Question
I need graphl.h and graphl.cpp in c++! I need this asap!! test.cpp #include #include #include graphl.h using namespace std; int main() { // part 1
I need graphl.h and graphl.cpp in c++! I need this asap!!
test.cpp
#include#include #include "graphl.h" using namespace std; int main() { // part 1 ifstream infile1("data31.txt"); if (!infile1) { cout
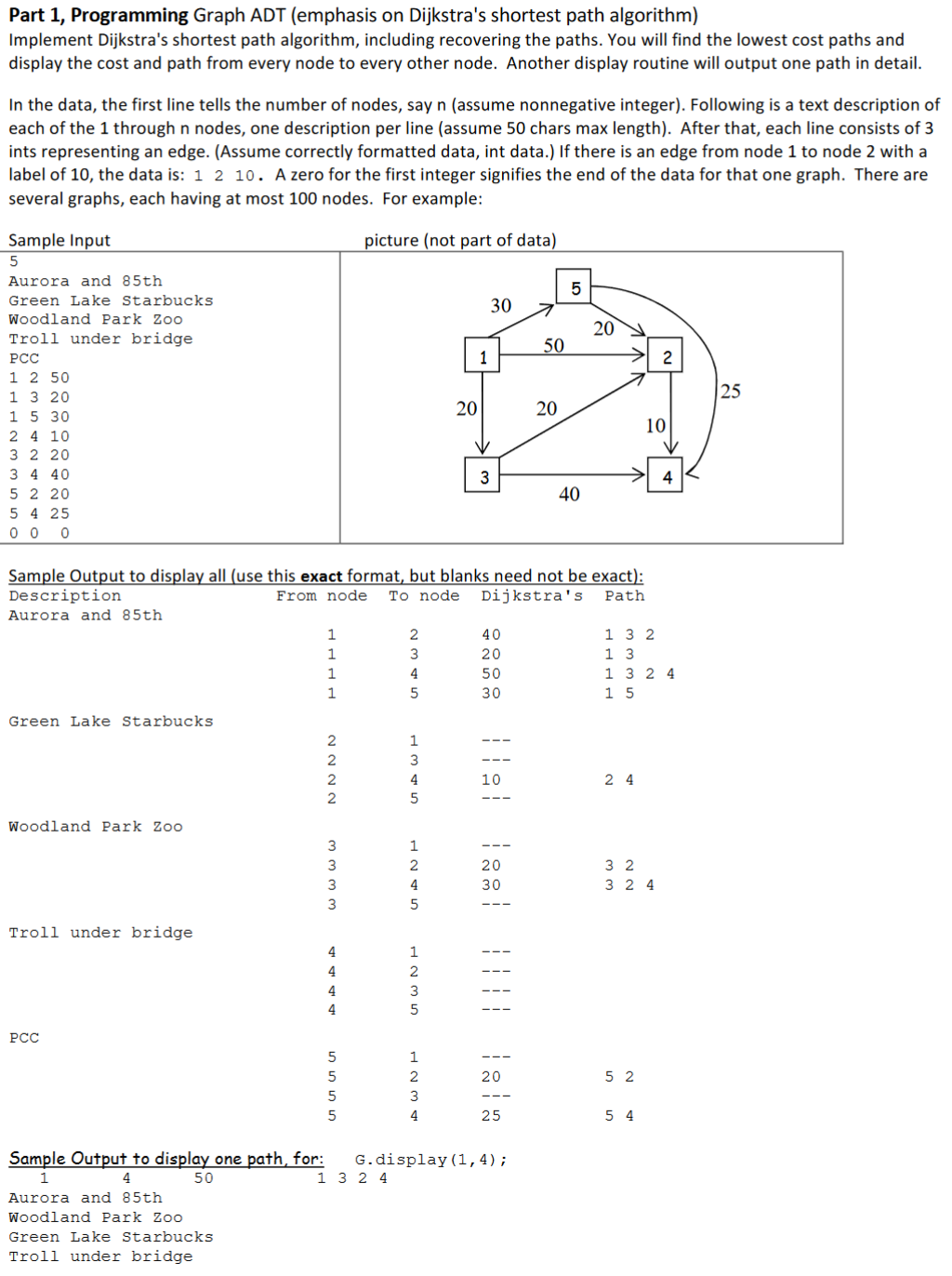
5 Aurora and 85th Green Lake Starbucks Woodland Park Zoo Troll under bridge PCC 1 2 50 1 3 20 1 5 30 2 4 10 3 2 20 3 4 40 5 2 20 5 4 25 0 0 0 3 aaa bbb ccc 1 2 10 1 3 5 2 3 20 3 2 4 0 0 0expected outcome:
Description From node To node Dijkstra's Path Aurora and 85th 1 2 40 1 3 2 1 3 20 1 3 1 4 50 1 3 2 4 1 5 30 1 5 Green Lake Starbucks 2 1 --- 2 3 --- 2 4 10 2 4 2 5 --- Woodland Park Zoo 3 1 --- 3 2 20 3 2 3 4 30 3 2 4 3 5 --- Troll under bridge 4 1 --- 4 2 --- 4 3 --- 4 5 --- PCC 5 1 --- 5 2 20 5 2 5 3 --- 5 4 25 5 4 3 1 --- Description From node To node Dijkstra's Path aaa 1 2 9 1 3 2 1 3 5 1 3 bbb 2 1 --- 2 3 20 2 3 ccc 3 1 --- 3 2 4 3 2 3 1 ---nodedata.h
#ifndef NODEDATA_H #define NODEDATA_H #include#include #include using namespace std; // simple class containing one string to use for testing // not necessary to comment further class NodeData { friend ostream & operator(const NodeData &) const; bool operator=(const NodeData &) const; private: string data; }; #endif nodedata.cpp
#include "nodedata.h" //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- // constructors/destructor NodeData::NodeData() { data = ""; } // default NodeData::~NodeData() { } // needed so strings are deleted properly NodeData::NodeData(const NodeData& nd) { data = nd.data; } // copy NodeData::NodeData(const string& s) { data = s; } // cast string to NodeData //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- // operator= NodeData& NodeData::operator=(const NodeData& rhs) { if (this != &rhs) { data = rhs.data; } return *this; } //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- // operator==,!= bool NodeData::operator==(const NodeData& rhs) const { return data == rhs.data; } bool NodeData::operator!=(const NodeData& rhs) const { return data != rhs.data; } //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- // operator,= bool NodeData::operator(const NodeData& rhs) const { return data > rhs.data; } bool NodeData::operator=(const NodeData& rhs) const { return data >= rhs.data; } //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- // setData // returns true if the data is set, false when bad data, i.e., is eof bool NodeData::setData(istream& infile) { getline(infile, data); return !infile.eof(); // eof function is true when eof char is read } //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- // operatorTo line up numbers use setw() (must #include
). For example, if n is an int, 10 chars are printed including n. Default is right justified, padding with blanks on the left: cout Part 1, Programming Graph ADT (emphasis on Dijkstra's shortest path algorithm) Implement Dijkstra's shortest path algorithm, including recovering the paths. You will find the lowest cost paths and display the cost and path from every node to every other node. Another display routine will output one path in detail. In the data, the first line tells the number of nodes, say n (assume nonnegative integer). Following is a text description of each of the 1 through n nodes, one description per line (assume 50 chars max length). After that, each line consists of 3 ints representing an edge. (Assume correctly formatted data, int data.) If there is an edge from node 1 to node 2 with a label of 10, the data is: 12 10. A zero for the first integer signifies the end of the data for that one graph. There are several graphs, each having at most 100 nodes. For example
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


