Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
i need help entering all the info and calculations Concentration and Rate Data: Experiment #1 Beaker A: XML 0.8 MK 1.0 mL 0.01 M Na
i need help entering all the info and calculations 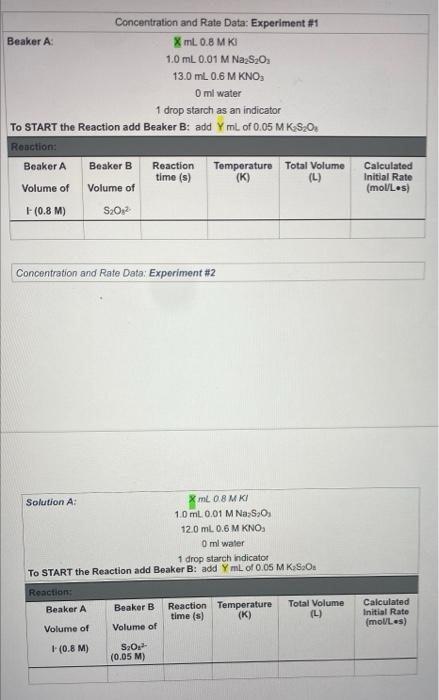
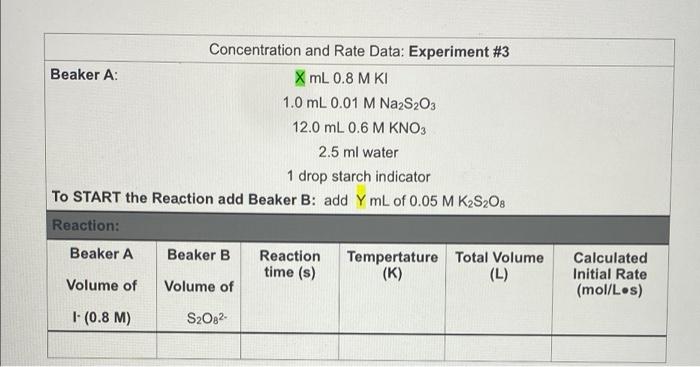
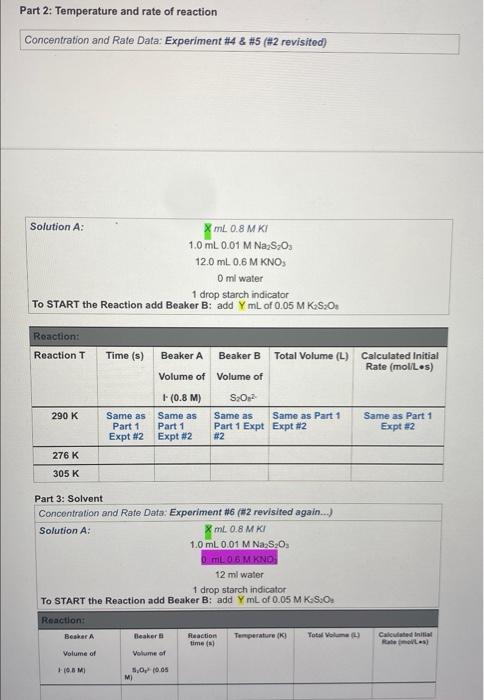

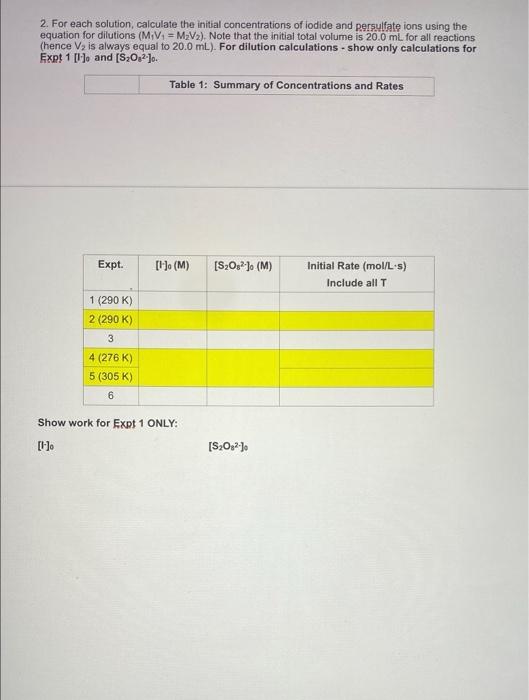
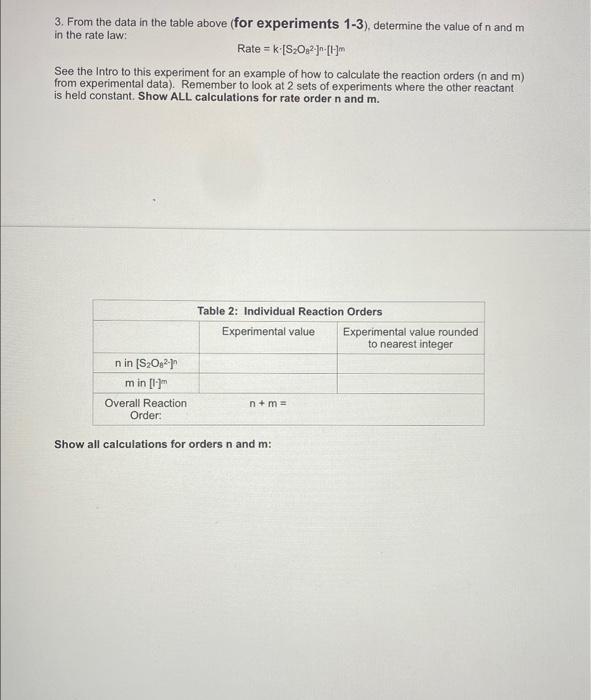


Concentration and Rate Data: Experiment #1 Beaker A: XML 0.8 MK 1.0 mL 0.01 M Na S20 13.0 mL 0.6 M KNO Oml water 1 drop starch as an indicator TO START the Reaction add Beaker B: add YmL of 0.05 M K.S.O. Reaction: Beaker A Beaker B Reaction Temperature Total Volume time (s) (K) (L) Volume of Volume of (0.8 M) S.O. Calculated Initial Rate (molles) Concentration and Rate Data: Experiment #2 Solution A: 8 ml 08 MKI 1.0 ml. 0.01 M Na SO, 12.0 ml. 0.6 M KNO O ml water 1 drop starch indicator TO START the Reaction add Beaker B: add YmL of 0.05 MKS.O. Reaction: Beaker A Beaker B Reaction Temperature time (s) (K) Total Volume (L) Calculated Initial Rate (molles) Volume of Volume of (0.8 M) S.O. (0.05 M) Concentration and Rate Data: Experiment #3 Beaker A: X mL 0.8 M KI 1.0 mL 0.01 M Na2S2O3 12.0 mL 0.6 M KNO3 2.5 ml water 1 drop starch indicator TO START the Reaction add Beaker B: add Y mL of 0.05 M KzS208 Reaction: Beaker A Beaker B Reaction Tempertature Total Volume time (s) (K) (L) Volume of Volume of Calculated Initial Rate (mol/Les) 1- (0.8 M) S2082 Part 2: Temperature and rate of reaction Concentration and Rate Data: Experiment #4 & #5 (#2 revisited) Solution A: mL 0.8 M KI 1.0 mL 0.01 M Na, S.O 12.0 mL 0.6 M KNO Oml water 1 drop starch indicator TO START the Reaction add Beaker B: add YmL of 0.05 M KS:O: Reaction: Reaction T Time (s) Beaker A Beaker B Total Volume (L) Calculated Initial Rate (molles) Volume of Volume of 290 K Same as Part 1 Expt #2 (0.8 M) Same as Part 1 Expt #2 S02 Same as Same as Part 1 Part 1 Expt Expt #2 #2 Same as Part 1 Expt #2 276 K 305 K Part 3: Solvent Concentration and Rate Data: Experiment #6 (#2 revisited again...) Solution A: mL 0.8 MK 1.0 mL 0.01 M Na S. D.ML. 06 M KNO 12 ml water 1 drop starch indicator TO START the Reaction add Beaker B: add YmL of 0.05 MK S.O. Reaction: Besker Beaker Reaction Temperature ( Total Wall (1) Volume of Volume of Calvin Rates 100 M 5,0,0.05 M) Calculations 1. For experiments 1-6 calculate the Inbal Rate of the reaction last column in each table ABOVE), according to equation below. Show ALL calculations for at 5.0 x 10 mols 5,022-consumed Initial Rate = total volume (L) reaction time) SHOW ALL Initial rate calculations for the six experiments here: 2. For each solution, calculate the initial concentrations of iodide and persons using the equation for dilutions (M.V. - MV.). Note that the initial total volume 5200 ml for all reactions (hence V is always equal to 20,0 mL). For dilution calculations show only calculations for Exp: 1) and (520) Table 1: Summary of Concentrations and Rates 2. For each solution, calculate the initial concentrations of lodide and Resulfate ions using the equation for dilutions (MiV, = M2V2). Note that the initial total volume is 20.0 mL for all reactions (hence V2 is always equal to 20.0 mL). For dilution calculations - show only calculations for Expt 1 [14] and [S:0,2].. Table 1: Summary of Concentrations and Rates Expt. [1]. (M) [S2O32). (M) Initial Rate (mol/ Ls) Include all T 1 (290 K) 2 (290 K) 3 4 (276K) 5 (305 K) 6 Show work for Expt 1 ONLY: [-] [S,Os2-) 3. From the data in the table above (for experiments 1-3), determine the value of n and m in the rate law: Rate = k [S2O32-][ See the Intro to this experiment for an example of how to calculate the reaction orders (n and m) from experimental data). Remember to look at 2 sets of experiments where the other reactant is held constant. Show ALL calculations for rate order n and m. Table 2: Individual Reaction Orders Experimental value Experimental value rounded to nearest Integer nin (S20821 min (1) Overall Reaction Order: num= Show all calculations for orders n and m: 4. Calculate the value of k for each reaction using the values from Tables and 2 (use the integer- rounded reaction orders, n and m), Show ALL calculations k (not the average). Table 3: Rate Constants for Reactions 1-3 UNITS of rate Experiment constant k Rate Constant k 2 3 AVERAGE Show work for k calculations for Experiments 1, 2 and 3: Table 4: Rate Constants for Reactions 2, 4 and 5 UNITS of rate constant k Experiment Rate Constant 2 (copy from Table 3) 4 5 Show work for k calculations for Experiments 4 and 5: Answer the following questions (use only up to 2 sentences when appropriate). 1) Should the rate constants be the same or different between experiments 1, 2 and 3? BRIEFLY explain your answer. 2) What is 1 SPECIFIC possible source of error in this experiment and how does it affect your results? Think of an error that would have a direct effect in your final rate law or reaction order Through the calculations, would this error give you a higher or lower result for the parameter in question? Note: "human error is not a valid answert Also, do not use rounding or calculations error 3) Compare experiments 2,4 and 6. Use 1 sentence to describe the relationship between temperature and the rate of reaction 4) Compare experiments 2 and 6. Uso 1 sentence to describe how the change in solvent affects the rate of reaction? 5) Calculate Ea (in kJ/mol) by using Experiments 4 and 5 data and the Arrhenius equation. You must show ALL work 6) Calculate Ea finkl/mol) AGAIN, this time by graphing the three data points from Table 4. You must show ALL work. Also include a picture of your MS Excel graph with the trending equation Concentration and Rate Data: Experiment #1 Beaker A: XML 0.8 MK 1.0 mL 0.01 M Na S20 13.0 mL 0.6 M KNO Oml water 1 drop starch as an indicator TO START the Reaction add Beaker B: add YmL of 0.05 M K.S.O. Reaction: Beaker A Beaker B Reaction Temperature Total Volume time (s) (K) (L) Volume of Volume of (0.8 M) S.O. Calculated Initial Rate (molles) Concentration and Rate Data: Experiment #2 Solution A: 8 ml 08 MKI 1.0 ml. 0.01 M Na SO, 12.0 ml. 0.6 M KNO O ml water 1 drop starch indicator TO START the Reaction add Beaker B: add YmL of 0.05 MKS.O. Reaction: Beaker A Beaker B Reaction Temperature time (s) (K) Total Volume (L) Calculated Initial Rate (molles) Volume of Volume of (0.8 M) S.O. (0.05 M) Concentration and Rate Data: Experiment #3 Beaker A: X mL 0.8 M KI 1.0 mL 0.01 M Na2S2O3 12.0 mL 0.6 M KNO3 2.5 ml water 1 drop starch indicator TO START the Reaction add Beaker B: add Y mL of 0.05 M KzS208 Reaction: Beaker A Beaker B Reaction Tempertature Total Volume time (s) (K) (L) Volume of Volume of Calculated Initial Rate (mol/Les) 1- (0.8 M) S2082 Part 2: Temperature and rate of reaction Concentration and Rate Data: Experiment #4 & #5 (#2 revisited) Solution A: mL 0.8 M KI 1.0 mL 0.01 M Na, S.O 12.0 mL 0.6 M KNO Oml water 1 drop starch indicator TO START the Reaction add Beaker B: add YmL of 0.05 M KS:O: Reaction: Reaction T Time (s) Beaker A Beaker B Total Volume (L) Calculated Initial Rate (molles) Volume of Volume of 290 K Same as Part 1 Expt #2 (0.8 M) Same as Part 1 Expt #2 S02 Same as Same as Part 1 Part 1 Expt Expt #2 #2 Same as Part 1 Expt #2 276 K 305 K Part 3: Solvent Concentration and Rate Data: Experiment #6 (#2 revisited again...) Solution A: mL 0.8 MK 1.0 mL 0.01 M Na S. D.ML. 06 M KNO 12 ml water 1 drop starch indicator TO START the Reaction add Beaker B: add YmL of 0.05 MK S.O. Reaction: Besker Beaker Reaction Temperature ( Total Wall (1) Volume of Volume of Calvin Rates 100 M 5,0,0.05 M) Calculations 1. For experiments 1-6 calculate the Inbal Rate of the reaction last column in each table ABOVE), according to equation below. Show ALL calculations for at 5.0 x 10 mols 5,022-consumed Initial Rate = total volume (L) reaction time) SHOW ALL Initial rate calculations for the six experiments here: 2. For each solution, calculate the initial concentrations of iodide and persons using the equation for dilutions (M.V. - MV.). Note that the initial total volume 5200 ml for all reactions (hence V is always equal to 20,0 mL). For dilution calculations show only calculations for Exp: 1) and (520) Table 1: Summary of Concentrations and Rates 2. For each solution, calculate the initial concentrations of lodide and Resulfate ions using the equation for dilutions (MiV, = M2V2). Note that the initial total volume is 20.0 mL for all reactions (hence V2 is always equal to 20.0 mL). For dilution calculations - show only calculations for Expt 1 [14] and [S:0,2].. Table 1: Summary of Concentrations and Rates Expt. [1]. (M) [S2O32). (M) Initial Rate (mol/ Ls) Include all T 1 (290 K) 2 (290 K) 3 4 (276K) 5 (305 K) 6 Show work for Expt 1 ONLY: [-] [S,Os2-) 3. From the data in the table above (for experiments 1-3), determine the value of n and m in the rate law: Rate = k [S2O32-][ See the Intro to this experiment for an example of how to calculate the reaction orders (n and m) from experimental data). Remember to look at 2 sets of experiments where the other reactant is held constant. Show ALL calculations for rate order n and m. Table 2: Individual Reaction Orders Experimental value Experimental value rounded to nearest Integer nin (S20821 min (1) Overall Reaction Order: num= Show all calculations for orders n and m: 4. Calculate the value of k for each reaction using the values from Tables and 2 (use the integer- rounded reaction orders, n and m), Show ALL calculations k (not the average). Table 3: Rate Constants for Reactions 1-3 UNITS of rate Experiment constant k Rate Constant k 2 3 AVERAGE Show work for k calculations for Experiments 1, 2 and 3: Table 4: Rate Constants for Reactions 2, 4 and 5 UNITS of rate constant k Experiment Rate Constant 2 (copy from Table 3) 4 5 Show work for k calculations for Experiments 4 and 5: Answer the following questions (use only up to 2 sentences when appropriate). 1) Should the rate constants be the same or different between experiments 1, 2 and 3? BRIEFLY explain your answer. 2) What is 1 SPECIFIC possible source of error in this experiment and how does it affect your results? Think of an error that would have a direct effect in your final rate law or reaction order Through the calculations, would this error give you a higher or lower result for the parameter in question? Note: "human error is not a valid answert Also, do not use rounding or calculations error 3) Compare experiments 2,4 and 6. Use 1 sentence to describe the relationship between temperature and the rate of reaction 4) Compare experiments 2 and 6. Uso 1 sentence to describe how the change in solvent affects the rate of reaction? 5) Calculate Ea (in kJ/mol) by using Experiments 4 and 5 data and the Arrhenius equation. You must show ALL work 6) Calculate Ea finkl/mol) AGAIN, this time by graphing the three data points from Table 4. You must show ALL work. Also include a picture of your MS Excel graph with the trending equation 







Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


