I need help solving these. ALL of the answers I have input are wrong even though some of them give me numbers. Most of them give me Nan.
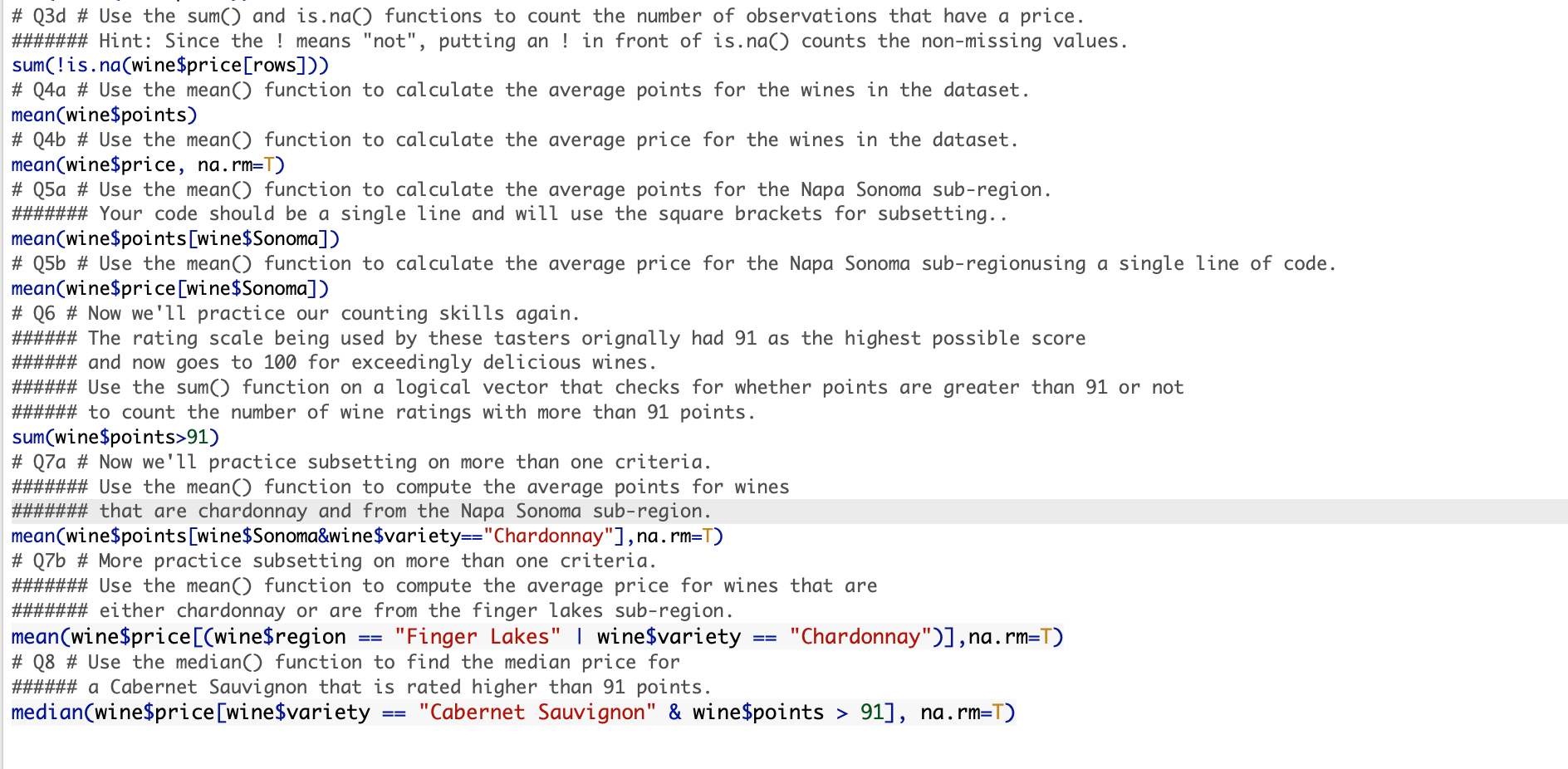
\# Q3d \# Use the sum() and is.na() functions to count the number of observations that have a price. \#\#\#\#\#\# Hint: Since the ! means "not", putting an ! in front of is.na() counts the non-missing values. sum(!is.na(wine\$price[rows])) \# Q4a \# Use the mean() function to calculate the average points for the wines in the dataset. mean(wine\$points) \# Q4b \# Use the mean() function to calculate the average price for the wines in the dataset. mean (wine $ price, narm=T ) \# Q5a \# Use the mean() function to calculate the average points for the Napa Sonoma sub-region. \#\#\#\#\#\# Your code should be a single line and will use the square brackets for subsetting.. mean(wine\$points [wine\$Sonoma]) \# Q5b \# Use the mean() function to calculate the average price for the Napa Sonoma sub-regionusing a single line of code. mean(wine\$price [wine\$Sonoma]) \# Q6 \# Now we'll practice our counting skills again. \#\#\#\#\# The rating scale being used by these tasters orignally had 91 as the highest possible score \#\#\#\#\#\# and now goes to 100 for exceedingly delicious wines. \#\#\#\#\# Use the sum() function on a logical vector that checks for whether points are greater than 91 or not \#\#\#\#\# to count the number of wine ratings with more than 91 points. sum(wine\$points>91) \# Q7a \# Now we'll practice subsetting on more than one criteria. \#\#\#\#\#\#\# Use the mean() function to compute the average points for wines \#\#\#\#\#\# that are chardonnay and from the Napa Sonoma sub-region. mean(wine $ points [wine $ Sonoma\&wine $ variety=="Chardonnay"], na.rm=T) \# Q7b \# More practice subsetting on more than one criteria. \#\#\#\#\#\# Use the mean() function to compute the average price for wines that are \#\#\#\#\#\# either chardonnay or are from the finger lakes sub-region. mean(wine\$price[(wine\$region == "Finger Lakes" | wine\$variety == "Chardonnay")], na.rm=T) \# Q8 \# Use the median() function to find the median price for \#\#\#\#\# a Cabernet Sauvignon that is rated higher than 91 points. median(wine\$price[wine\$variety == "Cabernet Sauvignon" \& wine\$points > 91], na.rm=T) \# Q3d \# Use the sum() and is.na() functions to count the number of observations that have a price. \#\#\#\#\#\# Hint: Since the ! means "not", putting an ! in front of is.na() counts the non-missing values. sum(!is.na(wine\$price[rows])) \# Q4a \# Use the mean() function to calculate the average points for the wines in the dataset. mean(wine\$points) \# Q4b \# Use the mean() function to calculate the average price for the wines in the dataset. mean (wine $ price, narm=T ) \# Q5a \# Use the mean() function to calculate the average points for the Napa Sonoma sub-region. \#\#\#\#\#\# Your code should be a single line and will use the square brackets for subsetting.. mean(wine\$points [wine\$Sonoma]) \# Q5b \# Use the mean() function to calculate the average price for the Napa Sonoma sub-regionusing a single line of code. mean(wine\$price [wine\$Sonoma]) \# Q6 \# Now we'll practice our counting skills again. \#\#\#\#\# The rating scale being used by these tasters orignally had 91 as the highest possible score \#\#\#\#\#\# and now goes to 100 for exceedingly delicious wines. \#\#\#\#\# Use the sum() function on a logical vector that checks for whether points are greater than 91 or not \#\#\#\#\# to count the number of wine ratings with more than 91 points. sum(wine\$points>91) \# Q7a \# Now we'll practice subsetting on more than one criteria. \#\#\#\#\#\#\# Use the mean() function to compute the average points for wines \#\#\#\#\#\# that are chardonnay and from the Napa Sonoma sub-region. mean(wine $ points [wine $ Sonoma\&wine $ variety=="Chardonnay"], na.rm=T) \# Q7b \# More practice subsetting on more than one criteria. \#\#\#\#\#\# Use the mean() function to compute the average price for wines that are \#\#\#\#\#\# either chardonnay or are from the finger lakes sub-region. mean(wine\$price[(wine\$region == "Finger Lakes" | wine\$variety == "Chardonnay")], na.rm=T) \# Q8 \# Use the median() function to find the median price for \#\#\#\#\# a Cabernet Sauvignon that is rated higher than 91 points. median(wine\$price[wine\$variety == "Cabernet Sauvignon" \& wine\$points > 91], na.rm=T)







