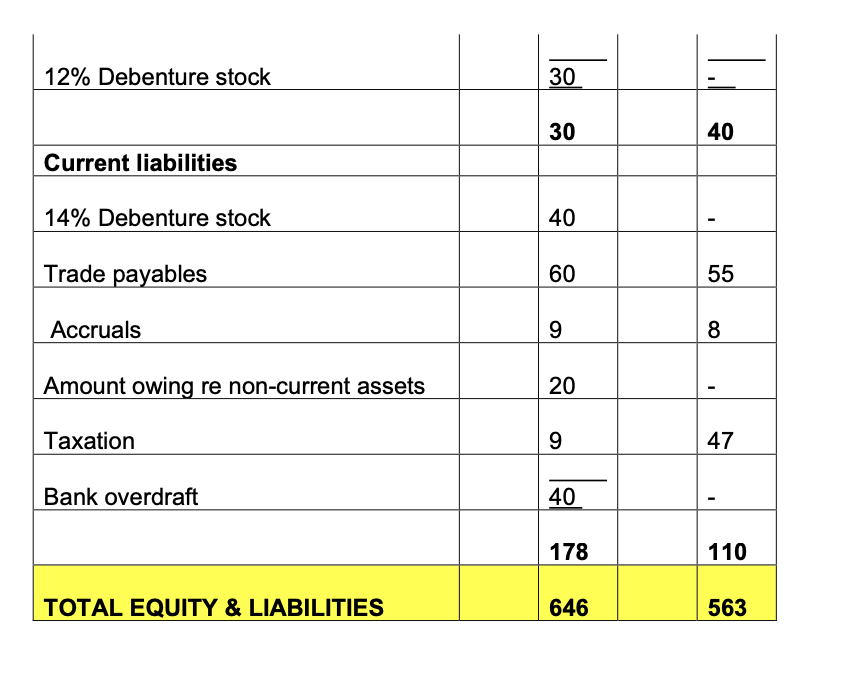
Question 5: Part 1: 2020 2019 Statement of financial position at 31 July 2020 '000 '000 Non-current Assets Property, plant and equipment at cost 490 450 Less: Accumulated depreciation (370) (330) Net Book Value 120 120 Investments at cost 44 139 164 Current assets Inventories 289 176 176 Trade receivables 231 106 Less: Allowance for doubtful debts (26) (4) 205 102 Prepayments 13 12 Cash at bank and in hand 109 507 399 TOTAL ASSETS 646 563 EQUITY & LIABILITIES Ordinary share capital 230 180 Preference share capital 20 20 Share premium account 30 Retained earnings 158 213 438 413 Non-current liabilities 14% Debenture stock 40 12% Debenture stock 30 30 40 Current liabilities 14% Debenture stock 40 Trade payables 60 55 Accruals 9 8 Amount owing re non-current assets 20 Taxation 9 47 Bank overdraft 40 178 110 TOTAL EQUITY & LIABILITIES 646 563
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


