I need help with problems B and C on their methods and final answers
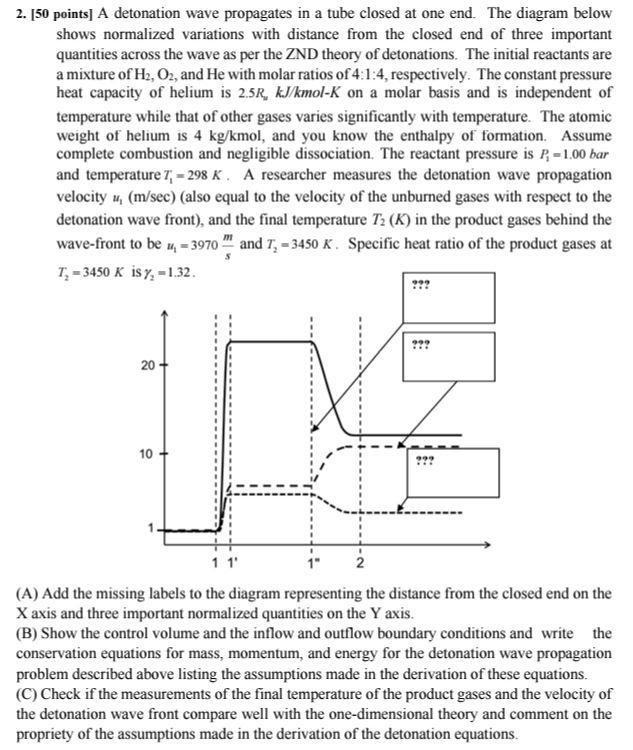
2. [50 points] A detonation wave propagates in a tube closed at one end. The diagram below shows normalized variations with distance from the closed end of three important quantities across the wave as per the ZND theory of detonations. The initial reactants are a mixture of H2,O2, and He with molar ratios of 4:1:4, respectively. The constant pressure heat capacity of helium is 2.5RwkJ/kmolK on a molar basis and is independent of temperature while that of other gases varies significantly with temperature. The atomic weight of helium is 4kg/kmol, and you know the enthalpy of formation. Assume complete combustion and negligible dissociation. The reactant pressure is P1=1.00bar and temperature T1=298K. A researcher measures the detonation wave propagation velocity u1(m/sec) (also equal to the velocity of the unburned gases with respect to the detonation wave front), and the final temperature T2(K) in the product gases behind the wave-front to be u1=3970sm and T2=3450K. Specific heat ratio of the product gases at T2=3450 (A) Add the missing labels to the diagram representing the distance from the closed end on the X axis and three important normalized quantities on the Y axis. (B) Show the control volume and the inflow and outflow boundary conditions and write the conservation equations for mass, momentum, and energy for the detonation wave propagation problem described above listing the assumptions made in the derivation of these equations. (C) Check if the measurements of the final temperature of the product gases and the velocity of the detonation wave front compare well with the one-dimensional theory and comment on the propriety of the assumptions made in the derivation of the detonation equations. 2. [50 points] A detonation wave propagates in a tube closed at one end. The diagram below shows normalized variations with distance from the closed end of three important quantities across the wave as per the ZND theory of detonations. The initial reactants are a mixture of H2,O2, and He with molar ratios of 4:1:4, respectively. The constant pressure heat capacity of helium is 2.5RwkJ/kmolK on a molar basis and is independent of temperature while that of other gases varies significantly with temperature. The atomic weight of helium is 4kg/kmol, and you know the enthalpy of formation. Assume complete combustion and negligible dissociation. The reactant pressure is P1=1.00bar and temperature T1=298K. A researcher measures the detonation wave propagation velocity u1(m/sec) (also equal to the velocity of the unburned gases with respect to the detonation wave front), and the final temperature T2(K) in the product gases behind the wave-front to be u1=3970sm and T2=3450K. Specific heat ratio of the product gases at T2=3450 (A) Add the missing labels to the diagram representing the distance from the closed end on the X axis and three important normalized quantities on the Y axis. (B) Show the control volume and the inflow and outflow boundary conditions and write the conservation equations for mass, momentum, and energy for the detonation wave propagation problem described above listing the assumptions made in the derivation of these equations. (C) Check if the measurements of the final temperature of the product gases and the velocity of the detonation wave front compare well with the one-dimensional theory and comment on the propriety of the assumptions made in the derivation of the detonation equations







