I just need the graph in the 4th photo, the other photos are for reference.

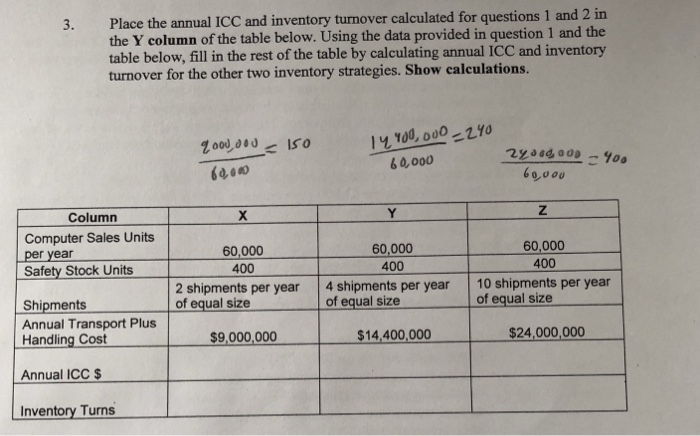
Objective: To demonstrate how inventory carrying cost is calculated. Information: Inventory carrying cost (ICC) is a major logistics cost that reflects the cost of holding inventory. A unique ICC is usually calculated for each product because products have different raw materials costs, production costs, damage rates and obsolescence rates. In addition, ICC can be calculated for a product at any stage of development because the dollar value of the inventory changes as the product moves through the logistical pipeline (e.g. as a raw material, work-in- process inventory or finished product). This case will focus on the calculation of ICC for a finished product. ICC is usually measured by determining the dollar value of the average amount of inventory in the logistics pipeline and multiplying that dollar value by a corporate ICC percentage which is developed for each product for the year. Basic Formula: Annual ICC S= AXBXC Where Product average inventory (# of units) BS cost per unit ICC % (Specific costs expressed as a % of cost per unit) = Determining A, B & C: Finished product average inventory -1/2 order quantity+ all safety stock. For example, when a warehouse orders and receives shipments of 10 units every 10 days and ships 1 unit per day to the retail store and carries a safety stock of 2 units, the average inventory is 1/2 (10) +2-7 units. A Product cost increases as it is produced and moved. Manufacturers use variable manufacturing cost per unit and retailers use the cost of goods sold to reflect production cost. Both manufacturer and retailer add transportation and handling costs per unit to reflect the cost of moving the product to its storage location. B Inventory carrying costs are detailed in the textbook. The primary costs that change when the amount of inventory held changes are: opportunity cost of capital, inventory taxes, inventory insurance, inventory cycle counting, inventory obsolescence, inventory damage, inventory theft and inventory relocation. These costs are usually individually determined and added together to create a single ICC % for the year. C Detailed Formula: Annual ICC$ -[1/2 (order quantity)+ safety stocks] X S product cost/unit + transportation & handling cost/unit X [ICC %'s added together] For example, suppose a manufacturer ships 5,000 basketballs each month to a warehouse and the warehouse is $60,000 per year and warehouse handling cost is $30,000 per year. The inventory carrying cost percentage for basketballs this year is 45%. Annual ICC$ [1/2 (5,000)+200]x [$6.00/unit +($90,000+ 60,000 basketballs/year)]X 1.45] Annual ICC$ 2,700 units X $7.50/unit X.45-$9,112.50 Once annual ICC S is calculated, any partial year calculations are determined directly. For example, monthly ICCS = annual ICCS 12. ICC and average inventory in the logistics pipeline are directly related. Most firms track the number of times per year that the average inventory is replaced. This is called Inventory Turnover. For example, if annual sales- 600 units and the warehouse receives 6 shipments of 100 units that year (1 shipment every two months), then the warehouse average inventory 1/2 (100) or 50 units and this average inventory will turn over 12 times this year or Inventory Turnover equals 600/50 units 12 times. Application: 1. Using the detailed formula for ICC and the following information, Calculate the f finished product inventory carrying cost for the IBM 586 computer. IBM stores the computers that it produces in it's only company field warehouse. The warehouse received one computer shipment each quarter this year. Each shipment contained 15,000 computers. The warehouse kept a safety stock of 400 computers. The demand was 15,000 computers per quarter from retailers. IBM sold the computers to retailers for $5,000 each. IBM's variable manufacturing costs were $2,800 per computer. IBM's fixed manufacturing costs averaged S500 per computer. The transport cost from plant to warehouse location was $13,200,000 per year. The handling costs to receive and store shipments for the year was $1,200,000. Cost data collected (as a percent of inventory value): -Opportunity cost of capital (32%) -Taking inventory (cycle counting) in warehouse (2%) Warehouse managersalar-40% -State inventory tax (5%) -Insurance on inventory (4%) - Inventory relocation to avoid obsolescence (1%) -inventory obsolescence cost (2%) Firedamageofwarehouse-inventory(5%) -Inventory damage in warehouse (396) "Inventory theft in warehouse (4%) Calculation: 53% Place the annual ICC and inventory turnover calculated for questions 1 and 2 in the Y column of the table below. Using the data provided in question 1 and the table below, fill in the rest of the table by calculating annual ICC and inventory turnover for the other two inventory strategies. Show calculations. 3. 6 0,000 60,000 Column Computer Sales Units per year Safety Stock Units 60,000 400 2 shipments per year 4 shipments per year 10 shipments per year 60,000 400 60,000 400 Shipments Annual Transport Plus Handling Cost of equal size of equal size sport Plusequal size 9,000,000 14,400,000 $24,000,000 Annual ICCS Inventory Tuns