Question: I need a summary of this article, agre e or disagree. I need 250 to 300 words, two paragraphs. I need it as soon as
I need a summary of this article, agree or disagree. I need 250 to 300 words, two paragraphs. I need it as soon as possible please.




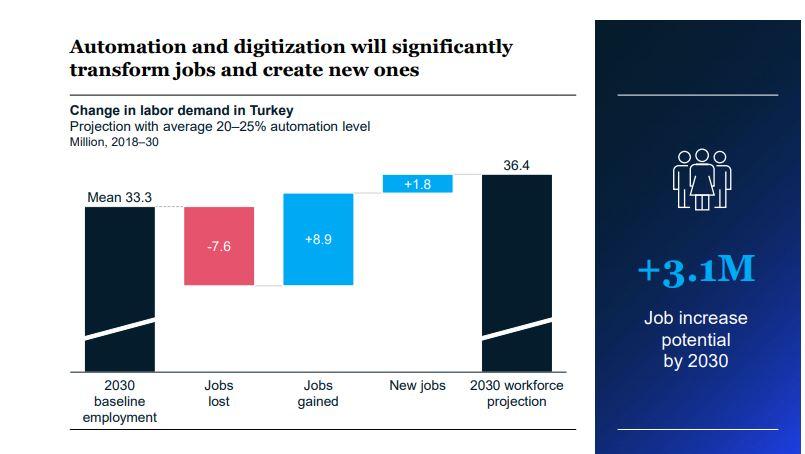

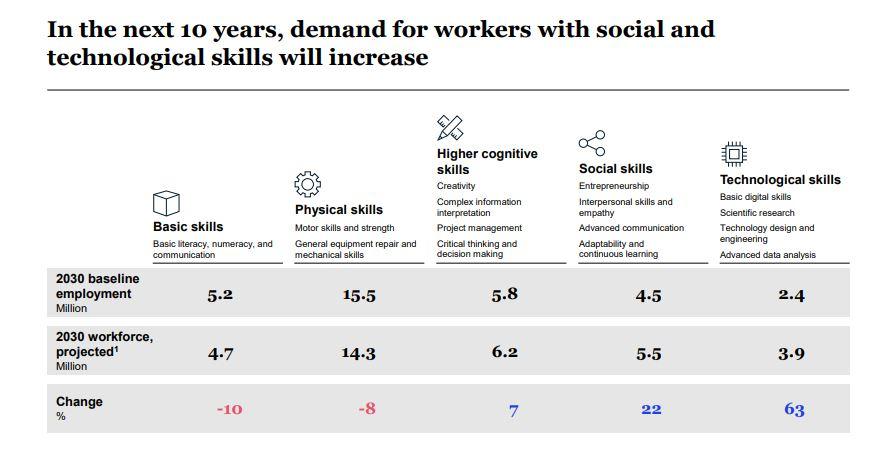
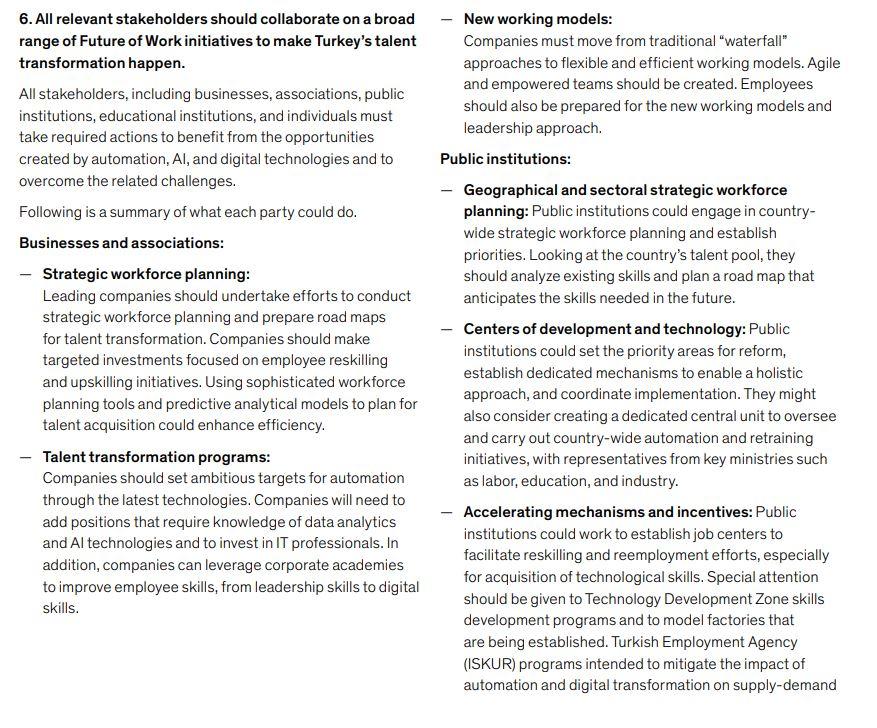


Future of Work: Turkey's Talent Transformation in the Digital Era - Report Summary Advances in automation, artificial intelligence (AI), and digital technologies are changing the way we work, the activities we perform, and the skills we need to succeed. Catching this rapid transformation wave is of the utmost importance to ensure sustainable growth. McKinsey & Company has focused in the past decade on Future of Work research and served its clients on this topic. In addition, the McKinsey Global Institute (MGI), the business On a global scale, current technologies have the potential to and economics research arm of McKinsey, has studied the help automate 50 percent of jobs. In Turkey, with the current effects of automation on workforces and skills since 2015 technologies, six out of ten occupations could be automated and has described options that could help stakeholders by 30 percent. The analyses in this report are based on a benefit from potential changes in business models. scenario in which average levels of automation in Turkey are MGI considers adoption of digital technologies the most 20 to 25 percent by 2030. important factor in future economic growth. Research shows the report foresees that in the next decade, automation, that adoption of digital technologies will account for about 60 AI, and digital technologies, along with complementary percent of the potential productivity increase by 2030. This investments, have the potential to create 3.1 million net holds true for Turkey: automation, Al, and digital technologies new jobs, considering the economic impact and societal have the potential to boost the country's economy, so it is changes the technology will bring. By 2030, with the impact critically important to understand the opportunities and of automation and digitization, 7.6 million jobs could be challenges regarding the future of work and to prepare the lost, and 8.9 million new jobs could be created, a net gain Turkish workforce for the upcoming transformation. of 1.3 million jobs. In addition, 1.8 million jobs that currently McKinsey & Company Turkey has worked over the past 6 do not exist could be created, many of them in technology- months to create this report based on the experience and related sectors. To enable this change, 21.1 million people expertise of its 250 employees and insights from MGI. in the Turkish workforce will need to improve their skills by We examined the impact of productivity growth driven by leveraging technology while remaining employed in their current jobs. Automation and digitization are expected to automation, AI, and digital technologies on different sectors and occupations. We addressed the opportunities that will affect 7.6 million employees through significant reskilling and emerge to transform Turkey's talent marketplace and the job displacements. In addition, 7.7 million new employees who challenges that must be overcome, supported by a fact base will join the workforce will need to be equipped with the latest that will help stakeholders prioritize efforts to adapt the skills required. workplace to this new world. We hope that this report will To ensure the success of Turkey's talent transformation, shed light on the benefits that automation and increased a common focal point and collective, concerted action productivity will bring to the country by 2030. are needed. It is critical that all stakeholders, including businesses, associations, public institutions, educational institutions and individuals, take the required actions. Methodology In preparing this report, we used a rich data set, including detailed country-wide occupation and wage data for each sector and Turkey-specific indicators related to education, energy, infrastructure, technology, and macroeconomics. We employed a threefold methodology to create scenarios for jobs lost, jobs gained through automation, and impact on skill requirements. For jobs lost through automation, we assessed 800 occupations and 2,000 work activities for 18 skills and identified each activity's time susceptible to automation as lost work time. For example, a customer service representative performs more than 20 activities. We found that activities such as product stock control and reporting of activities and sales could be automated, whereas activities such as welcoming customers and visitors and providing personalized advice regarding products and services have limited automation potential. Similarly, while a production worker's activities such as production planning and product packaging could be automated, activities such as tracking product quality control via the system and managing production teams have limited automation potential. In addition, we modeled the impact of more than 20 global trends on labor demand in order to calculate the impact of productivity growth on economy and workforce growth. We took rising incomes, aging population, development and deployment of new technologies, infrastructure investments, energy transitions, and efficiency and creation of new markets as factors that could influence labor force demand growth by 2030. For the implications of skill changes, we defined current and required skills for the changing nature of jobs by mapping each of 2,000 activities to 25 skills in five categories and understood the skill gap to be closed through talent transformation. We analyzed the results by comparing them with data for 46 other countries. We studied in detail how the changes will affect 15 different sectors. We held discussions with representatives of business, academia, media, the social sector, and government to interpret the results, fine-tune implication estimations, and exchange ideas on potential actions that stakeholders could take to help us develop an assessment of Turkey's talent transformation in the digital era. Automation and digitization will significantly transform jobs and create new ones Change in labor demand in Turkey Projection with average 20-25% automation level Million, 2018-30 36.4 +1.8 LT1 Mean 33.3 -7.6 +8.9 +3.1M Job increase potential by 2030 2030 baseline employment Jobs lost Jobs gained New jobs 2030 workforce projection As a result, the Turkish economy has the potential for a 5. The workforce will need to acquire stronger social skills net job increase by of 3.1 million 2030, and expected total and advanced technological skills. demand for a workforce of 36.4 million. Workplace skills of the future fall into five categories: physical Taking a sectoral view, the job increases will manifest and manual, basic cognitive, higher cognitive, social and most strongly in service sectors-retail sales and service, emotional, and technological. In most sectors in Turkey, the healthcare services and care providers, food and beverage, greatest increase in time spent on work activities that require and accommodation. Occupation groups reflect similar certain abilities is expected to be for technological and social trends. The number of jobs that require customer interaction skills. By contrast, since activities such as data entry and and the number of care providers will increase. We expect equipment operation are more susceptible to automation, 30 percent growth in the retail sales and service industry the demand for basic cognitive skills and physical skills could workforce. Healthcare services and care providers are decrease in most sectors. expected to grow by 40 percent, and the food and beverage In 2030, if the anticipated talent transformation can and accommodation sectors are expected grow by 20 be ensured, the greatest change is expected to be in percent. technological skills, with a rate of 63 percent. While social 4. Upskilling and reskilling initiatives will play a key role in skills are expected to increase by 22 percent and higher talent transformation. cognitive skills by 7 percent, basic cognitive skills and physical skills are forecast to decrease by 10 and 8 percent, In order to ensure Turkey's talent transformation, 21.1 million workers will need to improve their skills, leveraging respectively. technology while remaining employed in their current jobs. In addition, automation and digitization are expected to have an increased impact on 7.6 million employees who will experience significant reskilling and job displacements. Within this group, 5.6 million people are expected to change roles by upskilling and 2.0 million are expected to gain new skills to be able to work in different sectors or in different occupations. It will be critical to equip 7.7 million new employees with required skills as they join the workforce. In the next 10 years, demand for workers with social and technological skills will increase LL Basic skills Basic literacy, numeracy, and communication Physical skills Motor skills and strength General equipment repair and mechanical skills Higher cognitive skills Creativity Complex information interpretation Project management Critical thinking and decision making Social skills Entrepreneurship Interpersonal skills and empathy Advanced communication Adaptability and continuous learning Technological skills Basic digital skills Scientific research Technology design and engineering Advanced data analysis 2030 baseline employment Million 5.2 15-5 5.8 4.5 2.4 2030 workforce, projected Million 4.7 14.3 6.2 5.5 3.9 Change -10 -8 7 22 63 % 6. All relevant stakeholders should collaborate on a broad - New working models: range of Future of Work initiatives to make Turkey's talent Companies must move from traditional "waterfall". transformation happen. approaches to flexible and efficient working models. Agile All stakeholders, including businesses, associations, public and empowered teams should be created. Employees institutions, educational institutions, and individuals must should also be prepared for the new working models and take required actions to benefit from the opportunities leadership approach. created by automation, Al, and digital technologies and to Public institutions: overcome the related challenges. - Geographical and sectoral strategic workforce Following is a summary of what each party could do. planning: Public institutions could engage in country- Businesses and associations: wide strategic workforce planning and establish priorities. Looking at the country's talent pool, they - Strategic workforce planning: should analyze existing skills and plan a road map that Leading companies should undertake efforts to conduct anticipates the skills needed in the future. strategic workforce planning and prepare road maps for talent transformation. Companies should make - Centers of development and technology: Public targeted investments focused on employee reskilling institutions could set the priority areas for reform, and upskilling initiatives. Using sophisticated workforce establish dedicated mechanisms to enable a holistic approach, and coordinate implementation. They might planning tools and predictive analytical models to plan for also consider creating a dedicated central unit to oversee talent acquisition could enhance efficiency. and carry out country-wide automation and retraining Talent transformation programs: initiatives, with representatives from key ministries such Companies should set ambitious targets for automation as labor, education, and industry. through the latest technologies. Companies will need to add positions that require knowledge of data analytics - Accelerating mechanisms and incentives: Public and Al technologies and to invest in IT professionals. In institutions could work to establish job centers to addition, companies can leverage corporate academies facilitate reskilling and reemployment efforts, especially for acquisition of technological skills. Special attention to improve employee skills, from leadership skills to digital skills. should be given to Technology Development Zone skills development programs and to model factories that are being established. Turkish Employment Agency (ISKUR) programs intended to mitigate the impact of automation and digital transformation on supply-demand balance in the employment market should be revised and implemented. Furthermore, the asset-liability balance in the social security system can be closely followed considering potential disrupting effects of the technologies on the employment market. Social security and premium models aligned with the digital transformation level can be evaluated and implemented in order to balance the pace of transformation. Educational institutions: Revising the education model: The education system should revamp school curricula to incorporate in-demand skills. Relevant classes could be made compulsory at appropriate levels. Universities and educational institutions should create programs tailored to future skills, open to adults through seminars, certificate programs, and online training. - Improving learning experience: The classroom experience should be more personalized, shifting from traditional content on traditional schedules to building job skills anytime, anywhere. The new learning experience can be built through collaborating with community centers, employing experts, and using peer-to-peer or project-based instruction. Content should include problem-solving skills, rapid prototyping, and asking the right questions. - Lifelong learning: The education system needs to build the mind-set of "learning to learn," emphasizing the willingness to continuously adopt new skills. This approach allows students to build the foundations of critical thinking, problem solving, and lifelong learning. Local governments can assume a key role to access a higher number of people in order to support lifelong learning. Individuals: - Continuous learning and self-development: Individuals must own their own learning journeys by continuously updating skills throughout their careers. Leaders should understand individuals' need for capability building, both for themselves and for their organizations, and should lead the transformation. - Social and technological skills: Individuals must focus on developing the key skills and attributes of the future, including social skills (such as resilience and adaptability), technological skills (such as programming and data analysis), and cognitive skills (such as critical thinking, problem solving, and creativity). Leaders should prepare their organizations for building such capabilities. - Lifelong flexible career paths: Individuals will have to embrace a startup of you" mind-set and take an entrepreneurial approach to their careers. Project- based, independent, and part-time jobs are on the rise. Individuals should prepare themselves for lifelong flexible career paths. Automation, AI, and digital technologies offer big opportunities for Turkey to improve productivity and generate many new jobs. To take advantage of this opportunity, Turkey should invest in talent transformation to develop the new skills required in the workplace of the future. It is critical for all stakeholders to work together to achieve this transformation. We believe that this talent transformation journey will unlock the country's strong potential. Future of Work: Turkey's Talent Transformation in the Digital Era - Report Summary Advances in automation, artificial intelligence (AI), and digital technologies are changing the way we work, the activities we perform, and the skills we need to succeed. Catching this rapid transformation wave is of the utmost importance to ensure sustainable growth. McKinsey & Company has focused in the past decade on Future of Work research and served its clients on this topic. In addition, the McKinsey Global Institute (MGI), the business On a global scale, current technologies have the potential to and economics research arm of McKinsey, has studied the help automate 50 percent of jobs. In Turkey, with the current effects of automation on workforces and skills since 2015 technologies, six out of ten occupations could be automated and has described options that could help stakeholders by 30 percent. The analyses in this report are based on a benefit from potential changes in business models. scenario in which average levels of automation in Turkey are MGI considers adoption of digital technologies the most 20 to 25 percent by 2030. important factor in future economic growth. Research shows the report foresees that in the next decade, automation, that adoption of digital technologies will account for about 60 AI, and digital technologies, along with complementary percent of the potential productivity increase by 2030. This investments, have the potential to create 3.1 million net holds true for Turkey: automation, Al, and digital technologies new jobs, considering the economic impact and societal have the potential to boost the country's economy, so it is changes the technology will bring. By 2030, with the impact critically important to understand the opportunities and of automation and digitization, 7.6 million jobs could be challenges regarding the future of work and to prepare the lost, and 8.9 million new jobs could be created, a net gain Turkish workforce for the upcoming transformation. of 1.3 million jobs. In addition, 1.8 million jobs that currently McKinsey & Company Turkey has worked over the past 6 do not exist could be created, many of them in technology- months to create this report based on the experience and related sectors. To enable this change, 21.1 million people expertise of its 250 employees and insights from MGI. in the Turkish workforce will need to improve their skills by We examined the impact of productivity growth driven by leveraging technology while remaining employed in their current jobs. Automation and digitization are expected to automation, AI, and digital technologies on different sectors and occupations. We addressed the opportunities that will affect 7.6 million employees through significant reskilling and emerge to transform Turkey's talent marketplace and the job displacements. In addition, 7.7 million new employees who challenges that must be overcome, supported by a fact base will join the workforce will need to be equipped with the latest that will help stakeholders prioritize efforts to adapt the skills required. workplace to this new world. We hope that this report will To ensure the success of Turkey's talent transformation, shed light on the benefits that automation and increased a common focal point and collective, concerted action productivity will bring to the country by 2030. are needed. It is critical that all stakeholders, including businesses, associations, public institutions, educational institutions and individuals, take the required actions. Methodology In preparing this report, we used a rich data set, including detailed country-wide occupation and wage data for each sector and Turkey-specific indicators related to education, energy, infrastructure, technology, and macroeconomics. We employed a threefold methodology to create scenarios for jobs lost, jobs gained through automation, and impact on skill requirements. For jobs lost through automation, we assessed 800 occupations and 2,000 work activities for 18 skills and identified each activity's time susceptible to automation as lost work time. For example, a customer service representative performs more than 20 activities. We found that activities such as product stock control and reporting of activities and sales could be automated, whereas activities such as welcoming customers and visitors and providing personalized advice regarding products and services have limited automation potential. Similarly, while a production worker's activities such as production planning and product packaging could be automated, activities such as tracking product quality control via the system and managing production teams have limited automation potential. In addition, we modeled the impact of more than 20 global trends on labor demand in order to calculate the impact of productivity growth on economy and workforce growth. We took rising incomes, aging population, development and deployment of new technologies, infrastructure investments, energy transitions, and efficiency and creation of new markets as factors that could influence labor force demand growth by 2030. For the implications of skill changes, we defined current and required skills for the changing nature of jobs by mapping each of 2,000 activities to 25 skills in five categories and understood the skill gap to be closed through talent transformation. We analyzed the results by comparing them with data for 46 other countries. We studied in detail how the changes will affect 15 different sectors. We held discussions with representatives of business, academia, media, the social sector, and government to interpret the results, fine-tune implication estimations, and exchange ideas on potential actions that stakeholders could take to help us develop an assessment of Turkey's talent transformation in the digital era. Automation and digitization will significantly transform jobs and create new ones Change in labor demand in Turkey Projection with average 20-25% automation level Million, 2018-30 36.4 +1.8 LT1 Mean 33.3 -7.6 +8.9 +3.1M Job increase potential by 2030 2030 baseline employment Jobs lost Jobs gained New jobs 2030 workforce projection As a result, the Turkish economy has the potential for a 5. The workforce will need to acquire stronger social skills net job increase by of 3.1 million 2030, and expected total and advanced technological skills. demand for a workforce of 36.4 million. Workplace skills of the future fall into five categories: physical Taking a sectoral view, the job increases will manifest and manual, basic cognitive, higher cognitive, social and most strongly in service sectors-retail sales and service, emotional, and technological. In most sectors in Turkey, the healthcare services and care providers, food and beverage, greatest increase in time spent on work activities that require and accommodation. Occupation groups reflect similar certain abilities is expected to be for technological and social trends. The number of jobs that require customer interaction skills. By contrast, since activities such as data entry and and the number of care providers will increase. We expect equipment operation are more susceptible to automation, 30 percent growth in the retail sales and service industry the demand for basic cognitive skills and physical skills could workforce. Healthcare services and care providers are decrease in most sectors. expected to grow by 40 percent, and the food and beverage In 2030, if the anticipated talent transformation can and accommodation sectors are expected grow by 20 be ensured, the greatest change is expected to be in percent. technological skills, with a rate of 63 percent. While social 4. Upskilling and reskilling initiatives will play a key role in skills are expected to increase by 22 percent and higher talent transformation. cognitive skills by 7 percent, basic cognitive skills and physical skills are forecast to decrease by 10 and 8 percent, In order to ensure Turkey's talent transformation, 21.1 million workers will need to improve their skills, leveraging respectively. technology while remaining employed in their current jobs. In addition, automation and digitization are expected to have an increased impact on 7.6 million employees who will experience significant reskilling and job displacements. Within this group, 5.6 million people are expected to change roles by upskilling and 2.0 million are expected to gain new skills to be able to work in different sectors or in different occupations. It will be critical to equip 7.7 million new employees with required skills as they join the workforce. In the next 10 years, demand for workers with social and technological skills will increase LL Basic skills Basic literacy, numeracy, and communication Physical skills Motor skills and strength General equipment repair and mechanical skills Higher cognitive skills Creativity Complex information interpretation Project management Critical thinking and decision making Social skills Entrepreneurship Interpersonal skills and empathy Advanced communication Adaptability and continuous learning Technological skills Basic digital skills Scientific research Technology design and engineering Advanced data analysis 2030 baseline employment Million 5.2 15-5 5.8 4.5 2.4 2030 workforce, projected Million 4.7 14.3 6.2 5.5 3.9 Change -10 -8 7 22 63 % 6. All relevant stakeholders should collaborate on a broad - New working models: range of Future of Work initiatives to make Turkey's talent Companies must move from traditional "waterfall". transformation happen. approaches to flexible and efficient working models. Agile All stakeholders, including businesses, associations, public and empowered teams should be created. Employees institutions, educational institutions, and individuals must should also be prepared for the new working models and take required actions to benefit from the opportunities leadership approach. created by automation, Al, and digital technologies and to Public institutions: overcome the related challenges. - Geographical and sectoral strategic workforce Following is a summary of what each party could do. planning: Public institutions could engage in country- Businesses and associations: wide strategic workforce planning and establish priorities. Looking at the country's talent pool, they - Strategic workforce planning: should analyze existing skills and plan a road map that Leading companies should undertake efforts to conduct anticipates the skills needed in the future. strategic workforce planning and prepare road maps for talent transformation. Companies should make - Centers of development and technology: Public targeted investments focused on employee reskilling institutions could set the priority areas for reform, and upskilling initiatives. Using sophisticated workforce establish dedicated mechanisms to enable a holistic approach, and coordinate implementation. They might planning tools and predictive analytical models to plan for also consider creating a dedicated central unit to oversee talent acquisition could enhance efficiency. and carry out country-wide automation and retraining Talent transformation programs: initiatives, with representatives from key ministries such Companies should set ambitious targets for automation as labor, education, and industry. through the latest technologies. Companies will need to add positions that require knowledge of data analytics - Accelerating mechanisms and incentives: Public and Al technologies and to invest in IT professionals. In institutions could work to establish job centers to addition, companies can leverage corporate academies facilitate reskilling and reemployment efforts, especially for acquisition of technological skills. Special attention to improve employee skills, from leadership skills to digital skills. should be given to Technology Development Zone skills development programs and to model factories that are being established. Turkish Employment Agency (ISKUR) programs intended to mitigate the impact of automation and digital transformation on supply-demand balance in the employment market should be revised and implemented. Furthermore, the asset-liability balance in the social security system can be closely followed considering potential disrupting effects of the technologies on the employment market. Social security and premium models aligned with the digital transformation level can be evaluated and implemented in order to balance the pace of transformation. Educational institutions: Revising the education model: The education system should revamp school curricula to incorporate in-demand skills. Relevant classes could be made compulsory at appropriate levels. Universities and educational institutions should create programs tailored to future skills, open to adults through seminars, certificate programs, and online training. - Improving learning experience: The classroom experience should be more personalized, shifting from traditional content on traditional schedules to building job skills anytime, anywhere. The new learning experience can be built through collaborating with community centers, employing experts, and using peer-to-peer or project-based instruction. Content should include problem-solving skills, rapid prototyping, and asking the right questions. - Lifelong learning: The education system needs to build the mind-set of "learning to learn," emphasizing the willingness to continuously adopt new skills. This approach allows students to build the foundations of critical thinking, problem solving, and lifelong learning. Local governments can assume a key role to access a higher number of people in order to support lifelong learning. Individuals: - Continuous learning and self-development: Individuals must own their own learning journeys by continuously updating skills throughout their careers. Leaders should understand individuals' need for capability building, both for themselves and for their organizations, and should lead the transformation. - Social and technological skills: Individuals must focus on developing the key skills and attributes of the future, including social skills (such as resilience and adaptability), technological skills (such as programming and data analysis), and cognitive skills (such as critical thinking, problem solving, and creativity). Leaders should prepare their organizations for building such capabilities. - Lifelong flexible career paths: Individuals will have to embrace a startup of you" mind-set and take an entrepreneurial approach to their careers. Project- based, independent, and part-time jobs are on the rise. Individuals should prepare themselves for lifelong flexible career paths. Automation, AI, and digital technologies offer big opportunities for Turkey to improve productivity and generate many new jobs. To take advantage of this opportunity, Turkey should invest in talent transformation to develop the new skills required in the workplace of the future. It is critical for all stakeholders to work together to achieve this transformation. We believe that this talent transformation journey will unlock the country's strong potential
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


