Question: I need help in python assignment please help Please i really need help I have no idea how to even start. P CS 112 Class
I need help in python assignment please help
 Please i really need help I have no idea how to even start.
Please i really need help I have no idea how to even start.
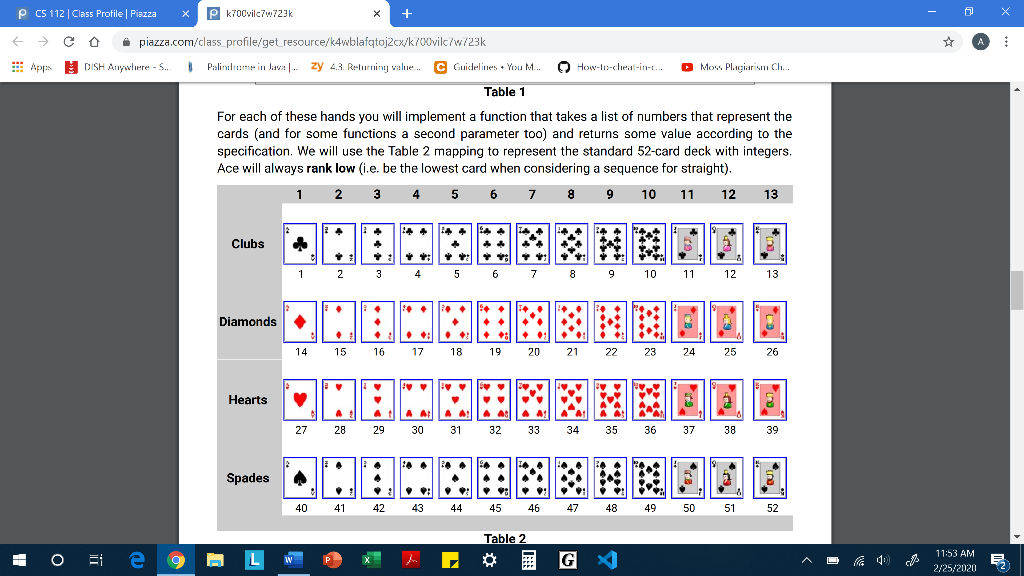
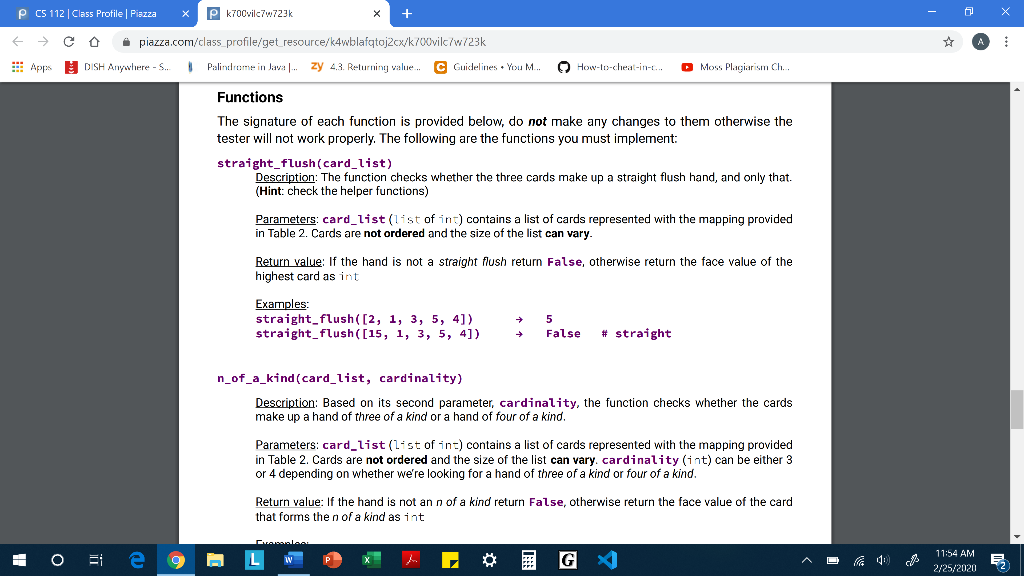
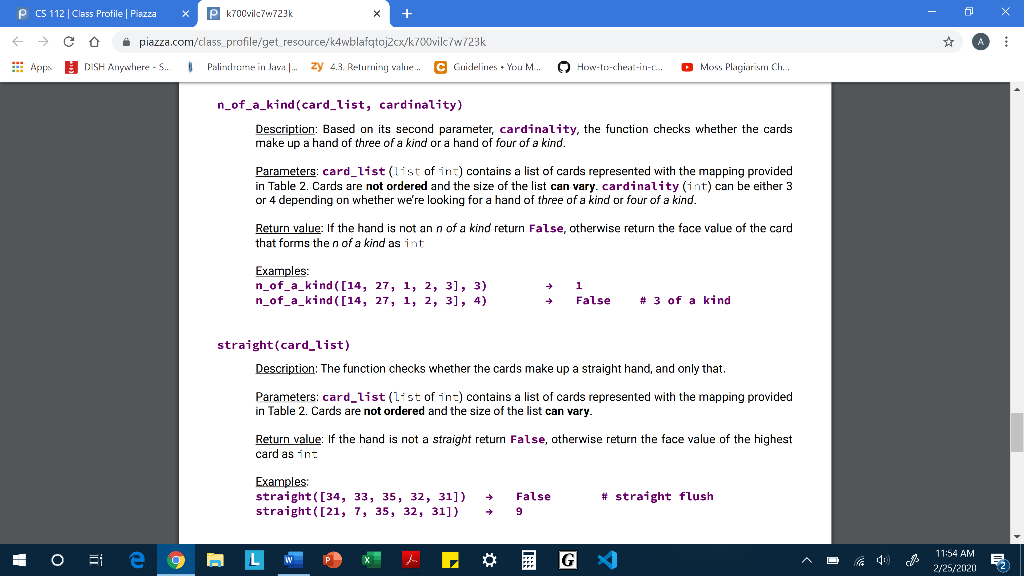
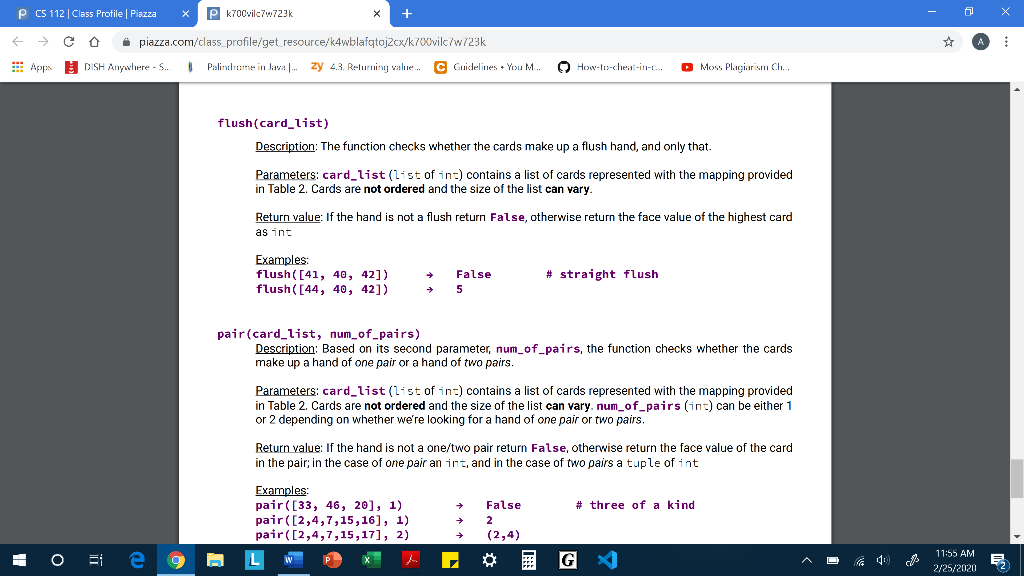
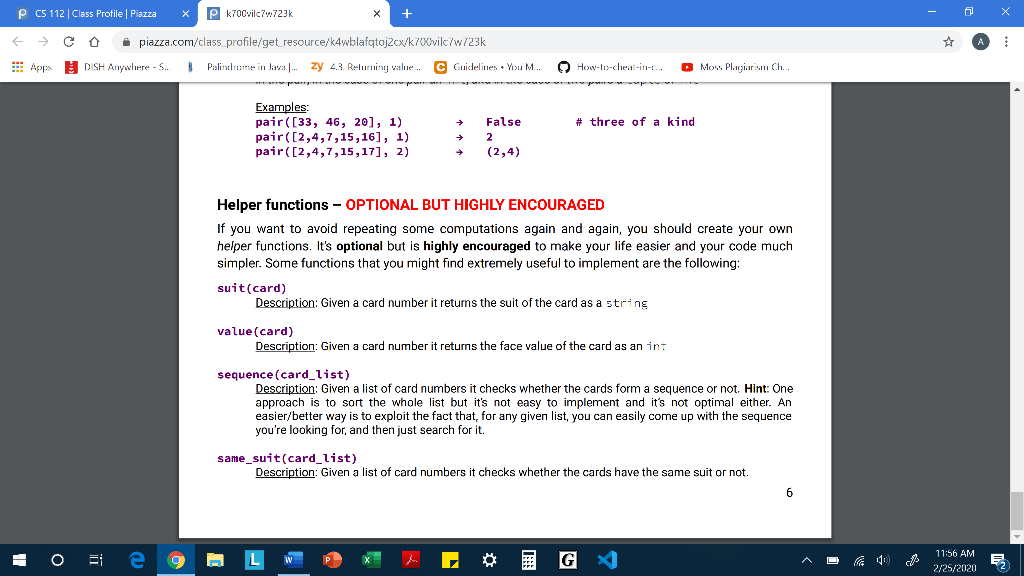
P CS 112 Class Profile | Piazza X Pk7O0vilc7w723k - 0 X E C Apps o piazza.com/class_profile/get_resource/k4wblafqtoj2cx/k700vilc/w/23k DISH Anywhere - S. Palubrome in Java.. zy 43. Returning value... C Guidelines. You M... V How-to-cheat-in-... Moss Plagiarism Ch. testers.py Background Loop statements allow us to run the same block of code repeatedly, with the chance to use different values for variables each time as the accumulated effects pile up. Lists are sequences that can be inspected value-by-value and modified at will. In this assignment we will use loops to perform calculations over one-dimensional lists (in future assignments we will work with multi-dimensional lists too). However, working with one-dimensional lists doesn't necessarily mean that a single while/for loop is always enough, sometimes a repeated iteration over a list might require a (double or even triple) nested loop. Guidelines You are not allowed to import anything. You are not allowed to use sets, dictionaries You are not allowed to use anything that hasn't been covered in class, including the list comprehension construct (if you don't know it, don't worry, it's impossible to use it by accident!) From built-in functions, you are allowed to call only range(), len(), abs(), int(), str() From list methods, you are allowed to use only .append(). Please do not ask on piazza whether you can use .sort()..index(), .count() etc. You are not allowed to hard-code exhaustive if-elif-elif statements to handle all possible list lengths. Your code should work with any length of list even if it were larger than 13. You can only use slicing if it doesn't bypass a restriction. For example, you can't use slicing to reverse a list since .reverse() is not allowed either. A D " 11:51 AM 2/25/20202 P CS 112 Class Profile | Piazza x P k700vilc76.723k - 0 X E C Apps o piazza.com/class_profile/get_resource/k4wblafqtoj2cx/k700vilc/w/23k DISH Anywhere - S. Palindrome in Java ... zy 43. Returning value... C Guidelines. You M... How-to-cheat-in-. Moss Plagiarism Ch. Scenario You're working for the same software company that you did in PA3 and your manager asks you to write a new version of the poker application, only this time it's going to be more powerful and customizable for more variants of the poker game. More specifically, it should work with any number of cards, not just 3 as before but with larger numbers too (e.g. 4, 5, 7, etc.). For the purposes of this assignment we will assume that the hand can have any length from 3 up to 13 included. We will also assume that the following hands and ranks apply to all variants. Rank Description Straight flush ALL suited cards in sequence N of a kind N cards of same rank (N will be either 3 or 4) Straight ALL cards in sequence Flush ALL suited cards N pairs N different pairs of two cards of same rank (N will be either 1 or 2) Table 1 For each of these hands you will implement a function that takes a list of numbers that represent the cards (and for some functions a second parameter too) and returns some value according to the specification. We will use the Table 2 mapping to represent the standard 52-card deck with integers. Ace will always rank low (i.e. be the lowest card when considering a sequence for straight). 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 * 11:52 AM 2/25/2020 E 2 P CS 112 Class Profile | Piazza x P k700vilc76.723k - 0 X E C Apps V o piazza.com/class_profile/get_resource/k4wblafqtoj2cx/k700vilc/w/23k DISH Anywhere - S. Palubrome in Java.. zy 43. Returning value... C Guidelines. You M... How-to-cheat-in-... Moss Plagiarism Ch. Table 1 For each of these hands you will implement a function that takes a list of numbers that represent the cards (and for some functions a second parameter too) and returns some value according to the specification. We will use the Table 2 mapping to represent the standard 52-card deck with integers. Ace will always rank low (i.e. be the lowest card when considering a sequence for straight), 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 11 Diamonds 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 Hearts - QUINEEEEMNEZE 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 Table 2 11:53 AM E 2/25/202052 P CS 112 Class Profile | Piazza x P k700vilc76.723k - 0 X E C Apps o piazza.com/class_profile/get_resource/k4wblafqtoj2cx/k700vilc/w/23k DISH Anywhere - S. Palirubome in Java.. zy 4.3. Returning value... C Guidelines. You M... V How-to-cheat-in-t. Moss Plagiarism Ch... Assumptions You may assume that: The types of the values that are sent to the functions are the proper ones (card_list is a list of integers not floats, etc.), you don't have to validate them. The functions are going to be called with usable values (e.g. card_list doesn't contain negative numbers, etc.), you don't have to validate them. All card numbers that are passed into a function are guaranteed to be unique, you don't have to validate that either. A 4 11:53 AM E 2725/20202 P CS 112 Class Profile | Piazza X Pk7O0vilc7w723k - 0 X E C Apps o piazza.com/class_profile/get_resource/k4wblafqtoj2cx/k700vilc/w/23k DISH Anywhere - S. Palubrome in Java.. zy 43. Returning value... C Guidelines. You M... V How-to-cheat-in-... Moss Plagiarism Ch. Functions The signature of each function is provided below, do not make any changes to them otherwise the tester will not work properly. The following are the functions you must implement: straight flush(card list) Description: The function checks whether the three cards make up a straight flush hand, and only that. (Hint: check the helper functions) Parameters: card_list (list of int) contains a list of cards represented with the mapping provided in Table 2. Cards are not ordered and the size of the list can vary. Return value: If the hand is not a straight flush return false, otherwise return the face value of the highest card as int Examples: straight_flush([2, 1, 3, 5, 4]) straight_flush([15, 1, 3, 5, 4]) 5 False # straight n_of_a_kind(card_list, cardinality) Description: Based on its second parameter, cardinality, the function checks whether the cards make up a hand of three of a kind or a hand of four of a kind. Parameters: card_list(list of in:) contains a list of cards represented with the mapping provided t ordered and the size of the list can vary. cardinality (int) can be either 3 or 4 depending on whether we're looking for a hand of three of a kind or four of a kind. Return value: If the hand is not an n of a kind return false, otherwise return the face value of the card that forms then of a kind as int Sarada * 11:54 AM 2/25/2020 E 2 P CS 112 Class Profile | Piazza x P k700vilc76.723k - 0 X E C Apps o piazza.com/class_profile/get_resource/k4wblafqtoj2cx/k700vilc/w/23k DISH Anywhere - S. Palirubome in Java.. zy 4.3. Returning value... C Guidelines. You M... V How-to-cheat-in-t. Moss Plagiarism Ch... n_of_a_kind(card_list, cardinality) Description: Based on its second parameter, cardinality, the function checks whether the cards make up a hand of three of a kind or a hand of four of a kind. Parameters: card_list(list of int) contains a list of cards represented with the mapping provided in Table 2. Cards are not ordered and the size of the list can vary. cardinality (int) can be either 3 or 4 depending on whether we're looking for a hand of three of a kind or four of a kind. Return value: If the hand is not an n of a kind return False, otherwise return the face value of the card that forms the n of a kind as int Examples: n_of_a_kind ([14, 27, 1, 2, 3], 3) n_of_a_kind ([14, 27, 1, 2, 3], 4) False # 3 of a kind straight (card_list) Description: The function checks whether the cards make up a straight hand, and only that, Parameters: card_list(list of in:) contains a list of cards represented with the mapping provided in Table 2. Cards are not ordered and the size of the list can vary. Return value: If the hand is not a straight return false, otherwise return the face value of the highest card as in Examples straight([34, 33, 35, 32, 31]) straight([21, 7, 35, 32, 31]) # straight flush + = False 9 11:54 AM E 2/25/20202 P CS 112 Class Profile | Piazza x P k700vilc76.723k - 0 X E C Apps o piazza.com/class_profile/get_resource/k4wblafqtoj2cx/k700vilc/w/23k DISH Anywhere - S. Palirubome in Java.. zy 4.3. Returning value... C Guidelines. You M... V How-to-cheat-in-t. Moss Plagiarism Ch... flush(card_list) Description: The function checks whether the cards make up a flush hand, and only that. Parameters: card_list (list of ins) contains a list of cards represented with the mapping provided in Table 2. Cards are not ordered and the size of the list can vary. Return value: If the hand is not a flush return false, otherwise return the face value of the highest card as int Examples: flush([41, 40, 42]) flush([44, 40, 42]) # straight flush False 5 pair(card_list, num_of_pairs) Description: Based on its second parameter, num_of_pairs, the function checks whether the cards make up a hand of one pair or a hand of two pairs. Parameters: card_list (list of ins) contains a list of cards represented with the mapping provided in Table 2. Cards are not ordered and the size of the list can vary. num_of_pairs (int) can be either 1 or 2 depending on whether we're looking for a hand of one pair or two pairs. Return value: If the hand is not a one/two pair return False, otherwise return the face value of the card in the pair; in the case of one pair an int, and in the case of two pairs a tuple of int # three of a kind Examples pair([33, 46, 20], 1) pair([2,4,7,15,16], 1) pair([2,4,7,15,17], 2) False 2 (2,4) 11:55 AM E 2/25/202052 P CS 112 Class Profile | Piazza x P k700vilc76.723k - 0 X E C Apps o piazza.com/class_profile/get_resource/k4wblafqtoj2cx/k700vilc/w/23k DISH Anywhere - S. Palirubome in Java.. zy 4.3. Returning value... C Guidelines. You M... V How-to-cheat-in-t. Moss Plagiarism Ch... # three of a kind Examples: pair ([33, 46, 20], 1) pair ([2,4,7,15,16], 1) pair([2,4,7,15,17], 2) + False 2 (2,4) Helper functions - OPTIONAL BUT HIGHLY ENCOURAGED If you want to avoid repeating some computations again and again, you should create your own helper functions. It's optional but is highly encouraged to make your life easier and your code much simpler. Some functions that you might find extremely useful to implement are the following: suit(card) Description: Given a card number it returns the suit of the card as a string value (card) Description: Given a card number it returns the face value of the card as an int sequence (card_list) Description: Given a list of card numbers it checks whether the cards form a sequence or not. Hint: One approach is to sort the whole list but it's not easy to implement and it's not optimal either. An easier/better way is to exploit the fact that, for any given list, you can easily come up with the sequence you're looking for, and then just search for it. same_suit(card_list) Description: Given a list of card numbers it checks whether the cards have the same suit or not. i 30 Ei e 9 LW de E EG " 11:56 AM E 2/25/20202 P CS 112 Class Profile | Piazza X Pk7O0vilc7w723k - 0 X E C Apps o piazza.com/class_profile/get_resource/k4wblafqtoj2cx/k700vilc/w/23k DISH Anywhere - S. Palubrome in Java.. zy 43. Returning value... C Guidelines. You M... V How-to-cheat-in-... Moss Plagiarism Ch. testers.py Background Loop statements allow us to run the same block of code repeatedly, with the chance to use different values for variables each time as the accumulated effects pile up. Lists are sequences that can be inspected value-by-value and modified at will. In this assignment we will use loops to perform calculations over one-dimensional lists (in future assignments we will work with multi-dimensional lists too). However, working with one-dimensional lists doesn't necessarily mean that a single while/for loop is always enough, sometimes a repeated iteration over a list might require a (double or even triple) nested loop. Guidelines You are not allowed to import anything. You are not allowed to use sets, dictionaries You are not allowed to use anything that hasn't been covered in class, including the list comprehension construct (if you don't know it, don't worry, it's impossible to use it by accident!) From built-in functions, you are allowed to call only range(), len(), abs(), int(), str() From list methods, you are allowed to use only .append(). Please do not ask on piazza whether you can use .sort()..index(), .count() etc. You are not allowed to hard-code exhaustive if-elif-elif statements to handle all possible list lengths. Your code should work with any length of list even if it were larger than 13. You can only use slicing if it doesn't bypass a restriction. For example, you can't use slicing to reverse a list since .reverse() is not allowed either. A D " 11:51 AM 2/25/20202 P CS 112 Class Profile | Piazza x P k700vilc76.723k - 0 X E C Apps o piazza.com/class_profile/get_resource/k4wblafqtoj2cx/k700vilc/w/23k DISH Anywhere - S. Palindrome in Java ... zy 43. Returning value... C Guidelines. You M... How-to-cheat-in-. Moss Plagiarism Ch. Scenario You're working for the same software company that you did in PA3 and your manager asks you to write a new version of the poker application, only this time it's going to be more powerful and customizable for more variants of the poker game. More specifically, it should work with any number of cards, not just 3 as before but with larger numbers too (e.g. 4, 5, 7, etc.). For the purposes of this assignment we will assume that the hand can have any length from 3 up to 13 included. We will also assume that the following hands and ranks apply to all variants. Rank Description Straight flush ALL suited cards in sequence N of a kind N cards of same rank (N will be either 3 or 4) Straight ALL cards in sequence Flush ALL suited cards N pairs N different pairs of two cards of same rank (N will be either 1 or 2) Table 1 For each of these hands you will implement a function that takes a list of numbers that represent the cards (and for some functions a second parameter too) and returns some value according to the specification. We will use the Table 2 mapping to represent the standard 52-card deck with integers. Ace will always rank low (i.e. be the lowest card when considering a sequence for straight). 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 * 11:52 AM 2/25/2020 E 2 P CS 112 Class Profile | Piazza x P k700vilc76.723k - 0 X E C Apps V o piazza.com/class_profile/get_resource/k4wblafqtoj2cx/k700vilc/w/23k DISH Anywhere - S. Palubrome in Java.. zy 43. Returning value... C Guidelines. You M... How-to-cheat-in-... Moss Plagiarism Ch. Table 1 For each of these hands you will implement a function that takes a list of numbers that represent the cards (and for some functions a second parameter too) and returns some value according to the specification. We will use the Table 2 mapping to represent the standard 52-card deck with integers. Ace will always rank low (i.e. be the lowest card when considering a sequence for straight), 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 11 Diamonds 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 Hearts - QUINEEEEMNEZE 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 Table 2 11:53 AM E 2/25/202052 P CS 112 Class Profile | Piazza x P k700vilc76.723k - 0 X E C Apps o piazza.com/class_profile/get_resource/k4wblafqtoj2cx/k700vilc/w/23k DISH Anywhere - S. Palirubome in Java.. zy 4.3. Returning value... C Guidelines. You M... V How-to-cheat-in-t. Moss Plagiarism Ch... Assumptions You may assume that: The types of the values that are sent to the functions are the proper ones (card_list is a list of integers not floats, etc.), you don't have to validate them. The functions are going to be called with usable values (e.g. card_list doesn't contain negative numbers, etc.), you don't have to validate them. All card numbers that are passed into a function are guaranteed to be unique, you don't have to validate that either. A 4 11:53 AM E 2725/20202 P CS 112 Class Profile | Piazza X Pk7O0vilc7w723k - 0 X E C Apps o piazza.com/class_profile/get_resource/k4wblafqtoj2cx/k700vilc/w/23k DISH Anywhere - S. Palubrome in Java.. zy 43. Returning value... C Guidelines. You M... V How-to-cheat-in-... Moss Plagiarism Ch. Functions The signature of each function is provided below, do not make any changes to them otherwise the tester will not work properly. The following are the functions you must implement: straight flush(card list) Description: The function checks whether the three cards make up a straight flush hand, and only that. (Hint: check the helper functions) Parameters: card_list (list of int) contains a list of cards represented with the mapping provided in Table 2. Cards are not ordered and the size of the list can vary. Return value: If the hand is not a straight flush return false, otherwise return the face value of the highest card as int Examples: straight_flush([2, 1, 3, 5, 4]) straight_flush([15, 1, 3, 5, 4]) 5 False # straight n_of_a_kind(card_list, cardinality) Description: Based on its second parameter, cardinality, the function checks whether the cards make up a hand of three of a kind or a hand of four of a kind. Parameters: card_list(list of in:) contains a list of cards represented with the mapping provided t ordered and the size of the list can vary. cardinality (int) can be either 3 or 4 depending on whether we're looking for a hand of three of a kind or four of a kind. Return value: If the hand is not an n of a kind return false, otherwise return the face value of the card that forms then of a kind as int Sarada * 11:54 AM 2/25/2020 E 2 P CS 112 Class Profile | Piazza x P k700vilc76.723k - 0 X E C Apps o piazza.com/class_profile/get_resource/k4wblafqtoj2cx/k700vilc/w/23k DISH Anywhere - S. Palirubome in Java.. zy 4.3. Returning value... C Guidelines. You M... V How-to-cheat-in-t. Moss Plagiarism Ch... n_of_a_kind(card_list, cardinality) Description: Based on its second parameter, cardinality, the function checks whether the cards make up a hand of three of a kind or a hand of four of a kind. Parameters: card_list(list of int) contains a list of cards represented with the mapping provided in Table 2. Cards are not ordered and the size of the list can vary. cardinality (int) can be either 3 or 4 depending on whether we're looking for a hand of three of a kind or four of a kind. Return value: If the hand is not an n of a kind return False, otherwise return the face value of the card that forms the n of a kind as int Examples: n_of_a_kind ([14, 27, 1, 2, 3], 3) n_of_a_kind ([14, 27, 1, 2, 3], 4) False # 3 of a kind straight (card_list) Description: The function checks whether the cards make up a straight hand, and only that, Parameters: card_list(list of in:) contains a list of cards represented with the mapping provided in Table 2. Cards are not ordered and the size of the list can vary. Return value: If the hand is not a straight return false, otherwise return the face value of the highest card as in Examples straight([34, 33, 35, 32, 31]) straight([21, 7, 35, 32, 31]) # straight flush + = False 9 11:54 AM E 2/25/20202 P CS 112 Class Profile | Piazza x P k700vilc76.723k - 0 X E C Apps o piazza.com/class_profile/get_resource/k4wblafqtoj2cx/k700vilc/w/23k DISH Anywhere - S. Palirubome in Java.. zy 4.3. Returning value... C Guidelines. You M... V How-to-cheat-in-t. Moss Plagiarism Ch... flush(card_list) Description: The function checks whether the cards make up a flush hand, and only that. Parameters: card_list (list of ins) contains a list of cards represented with the mapping provided in Table 2. Cards are not ordered and the size of the list can vary. Return value: If the hand is not a flush return false, otherwise return the face value of the highest card as int Examples: flush([41, 40, 42]) flush([44, 40, 42]) # straight flush False 5 pair(card_list, num_of_pairs) Description: Based on its second parameter, num_of_pairs, the function checks whether the cards make up a hand of one pair or a hand of two pairs. Parameters: card_list (list of ins) contains a list of cards represented with the mapping provided in Table 2. Cards are not ordered and the size of the list can vary. num_of_pairs (int) can be either 1 or 2 depending on whether we're looking for a hand of one pair or two pairs. Return value: If the hand is not a one/two pair return False, otherwise return the face value of the card in the pair; in the case of one pair an int, and in the case of two pairs a tuple of int # three of a kind Examples pair([33, 46, 20], 1) pair([2,4,7,15,16], 1) pair([2,4,7,15,17], 2) False 2 (2,4) 11:55 AM E 2/25/202052 P CS 112 Class Profile | Piazza x P k700vilc76.723k - 0 X E C Apps o piazza.com/class_profile/get_resource/k4wblafqtoj2cx/k700vilc/w/23k DISH Anywhere - S. Palirubome in Java.. zy 4.3. Returning value... C Guidelines. You M... V How-to-cheat-in-t. Moss Plagiarism Ch... # three of a kind Examples: pair ([33, 46, 20], 1) pair ([2,4,7,15,16], 1) pair([2,4,7,15,17], 2) + False 2 (2,4) Helper functions - OPTIONAL BUT HIGHLY ENCOURAGED If you want to avoid repeating some computations again and again, you should create your own helper functions. It's optional but is highly encouraged to make your life easier and your code much simpler. Some functions that you might find extremely useful to implement are the following: suit(card) Description: Given a card number it returns the suit of the card as a string value (card) Description: Given a card number it returns the face value of the card as an int sequence (card_list) Description: Given a list of card numbers it checks whether the cards form a sequence or not. Hint: One approach is to sort the whole list but it's not easy to implement and it's not optimal either. An easier/better way is to exploit the fact that, for any given list, you can easily come up with the sequence you're looking for, and then just search for it. same_suit(card_list) Description: Given a list of card numbers it checks whether the cards have the same suit or not. i 30 Ei e 9 LW de E EG " 11:56 AM E 2/25/20202
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


