Question
I made the topology and tried adding the static routing, but I am unsure what I am doing wrong. I can ping the routers from
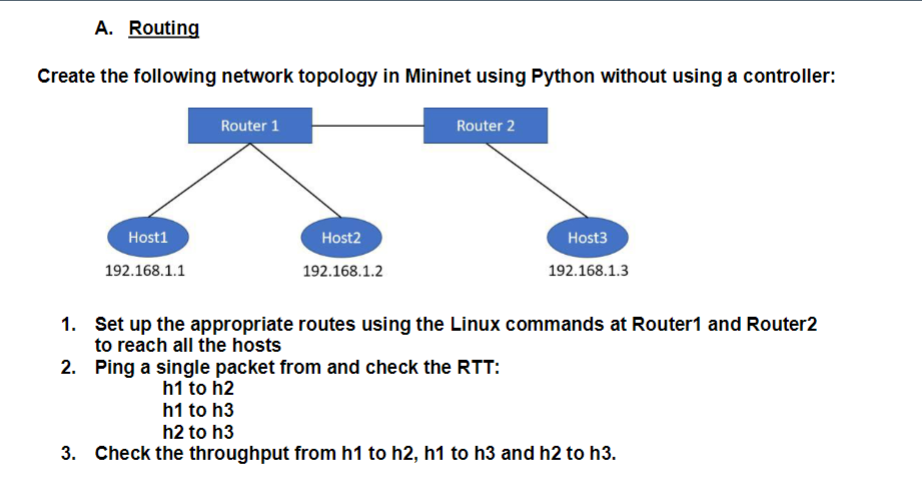
I made the topology and tried adding the static routing, but I am unsure what I am doing wrong. I can ping the routers from the host but not other hosts. A correction in the code with an explanation would be beneficial.
CODE:-
from mininet.topo import Topo
from mininet.net import Mininet
from mininet.log import setLogLevel, info
from mininet.cli import CLI
from mininet.link import TCLink
class CustomTopo( Topo ):
def build (self):
"Create custom topo."
# Add Hosts
h1 = self.addHost( 'h1', ip='192.168.1.1/24' )
h2 = self.addHost( 'h2', ip='192.168.1.2/24' )
h3 = self.addHost( 'h3', ip='192.168.1.3/24' )
# Add switch
r1 = self.addHost( 'r1' , ip="192.168.1.10/24")
r2 = self.addHost( 'r2' , ip="192.168.1.20/24")
# Add links
self.addLink( h1, r1 )
self.addLink( h2, r1 )
self.addLink( h3, r2 )
self.addLink( r1, r2 )
def runExperiment(net:Mininet):
h1, h2, h3 = net.hosts[0:3]
r1, r2 = net.hosts[3:]
print(" * r1 routes :-")
print(r1.cmd("route -n"))
print(" * r2 routes :-")
print(r2.cmd("route -n"))
print(" * h1 pinging h2 :-")
print(r1.cmd(f"ping -c1 {h2.IP()}"))
print(" * h1 pinging h3 :-")
print(r1.cmd(f"ping -c1 {h3.IP()}"))
print(" * h2 pinging h3 :-")
print(r2.cmd(f"ping -c1 {h3.IP()}"))
"""
# IF the host does not know where the destination is : default to asking from router
print(h1.cmd(f'ip route add default dev h1-eth0'))
print(h2.cmd(f'ip route add default dev h2-eth0'))
print(h3.cmd(f'ip route add default dev h3-eth0'))
# MAKE sure routers know the devices that are connected to it, so it answer the request
print(r1.cmd(f"ip route add {h1.IP()} dev r1-eth0"))
print(r1.cmd(f"ip route add {h2.IP()} dev r1-eth1"))
print(r1.cmd(f"ip route add {r2.IP()} dev r1-eth2"))
print(r1.cmd(f"ip route add {h3.IP()} via {r2.IP()} dev r1-eth2"))
print(r2.cmd(f"ip route add {h3.IP()} dev r2-eth0"))
print(r2.cmd(f"ip route add {r1.IP()} dev r2-eth1"))
print(r2.cmd(f"ip route add {h1.IP()} via {r1.IP()} dev r2-eth1"))
print(r2.cmd(f"ip route add {h2.IP()} via {r1.IP()} dev r2-eth1"))
"""
print(r1.cmd("ip route show"))
print(" * r1 routes :-")
print(r1.cmd("route -n"))
print(" * r2 routes :-")
print(r2.cmd("route -n"))
print(" * h1 pinging h2 :-")
print(h1.cmd(f"ping -c5 {h2.IP()}"))
print(" * h1 pinging h3 :-")
print(h1.cmd(f"ping -c5 {h3.IP()}"))
print(" * h2 pinging h3 :-")
print(h2.cmd(f"ping -c5 {h3.IP()}"))
CLI(net)
def MakeCustomTopo():
topo = CustomTopo( )
net = Mininet(topo,controller=None)
net.start()
runExperiment(net)
net.stop()
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Tell mininet to print useful information
setLogLevel('info')
MakeCustomTopo()
Create the following network topology in Mininet using Python without using a controller: 1. Set up the appropriate routes using the Linux commands at Router1 and Router2 to reach all the hosts 2. Ping a single packet from and check the RTT: h1 to h2 h1 to h3 h2 to h3 3. Check the throughput from h1 to h2, h1 to h3 and h2 to h3Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


