Question
I need help we are using JAVA and Please also create the main method to test the code and puts comments to help me better
I need help we are using JAVA and Please also create the main method to test the code and puts comments to help me better understand. Thank you
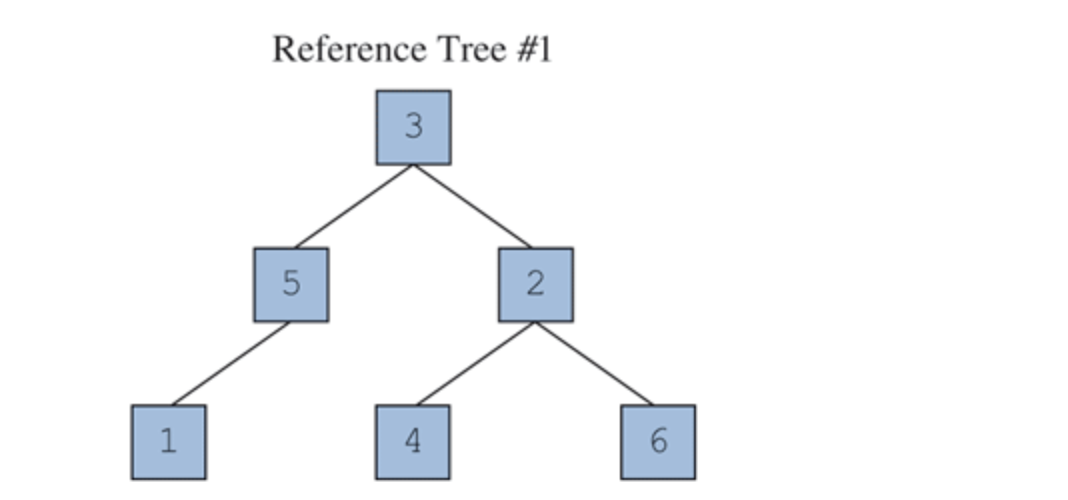
Write a method called countLeftNodes that returns the number of left children in the tree. A left child is a node that appears as the root of the left-hand subtree of another node. For example, reference tree #1 has 3 left children (the nodes storing the values 5, 1, and 4).
**************
IntTree.java
**************
/ Simple binary tree class that includes methods to construct a // tree of ints, to print the structure, and to print the data // using a preorder, inorder or postorder traversal. The trees // built have nodes numbered starting with 1 and numbered // sequentially level by level with no gaps in the tree. The // documentation refers to these as "sequential trees."
import java.util.*;
public class IntTree { private IntTreeNode overallRoot;
// pre : max > 0 // post: constructs a sequential tree with given number of // nodes public IntTree(int max) { if (max
// post: returns a sequential tree with n as its root unless // n is greater than max, in which case it returns an // empty tree private IntTreeNode buildTree(int n, int max) { if (n > max) { return null; } else { return new IntTreeNode(n, buildTree(2 * n, max), buildTree(2 * n + 1, max)); } }
// post: prints the tree contents using a preorder traversal public void printPreorder() { System.out.print("preorder:"); printPreorder(overallRoot); System.out.println(); }
// post: prints the tree contents using a preorder traversal // post: prints in preorder the tree with given root private void printPreorder(IntTreeNode root) { if (root != null) { System.out.print(" " + root.data); printPreorder(root.left); printPreorder(root.right); } }
// post: prints the tree contents using a inorder traversal public void printInorder() { System.out.print("inorder:"); printInorder(overallRoot); System.out.println(); }
// post: prints in inorder the tree with given root private void printInorder(IntTreeNode root) { if (root != null) { printInorder(root.left); System.out.print(" " + root.data); printInorder(root.right); } }
// post: prints the tree contents using a postorder traversal public void printPostorder() { System.out.print("postorder:"); printPostorder(overallRoot); System.out.println(); }
// post: prints in postorder the tree with given root private void printPostorder(IntTreeNode root) { if (root != null) { printPostorder(root.left); printPostorder(root.right); System.out.print(" " + root.data); } }
// post: prints the tree contents, one per line, following an // inorder traversal and using indentation to indicate // node depth; prints right to left so that it looks // correct when the output is rotated. public void printSideways() { printSideways(overallRoot, 0); }
// post: prints in reversed preorder the tree with given // root, indenting each line to the given level private void printSideways(IntTreeNode root, int level) { if (root != null) { printSideways(root.right, level + 1); for (int i = 0; i
IntTreeNode.java
********************
// Class for storing a single node of a binary tree of ints
public class IntTreeNode { public int data; public IntTreeNode left; public IntTreeNode right; // constructs a leaf node with given data public IntTreeNode(int data) { this(data, null, null); } // constructs a branch node with given data, left subtree, // right subtree public IntTreeNode(int data, IntTreeNode left, IntTreeNode right) { this.data = data; this.left = left; this.right = right; } }
Reference Tree #1 3 5 2 1 4 6Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


