Question: I NEED HELP WITH MY ASSIGNMENT In this assignment, we are building on the functionality you implemented to include the following: Delete a City Delete
I NEED HELP WITH MY ASSIGNMENT
In this assignment, we are building on the functionality you implemented to include the following:
Delete a City
Delete the entire City network
Send the message from coast to coast and back again (Your cities are now a doubly linked list with a next and previous pointer.
Add a City the head of the network
In the Lord of the Rings trilogy, there is a scene where the first beacon is lit in the towers of Minas Tirith. The second beacon then sees the fire, and knows to light its fire to send a signal to the third beacon, and so forth. This was a means of communicating in the days before telegraphs were invented as it was much faster than sending a human rider to deliver a message. Communication towers were equipped with signaling mechanisms, such as mirrors, that could spell out messages using the positions of the mirrors. Today, there are several examples of communication networks that are conceptually similar, but much more technically advanced, that route messages through multiple hubs between the sender and the receiver. For example, when you type a URL into a web browser, a request is sent through a network of service providers to the destination, and then packets of information are sent back to your machine. If I type www.google.com from my home in Boulder, my request follows this path:
1 192.168.2.1 (192.168.2.1)
2 c-24-9-60-1.hsd1.co.comcast.net (24.9.60.1)
3 te-9-7-ur02.boulder.co.denver.comcast.net
4 xe-13-3-1-0-ar01.aurora.co.denver.comcast.net
5 he-3-10-0-0-cr01.denver.co.ibone.comcast.net (68.86.92.25) te-1-1-0-4-cr01.chicago.il.ibone.comcast.net (68.86.95.205)
6 xe-2-0-0-0-pe01.910fifteenth.co.ibone.comcast.net (68.86.82.2)
7 as15169-1-c.910fifteenth.co.ibone.comcast.net (23.30.206.106)
8 72.14.234.57 (72.14.234.57)
9 209.85.251.111 (209.85.251.111)
10 den03s06-in-f16.1e100.net (74.125.225.208)
Each IP address is a hop in the network for my request, which is received at each service provider and then forwarded to the next service provider in the network, depending on the final destination of the message. (Note: I got this path by typing traceroute www.google.com in a terminal window. From campus, you will see a different path.)
Build your own communications network
In this assignment, youre going to simulate a communications network using a linked list. Each node in your linked list will represent a city and you need to be able to send a message between nodes from one side of the country to the other. Your program also needs to provide the capability to update the network by adding cities and still be able to transmit the message. (Note: Ill refer to the linked list as the network throughout this document.)
Include the following cities in your network:
Los Angeles
Phoenix
Denver
Dallas
St. Louis
Chicago
Atlanta
Washington, D.C.
New York
Boston
Implement each city as a struct with a name, a pointer connecting it to the next city in the network and the previous city in the network, and a place to store the message being sent. (You can assume the message is a string.) When you initially build your network, the order of the cities should be the same as the order listed above. After the network is built, you will provide the option of adding additional cities
First, display a menu
When your program starts, you should display a menu that presents the user with options for how to run your program. The menu needs to look like the one shown here:
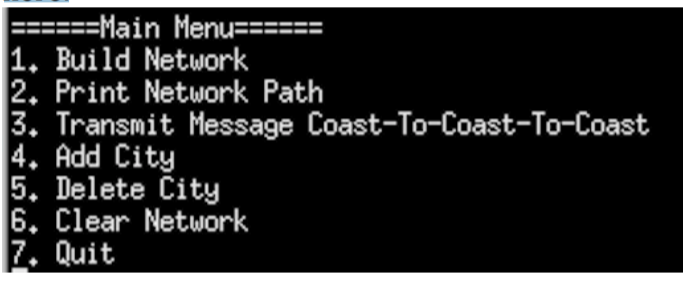
The user will select the number for the menu option and your program should respond accordingly to that number. Your menu options need to have the following functionality.
1. Build Network: This option builds the linked list using the cities listed above in the order they are listed. Each city needs to have a name, a pointer to the next city, and a message value, which will initially be an empty string. This option should be selected first to build the network, and can be selected anytime the user wants to rebuild the starting network after adding cities. As part of the Build Network functionality, you should print the name of each city in the network once the network is built in the following format:
NULL Phoenix Denver Dallas St. Louis Chicago Atlanta Washington, D.C. New York Boston -> NULL
2. Print Network Path: This option prints out the linked list in order from the head to the tail by following the next pointer for each city. You should print the name of each city. The function could be very useful to you when debugging your code. The format should be the same as the format in Build Network.
3. Transmit Message Coast-to-Coast-to-Coast: This option reads word by word from the messageIn.txt file and transmits the message starting at the beginning of the network and ending at the end of the network, and then sends the message back again to the beginning of the network. Using the cities in this write-up, the message would go from Los Angeles to Boston, passing through each city along the way, and then back to Los Angeles, passing through each city along the way. When a city receives the message, you should print
received
where is the name of the city and is the word received. When a city receives a word, the word should be deleted from the sender city, i.e set the message for the sender city to an empty string. Here is a screenshot of the output I get after transmitting the first two words in the file:
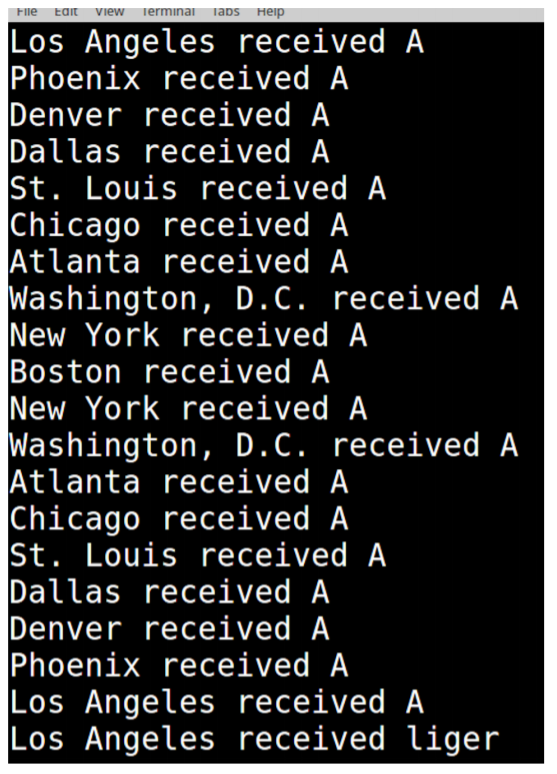
Note: The name of the file that contains the message should be a command line argument to your program.
4. Add City: This option allows the user to add a new city to the network. If the user selects this option, then they should be prompted for the name of the city and the city that the new city should follow in the network. For example, if the user wants to add Tucson after Phoenix in the network, then the first four cities in the network would be:
Los Angeles Phoenix Tucson Denver
You dont need to print anything when you add a new city, just call the Print Network function again from the menu if you want to verify that the city has been added.
If the user wants to add a new city to the head of the network, e.g. replace Los Angeles as the starting city, then they should type First when prompted for the previous city and your code should handle this special case.
Here is a screenshot showing the expected output for the add city functionality when the user selects Add City from the menu.
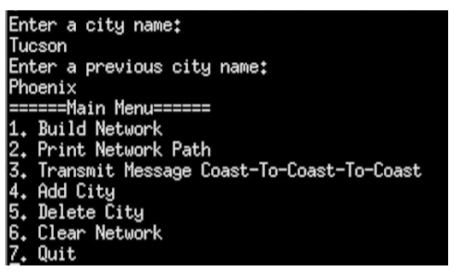
5. Delete City: This option allows the user to delete a city from the network. When the user selects this option, they should be prompted for the name of the city to delete. Your code should then update the next and previous pointers for the surrounding cities and free the memory for the deleted city.

6. Clear Network: This option allows the user to delete all cities in the network starting at the head city. After this functionality executes, the head of the list should be NULL and all cities should be deleted from the network. When a city is deleted, print the name of the city just before freeing the memory. Your clear network method should be called in the destructor of CommunicationNetwork, in addition to being a menu option.

7. Quit: This option allows the user to exit the program.
For each of the options presented, after the user makes their choice and your code runs for that option, you should re-display the menu to allow the user to select another option.
Structuring your program T
he specific cout statements that COG expects are shown in Appendix A. The functionality for your network will be implemented in a class called CommunicationNetwork. A suggested header file called CommunicationNetwork.h is provided for you on Moodle. Each of the menu options needs to be handled by calling methods in your CommunicationNetwork instance. You are welcome to structure your class differently than the .h provided, or write additional helper functions or methods to support those provided. Your code needs to be readable, efficient, and accomplish the task provided.
void CommunicationNetwork::addCity(string previousCity, string newCity)
/*Insert a new city into the linked list after the previousCity. The name of the new city is in the argument newCity. */
void CommunicationNetwork::transmitMsg(char *filename)
/*Open the file and transmit the message between all cities in the network word by word. A word needs to be received at the end of the network before sending the next word. Only one city can hold the message at a time; as soon as it is passed to the next city, it needs to be deleted from the sender city. */
void CommunicationNetwork::printNetwork()
/*Start at the head of the linked list and print the name of each city in order to the end of the list. */
void CommunicationNetwork::buildNetwork()
/*Build the initial network from the cities given in this writeup. The cities can be fixed in the function, you do not need to write the function to work with any list of cities. */
void CommunicationNetwork::deleteCity(string cityNameDelete)
/*Find the city in the network where city name matches cityNameDelete. Change the next and previous pointers for the surrounding cities and free the memory. */
void CommunicationNetwork::clearNetwork()
/*Delete all cities in the network, starting at the head city. */
messageIn.txt
A liger it's pretty much my favorite animal. It's like a lion and a tiger mixed - bred for its skills in magic.
MODEFIY THE CODE BELOW ACCORDINGLY
main.cpp file #include
#include
#include
#include
#include "CommunicationNetwork.h"
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
// Create new network
CommunicationNetwork network;
int user_choice= 0;
string newCity, previousCity; bool cosmo =true;
while (cosmo)
{
//Print Menu
cout
cout
cout
cout
cout
cout
//Prompt the user to enter chice
cin >> user_choice;
// Takes whatever the user entered and executes the corresponding function
switch (user_choice)
{
case 1:
//build a network
network.buildNetwork();
break;
case 2:
//print the netowrk
network.printNetwork();
break;
case 3:
//transfer the messge
network.transmitMsg(argv[1]);
break;
case 4:
//Add a new city to the exiting network
cin.ignore();
cout
getline(cin,newCity);
cout
getline(cin, previousCity);
network.addCity(previousCity, newCity);
break;
case 5: case 6: case 7:
cosmo = false; cout
}
}
return 0; }
CommunicationNetwrok.cpp
/**CommunicationNetwork.cpp*/
#include "CommunicationNetwork.h"
#include
#include
using namespace std;
/*Insert a new city into the linked list after the previousCity.
The name of the new city is in the argument newCity. */
void CommunicationNetwork::addCity(string previousCity, string newCity)
{
City *new_city = new City;
new_city->name = newCity;
new_city->message = "";
if (previousCity == "First")
{
new_city->next = headCity;
headCity = new_city;
}
else
{
City *current_city = headCity;
while (current_city != NULL)
{
if (current_city->name == previousCity)
{
new_city->next = current_city->next;
current_city->next = new_city;
break;
}
current_city = current_city->next;
}
}
}
/*Open the file and transmit the message between all cities
in the network word by word. A word needs to be received at
the end of the network before sending the next word. Only one
city can hold the message at a time; as soon as it is passed to
the next city, it needs to be deleted from the sender city. */
void CommunicationNetwork::transmitMsg(char *filename)
{
ifstream file;
file.open(filename);
if (!file.is_open())
{
cout
}
// Pulls out a word from the message sends it through each city then gets the next word
string word;
while (file >> word)
{
City *current_city = headCity;
current_city->message = word;
City *senderCity = new City;
while (current_city != NULL)
{
cout name message
if (current_city->next != NULL)
{
current_city->next->message = current_city->message;
if (current_city!= headCity)
{
senderCity->message = "";
}
senderCity = current_city;
}
current_city = current_city->next;
}
}
}
/*Start at the head of the linked list and print the name of each city
in order to the end of the list. */
void CommunicationNetwork::printNetwork()
{
City *current_city = headCity;
cout
while (current_city!=nullptr)
{
cout name ";
current_city = current_city->next;
}
cout
cout
}
/*Build the initial network from the cities given in this writeup.
The cities can be fixed in the function, you do not need to write
the function to work with any list of cities. */
void CommunicationNetwork::buildNetwork()
{
string initial_cities[10] = {
"Los Angeles",
"Phoenix",
"Denver",
"Dallas",
"St. Louis",
"Chicago",
"Atlanta",
"Washington, D.C.",
"New York",
"Boston",
};
City *city;
City *prev = new City;
for (int i = 0; i
{
city = new City;
city->name = initial_cities[i];
city->message = "";
city->next = NULL;
if (i == 0)
{
headCity = city;
prev = headCity;
}
else
{
prev->next = city;
prev = city;
}
}
printNetwork();
}
CommunicationNetwork.h file
#ifndef COMMUNICATIONNETWORK_H #define COMMUNICATIONNETWORK_H #include
using namespace std; class CommunicationNetwork { private: struct City {
string name;
string message ;
City *next;
}; City *headCity;
public: void addCity(string, string); void transmitMsg(char *filename); void printNetwork(); void buildNetwork(); };
#endif
=====Main Menu=== 1. Build Network Print Network Path 3, Transmit Message Coast-To-Coast-To-Coast 4. Add City 5, Delete City Clear Network 7, Quit --hC ae P9 --kk s urrs nooe yo ewwl tw Mtt it eetyC e n n-lit N nie adtsCtr Minn eat ii adi lei urrdelu BPTADCQ 1234567 =====Main Menu=== 1. Build Network Print Network Path 3, Transmit Message Coast-To-Coast-To-Coast 4. Add City 5, Delete City Clear Network 7, Quit --hC ae P9 --kk s urrs nooe yo ewwl tw Mtt it eetyC e n n-lit N nie adtsCtr Minn eat ii adi lei urrdelu BPTADCQ 1234567
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


