Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
I have a question about one of the textbook answers here on Chegg. For the solution of 17.9 in Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, The
I have a question about one of the textbook answers here on Chegg. For the solution of 17.9 in Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, The way Gamma is found is obscure to me. How do we go from 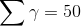 to
to 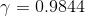 . Secondly, is the reason R(Up) = R(down) because they eventually reach the same reward since +50 is reduced by -1 and -50 increased by +1 which leads to equivalent reward by the end state?!
. Secondly, is the reason R(Up) = R(down) because they eventually reach the same reward since +50 is reduced by -1 and -50 increased by +1 which leads to equivalent reward by the end state?!
Below is the question followed by what I am referring to:
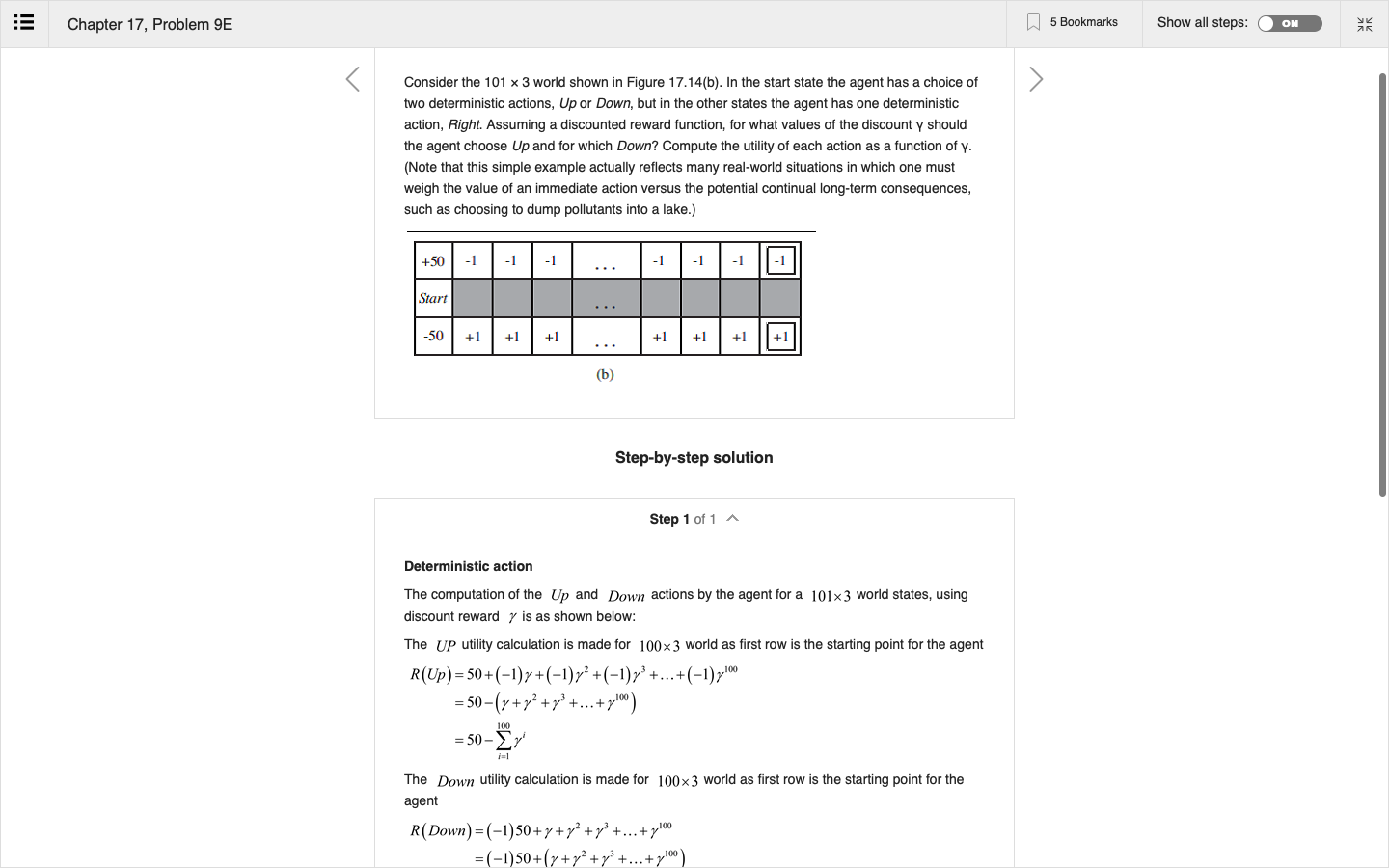
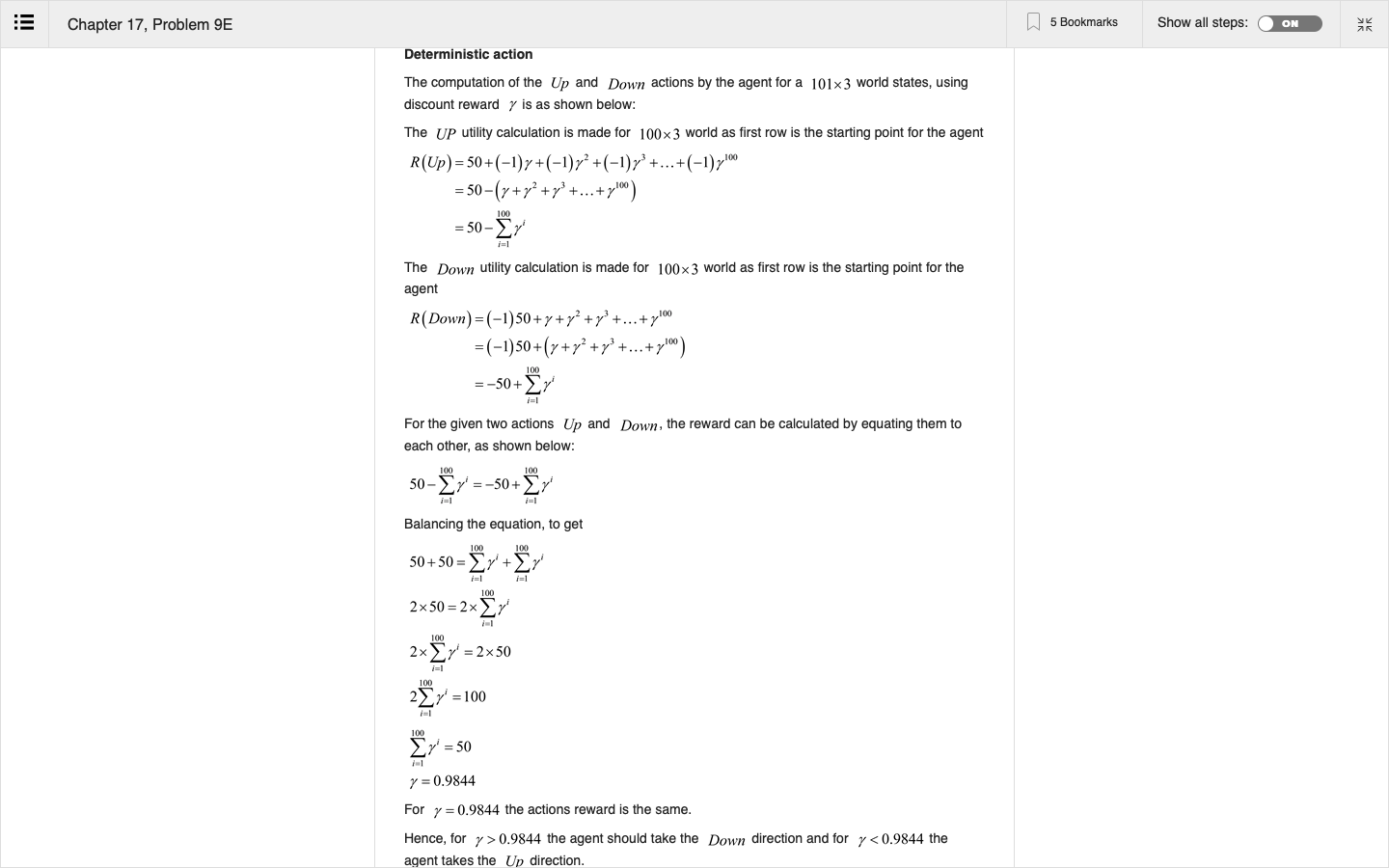
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


