I need help with the year end income statement and balance sheet please.
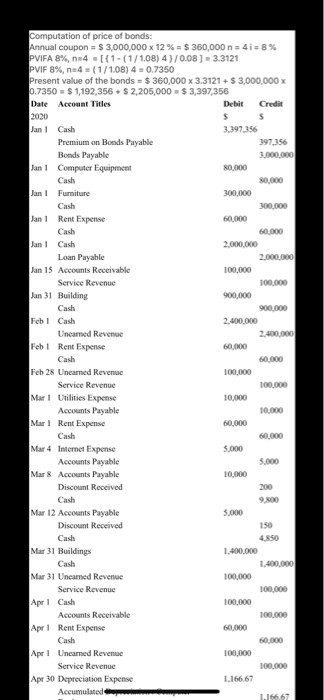
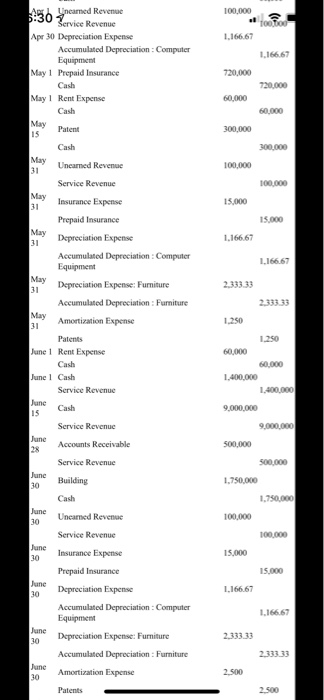
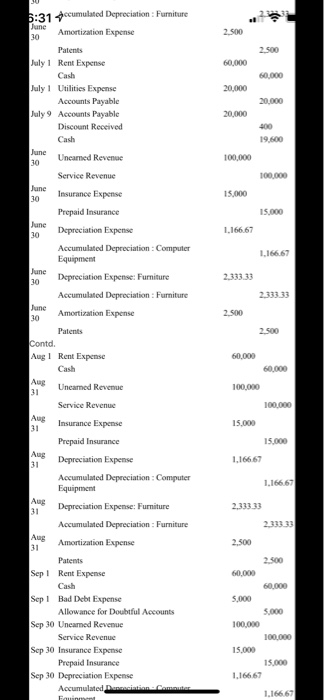
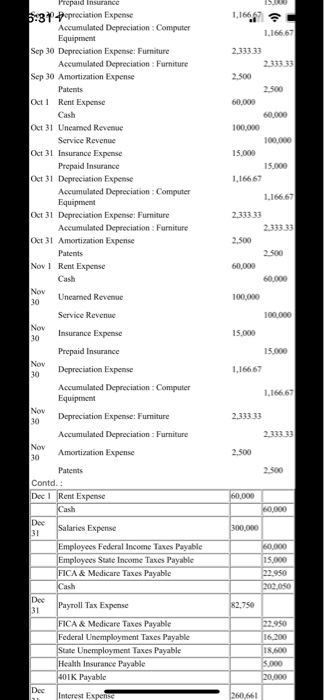
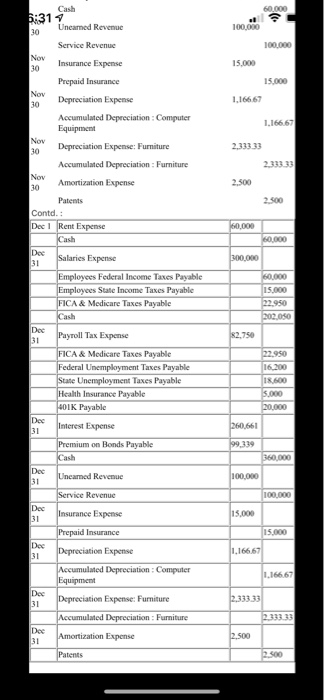
80,000 Computation of price of bonds: Annual coupon = $3,000,000 x 12% = $360,000 n = 4i=8% PVIFA 8%, n4[{1-(1/1.08) 4 } /0.08 ) = 3.3121 PVIF 8%, n=4 = (1/1.08) 4 = 0.7350 Present value of the bonds = $ 360,000 x 3.3121 + $ 3,000,000 x 0.7350 - $ 1,192,356 +$ 2,205,000 = $ 3,397,356 Date Account Titles Debit Credit 2020 $ s Jan 1 Cash 3.397356 Premium on Bonds Payable 397,356 Bonds Payable 3.000.000 Jan 1 Computer Equipment Cash 80,000 Jan Furniture 300,000 Cash 300.000 Jan 1 Rent Expense 60,000 Cash 60.000 Jan 1 Cash 2.000.000 Loan Payable 2.000.000 Jan 15 Accounts Receivable 100,000 Service Revenue 100,000 Jan 31 Building 900,000 Cash 900.000 Feb ! Cash 2.400,000 Uneamed Revenue Feb ! Rent Expense 60,000 Cash 60,000 Feb 28 Uncamned Revenue 100,000 Service Revenue 100,000 Mar1 Utilities Expense 10,000 Accounts Payable 10,000 Mar Rent Expense 60,000 Cash 60,000 Mar 4 Internet Expense Accounts Payable 5.000 Mar 8 Accounts Payable 10,000 Discount Received Cash 9,800 Mar 12 Accounts Payable 5.000 Discount Received 150 Cash 48SO Mar 31 Buildings 1.400.000 Cash 1,400,000 Mar 31 Uncamed Revenue 100,000 Service Revenue 100,000 Apr Cash 100,000 Accounts Receivable 100,000 Apr ! Rent Expense 60,000 Cash Apr ! Uncamed Revenue 100,000 Service Revenue 100,000 Apr 30 Depreciation Expense 1.166.67 Accumulated 1.166 67 5.000 100,000 too too 1.166.67 1.166.67 720,000 Apri Uncanned Revenue 5:30 Service Revenue Apr 30 Depreciation Expense Accumulated Depreciation : Computer Equipment May 1 Prepaid Insurance Cash May 1 Rent Expense Cash May 15 Cash 720.000 60,000 60.000 Patient 300,000 300.000 May 31 Uneamed Revenue 100,000 100,000 May 15,000 15.000 1.166.67 1.166.67 2.333.33 2 333 33 1.250 60,000 60,000 1.400.000 1.400,000 9,000,000 9,000,000 Service Revenue 31 Insurance Expense Prepaid Insurance May 31 Depreciation Expense Accumulated Depreciation: Computer Equipment May 31 Depreciation Expense: Furniture Accumulated Depreciation : Furniture May 31 Amortization Expense Patents June 1 Rent Expense Cash June 1 Cash Service Revenue June Cash 15 Service Revenue June Accounts Receivable 28 Service Revenue Junc 30 Building Cash Junc Uncamned Revenue 30 Service Revenue June 30 Insurance Expense Prepaid Insurance June Depreciation Expense 30 Accumulated Depreciation Computer Equipment June 30 Depreciation Expense: Furniture Accumulated Depreciation : Furniture June Amortization Expense 30 Patents 500,000 500,000 1.750,000 1,750,000 100,000 100,000 15.000 15.000 1.166.67 1.166.67 2,333.33 2,333.33 2.500 2.500 2.500 2.500 60,000 60.000 20,000 20,000 20,000 400 19,600 100,000 100.000 5:31 fccumulated Depreciation : Furniture June 30 Amortization Expense Patents July 1 Rent Expense Cash July 1 Utilities Expense Accounts Payable July 9 Accounts Payable Discount Received Cash June Uncamed Revenue 30 Service Revenue June 30 Insurance Expense Prepaid Insurance June 30 Depreciation Expense Accumulated Depreciation Computer Equipment June 30 Depreciation Expense: Furniture Accumulated Depreciation : Furniture June 30 Amortization Expense Patents Contd Aug! Rent Expense Cash 15,000 15,000 1.166.67 1.166.67 2.333.33 2,333.33 2.500 2.500 60,000 60.000 Aug 31 Unearned Revenue 100.000 Service Revenue 100,000 Aug 31 Insurance Expense 15,000 15.000 1.166 67 1.166 67 2.33333 2 333 33 2.500 Prepaid Insurance Aug 31 Depreciation Expense Accumulated Depreciation: Computer Equipment Aug 31 Depreciation Expense: Furniture Accumulated Depreciation : Furniture Aug Amortization Expense 31 Patents Sep! Rent Expense Cash Sep 1 Bad Debt Expense Allowance for Doubtful Accounts Sep 30 Uncarned Revenue Service Revenue Sep 30 Insurance Expense Prepaid Insurance Sep 30 Depreciation Expense Accumulated. Descem Fouinen 2.500 60,000 60.000 5.000 5.000 100,000 100,000 15.000 15.000 1.166 67 1.166.67 ISOD 1.1667 1.166.67 2.33333 2.333 33 2.500 2.500 60.000 60.000 100.000 100.000 15.000 15.000 1.166 67 1.166.67 2.33333 2.500 2.500 60,000 100,000 100,000 15,000 Prepaid Insurance 5:31 Pepreciation Expense Accumulated Depreciation: Computer Equipment Sep 30 Depreciation Expense: Furniture Accumulated Depreciation : Furniture Sep 30 Amortization Expense Patents Oct 1 Rent Expense Cash Oct 31 Unearned Revenue Service Revenue Oct 31 Insurance Expense Prepaid Insurance Oct 31 Depreciation Expense Accumulated Depreciation: Computer Equipment Oct 31 Depreciation Expense: Furniture Accumulated Depreciation : Furniture Oct 31 Amortization Expense Patents Nov 1 Rent Expense Cash Nov Unearned Revenue 30 Service Revenue Nov 30 Insurance Expense Prepaid Insurance Nov Depreciation Expense 30 Accumulated Depreciation Computer Equipment 30 Depreciation Expense: Furniture Accumulated Depreciation : Furniture Amortization Expense 30 Patents Contd. Dec 1 Rent Expense Cash Dee Salaries Expense 31 Employees Federal Income Taxes Payable Employees State Income Taxes Payable FICA & Medicare Taxes Payable Cash Dee Payroll Tax Expense 31 FICA & Medicare Taxes Payable Federal Unemployment Taxes Payable State Unemployment Taxes Payable Health Insurance Payable 401K Payable Dec Interest Expense 15.000 1.16667 2.33333 2.500 2.500 60,000 60,000 300,000 60.000 15.000 12.950 202.050 $2,750 22.950 16.200 18.600 5.000 20.000 260.661 60.000 100,000 100.000 15.000 15.000 1.16667 1.166 67 NON 2.33333 2.500 2.500 60,000 60.000 300.000 60.000 15.000 12.950 202.050 Cash 5:317 Unearned Revenue 30 Service Revenue Nov 30 Insurance Expense Prepaid Insurance Nov Depreciation Expense 30 Accumulated Depreciation: Computer Equipment 30 Depreciation Expense: Furniture Accumulated Depreciation : Furniture Nov 30 Amortization Expense Patents Contd.: Dec 1 Rent Expense Cash Dec Salaries Expense 31 Employees Federal Income Taxes Payable Employees State Income Taxes Payable FICA & Medicare Taxes Payable Cash Dec Payroll Tax Expense 31 FICA & Medicare Taxes Payable Federal Unemployment Taxes Payable State Unemployment Taxes Payable Health Insurance Payable 401K Payable Dec 31 Interest Expense Premium on Bonds Payable Cash Dec Uncarned Revenue 31 Service Revenue Dec Insurance Expense 31 Prepaid Insurance Dee 31 Depreciation Expense Accumulated Depreciation Computer Equipment Dee Depreciation Expense: Furniture 31 Accumulated Depreciation : Furniture Dee Amortization Expense 31 82.750 16.200 18 600 5.000 20.000 260,661 99,339 360,000 100,000 100,000 15.000 15.000 1.166,67 1.166.67 2.333.33 2.500 Patents rences Mailings Review View Help Professor Cote Project You have recently been hired to run the accounting department at a recently started law firm. The company officially opened its doors on January 1, 2020. Exhibit one below is the balance sheet for the company as of December 31, 2019. The company has not made any journal entries or done any record keeping for the accounting department. This balance sheet came from a tax accountant which prepared the companies first two years tax returns. The company wants you to use Excel and the year end is December 31. General Information: The company is a C-Corporation. The address will be made up by each person. The corporation is not a publicly traded law firm. It is made up of Megan, Alison, Dan, and Stacey (MADS). They own all the stock and our incorporated in Massachusetts. They have authorized 2,000,000 shares of common stock at a par value of $1 dollar. They have issued 400,000 shares which are already shown on your balance sheet below. Each owner has 100,000 shares and were issued at $30 dollars per share (already shown below). Unless noted differently, adjusting entries are made for every account that can be adjusted on a monthly basis Balance sheet as of December 31, 2019. Assets Cash $11,500,000 Land $500,000 Equity Common Stock $400,000 Paid In Capital CS $11,600,000 Please note that the law firm has done nothing except issue stock a buy some land the last two operation years. Now they are going to start running the business because they hired an accountant. Transactions January 1, 2020: The Law Firm is pretty solid in the cash area but wants to make sure that they have a good stash of cash to market the business effectively. They decide to issue bonds in increments of $10,000 dollars and they will issue 300 of them. The stated interest rate will be 12% and the interest will be paid annually. The bonds will have a 4 year life and the current market interest rate is 8%. D Focus a hp ACC311 (1) - Compatibility Mode - Word O Search References Mailings Review View Help 2 January 1, 2020: The Law Firm is pretty solid in the cash area but wants to make sure that they have good stash of cash to market the business effectively. They decide to issue bonds in increments of $10,000 dollars and they will issue 300 of them. The stated interest rate will be 12% and the interest will be paid annually. The bonds will have a 4 year life and the current market interest rate is 8%. Please assume all bonds were sold as one (make one journal entry), on January 1, 2020. First paymer of interest will be on December 31, 2020. Assume the company uses the effect interest rate method. January 1, 2020: The bonds sold quickly so on the same day the company bought a state of the art computers along with a network system. The purchased all this with cash. The total cost of the computer system was $80,000 dollars. The useful life of the computer system is 5 years and the salvag value is $10,000 dollars. As noted before, the owners what you to make month adjusting entries for deprecation January 1, 2020: Still on the high created by selling the bonds quickly, the owners buy some amazing furniture to fit the office out. Because it's a law firm the furniture can only be the best. The company bought the furniture with cash in the amount of $300,000 dollars. The salvage value will be $20,000 dollars and the useful life will be 10 years. January 1, 2020: The Law Firm needs a place to set up all this nice computer equipment and office furniture. So they enter into a 2 year lease for some prime A commercial real estate. The company will a 00 (hp) HCC311 (1) - Compatibility Mode - Word Search ferences Mailings Review View Help LUOR GIULIE UNIE WHENE LU YE. January 1, 2020: The Law Firm needs a place to set up all this nice computer equipment and office furniture. So they enter into a 2 year lease for some prime A commercial real estate. The company will have to pay rent (including this month) on the first of each month in the amount of $60,000 dollars. January 1, 2020: What a busy day. The law firm decided to break ground on their second location. They are going to build this building on the land listed on the balance sheet. You will need to make journal entries for each stage of the building project and possibly make a journal entry at the end of the year for capitalization of interest. The company decided to take out a loan to build the building in the amount of $2,000,000 dollars. The interest rate on the building loan is 8%. The only other debt the company has is the bonds they issued earlier in the day. The law firm will use some cash to build the building as well. Assume the building loan was issued today. The payments to the builders when as followed: January 31, $900,000 dollars, March 31, $1,400,000, and June 30, $1,750,000. Make journal entries to record payments to the builders. Also make a journal entry to record the loan. No deprecation will be taken on the building this year. Assume interest was paid at year end. This is a self-constructed asset. January 15, 2020: The Law after two years finally has its first sale. The sale was on account and it was for representation of Rex Ryan. The law suit was over something to do with talking too much. The total sale was for $100,000 dollars. February 1, 2020: The Law firm entered into a contract situation with the NHL. Our firm will provide legal services for 2 years for a set amount of $2,400,000 dollars. This amount was paid upfront and should be reported as unearned revenue. We will work equally over the next 24 months to earn this contract. We should make an adjusting entry each month accordingly, March 1, 2020: The Law firm received a bill from the National Grid for $10,000. The terms are 2/10, net 30. March 4, 2020: The Law firm received a bill from Charter Cable for internet service in the amount of $5,000 dollars. The terms were 3/10, net 30. March 8, 2020: The Law Firm paid the National Grid bill March 12, 2020: The Law firm paid Charter Cable. o 2 roo hp 0311(1) - Compatibility Mode - Word Search erences Mailings Review View Help 4 March 12, 2020: The Law firm paid Charter Cable. April 1, 2020: The Law firm received a check from Rex Ryan for payment in full. May 1, 2020: The Law firm bought a 4 year prepaid insurance policy. This is an umbrella policy which will cover the firm in regards to any possible situations. The firm paid cash in the amount of $720,000. Please make an adjusting entry to record the use of the insurance at the end of each month going forward. May 15, 2020: The Law firm bought a patent in the amount of $300,000 dollars. This patent has a limited life of 10 years. Please amortize the patent at the end of each month. Please use the direct method. June 1, 20120: The Law Firm was hired to represent Ray Lewis. It is alleged that he killed someone. The amount of the sale is $1,400,000 dollars which Ray paid in cash. June 15, 2020: The Law Firm was hired to sue a pharmsutical company. It was proven that a drug they produced makes people say accounting over and over again without stopping for days. The Law firm won this case and takes a 30% fee from the case verdict. The verdict was $30,000,000. June 28, 2020: The Law Firm has a sale in the amount of $500,000 dollars to a local gas station that may have polluted a river. This sale was on account Focus a (hp) rences Mailings Review View Help July 14, 2020: The law firm received a bill from National Grid for $20,000 dollars. The terms were 2/10 and net 30. July 9 2020: The law firm paid National Grid September 1, 2020: The Law Firm decides that it might be a good idea to set up an allowance account. The law firm decided to use the A/R approach. Based on historical and industry analysis the law firm sets the rate at 1% of accounts receivable. Make the adjusting entry as of September 1st. December 1, 2020: The Law Firm finally decides to pay salaries. This will be a monthly journal entry made at the end of each month. Total salaries paid each month will be $300,000 dollars. Assume no caps will be met by the end of the year. Federal Income tax will be at 20%, State Income Tax at 5%, FICA and Medicare at normal rates. Health Insurance will be paid by the Law Firm in the amount of $5,000 a month. 401K will only be paid by the Law Firm in the amount of $20,000 month. Unemployment taxes are at the maximum rates for state and federal governments. Remember that there must be an employee and employer entry each month. Instructions: Each month make sure you make all the necessary journal entries along with all the necessary adjusting entries. You must hand in the following: 1) You must submit through blackboard the following: A journal entry and adjusting entry sheet labeled so I know what the entry goes too.....this must be in excel 2) Year end income statement and balance sheet. Please do this in one excel file so you can upload it to blackboard. You can use the different worksheets to get all the material into the file...but honestly you can do whatever works for you in excel. Have fun! Focus O BI a hop 80,000 Computation of price of bonds: Annual coupon = $3,000,000 x 12% = $360,000 n = 4i=8% PVIFA 8%, n4[{1-(1/1.08) 4 } /0.08 ) = 3.3121 PVIF 8%, n=4 = (1/1.08) 4 = 0.7350 Present value of the bonds = $ 360,000 x 3.3121 + $ 3,000,000 x 0.7350 - $ 1,192,356 +$ 2,205,000 = $ 3,397,356 Date Account Titles Debit Credit 2020 $ s Jan 1 Cash 3.397356 Premium on Bonds Payable 397,356 Bonds Payable 3.000.000 Jan 1 Computer Equipment Cash 80,000 Jan Furniture 300,000 Cash 300.000 Jan 1 Rent Expense 60,000 Cash 60.000 Jan 1 Cash 2.000.000 Loan Payable 2.000.000 Jan 15 Accounts Receivable 100,000 Service Revenue 100,000 Jan 31 Building 900,000 Cash 900.000 Feb ! Cash 2.400,000 Uneamed Revenue Feb ! Rent Expense 60,000 Cash 60,000 Feb 28 Uncamned Revenue 100,000 Service Revenue 100,000 Mar1 Utilities Expense 10,000 Accounts Payable 10,000 Mar Rent Expense 60,000 Cash 60,000 Mar 4 Internet Expense Accounts Payable 5.000 Mar 8 Accounts Payable 10,000 Discount Received Cash 9,800 Mar 12 Accounts Payable 5.000 Discount Received 150 Cash 48SO Mar 31 Buildings 1.400.000 Cash 1,400,000 Mar 31 Uncamed Revenue 100,000 Service Revenue 100,000 Apr Cash 100,000 Accounts Receivable 100,000 Apr ! Rent Expense 60,000 Cash Apr ! Uncamed Revenue 100,000 Service Revenue 100,000 Apr 30 Depreciation Expense 1.166.67 Accumulated 1.166 67 5.000 100,000 too too 1.166.67 1.166.67 720,000 Apri Uncanned Revenue 5:30 Service Revenue Apr 30 Depreciation Expense Accumulated Depreciation : Computer Equipment May 1 Prepaid Insurance Cash May 1 Rent Expense Cash May 15 Cash 720.000 60,000 60.000 Patient 300,000 300.000 May 31 Uneamed Revenue 100,000 100,000 May 15,000 15.000 1.166.67 1.166.67 2.333.33 2 333 33 1.250 60,000 60,000 1.400.000 1.400,000 9,000,000 9,000,000 Service Revenue 31 Insurance Expense Prepaid Insurance May 31 Depreciation Expense Accumulated Depreciation: Computer Equipment May 31 Depreciation Expense: Furniture Accumulated Depreciation : Furniture May 31 Amortization Expense Patents June 1 Rent Expense Cash June 1 Cash Service Revenue June Cash 15 Service Revenue June Accounts Receivable 28 Service Revenue Junc 30 Building Cash Junc Uncamned Revenue 30 Service Revenue June 30 Insurance Expense Prepaid Insurance June Depreciation Expense 30 Accumulated Depreciation Computer Equipment June 30 Depreciation Expense: Furniture Accumulated Depreciation : Furniture June Amortization Expense 30 Patents 500,000 500,000 1.750,000 1,750,000 100,000 100,000 15.000 15.000 1.166.67 1.166.67 2,333.33 2,333.33 2.500 2.500 2.500 2.500 60,000 60.000 20,000 20,000 20,000 400 19,600 100,000 100.000 5:31 fccumulated Depreciation : Furniture June 30 Amortization Expense Patents July 1 Rent Expense Cash July 1 Utilities Expense Accounts Payable July 9 Accounts Payable Discount Received Cash June Uncamed Revenue 30 Service Revenue June 30 Insurance Expense Prepaid Insurance June 30 Depreciation Expense Accumulated Depreciation Computer Equipment June 30 Depreciation Expense: Furniture Accumulated Depreciation : Furniture June 30 Amortization Expense Patents Contd Aug! Rent Expense Cash 15,000 15,000 1.166.67 1.166.67 2.333.33 2,333.33 2.500 2.500 60,000 60.000 Aug 31 Unearned Revenue 100.000 Service Revenue 100,000 Aug 31 Insurance Expense 15,000 15.000 1.166 67 1.166 67 2.33333 2 333 33 2.500 Prepaid Insurance Aug 31 Depreciation Expense Accumulated Depreciation: Computer Equipment Aug 31 Depreciation Expense: Furniture Accumulated Depreciation : Furniture Aug Amortization Expense 31 Patents Sep! Rent Expense Cash Sep 1 Bad Debt Expense Allowance for Doubtful Accounts Sep 30 Uncarned Revenue Service Revenue Sep 30 Insurance Expense Prepaid Insurance Sep 30 Depreciation Expense Accumulated. Descem Fouinen 2.500 60,000 60.000 5.000 5.000 100,000 100,000 15.000 15.000 1.166 67 1.166.67 ISOD 1.1667 1.166.67 2.33333 2.333 33 2.500 2.500 60.000 60.000 100.000 100.000 15.000 15.000 1.166 67 1.166.67 2.33333 2.500 2.500 60,000 100,000 100,000 15,000 Prepaid Insurance 5:31 Pepreciation Expense Accumulated Depreciation: Computer Equipment Sep 30 Depreciation Expense: Furniture Accumulated Depreciation : Furniture Sep 30 Amortization Expense Patents Oct 1 Rent Expense Cash Oct 31 Unearned Revenue Service Revenue Oct 31 Insurance Expense Prepaid Insurance Oct 31 Depreciation Expense Accumulated Depreciation: Computer Equipment Oct 31 Depreciation Expense: Furniture Accumulated Depreciation : Furniture Oct 31 Amortization Expense Patents Nov 1 Rent Expense Cash Nov Unearned Revenue 30 Service Revenue Nov 30 Insurance Expense Prepaid Insurance Nov Depreciation Expense 30 Accumulated Depreciation Computer Equipment 30 Depreciation Expense: Furniture Accumulated Depreciation : Furniture Amortization Expense 30 Patents Contd. Dec 1 Rent Expense Cash Dee Salaries Expense 31 Employees Federal Income Taxes Payable Employees State Income Taxes Payable FICA & Medicare Taxes Payable Cash Dee Payroll Tax Expense 31 FICA & Medicare Taxes Payable Federal Unemployment Taxes Payable State Unemployment Taxes Payable Health Insurance Payable 401K Payable Dec Interest Expense 15.000 1.16667 2.33333 2.500 2.500 60,000 60,000 300,000 60.000 15.000 12.950 202.050 $2,750 22.950 16.200 18.600 5.000 20.000 260.661 60.000 100,000 100.000 15.000 15.000 1.16667 1.166 67 NON 2.33333 2.500 2.500 60,000 60.000 300.000 60.000 15.000 12.950 202.050 Cash 5:317 Unearned Revenue 30 Service Revenue Nov 30 Insurance Expense Prepaid Insurance Nov Depreciation Expense 30 Accumulated Depreciation: Computer Equipment 30 Depreciation Expense: Furniture Accumulated Depreciation : Furniture Nov 30 Amortization Expense Patents Contd.: Dec 1 Rent Expense Cash Dec Salaries Expense 31 Employees Federal Income Taxes Payable Employees State Income Taxes Payable FICA & Medicare Taxes Payable Cash Dec Payroll Tax Expense 31 FICA & Medicare Taxes Payable Federal Unemployment Taxes Payable State Unemployment Taxes Payable Health Insurance Payable 401K Payable Dec 31 Interest Expense Premium on Bonds Payable Cash Dec Uncarned Revenue 31 Service Revenue Dec Insurance Expense 31 Prepaid Insurance Dee 31 Depreciation Expense Accumulated Depreciation Computer Equipment Dee Depreciation Expense: Furniture 31 Accumulated Depreciation : Furniture Dee Amortization Expense 31 82.750 16.200 18 600 5.000 20.000 260,661 99,339 360,000 100,000 100,000 15.000 15.000 1.166,67 1.166.67 2.333.33 2.500 Patents rences Mailings Review View Help Professor Cote Project You have recently been hired to run the accounting department at a recently started law firm. The company officially opened its doors on January 1, 2020. Exhibit one below is the balance sheet for the company as of December 31, 2019. The company has not made any journal entries or done any record keeping for the accounting department. This balance sheet came from a tax accountant which prepared the companies first two years tax returns. The company wants you to use Excel and the year end is December 31. General Information: The company is a C-Corporation. The address will be made up by each person. The corporation is not a publicly traded law firm. It is made up of Megan, Alison, Dan, and Stacey (MADS). They own all the stock and our incorporated in Massachusetts. They have authorized 2,000,000 shares of common stock at a par value of $1 dollar. They have issued 400,000 shares which are already shown on your balance sheet below. Each owner has 100,000 shares and were issued at $30 dollars per share (already shown below). Unless noted differently, adjusting entries are made for every account that can be adjusted on a monthly basis Balance sheet as of December 31, 2019. Assets Cash $11,500,000 Land $500,000 Equity Common Stock $400,000 Paid In Capital CS $11,600,000 Please note that the law firm has done nothing except issue stock a buy some land the last two operation years. Now they are going to start running the business because they hired an accountant. Transactions January 1, 2020: The Law Firm is pretty solid in the cash area but wants to make sure that they have a good stash of cash to market the business effectively. They decide to issue bonds in increments of $10,000 dollars and they will issue 300 of them. The stated interest rate will be 12% and the interest will be paid annually. The bonds will have a 4 year life and the current market interest rate is 8%. D Focus a hp ACC311 (1) - Compatibility Mode - Word O Search References Mailings Review View Help 2 January 1, 2020: The Law Firm is pretty solid in the cash area but wants to make sure that they have good stash of cash to market the business effectively. They decide to issue bonds in increments of $10,000 dollars and they will issue 300 of them. The stated interest rate will be 12% and the interest will be paid annually. The bonds will have a 4 year life and the current market interest rate is 8%. Please assume all bonds were sold as one (make one journal entry), on January 1, 2020. First paymer of interest will be on December 31, 2020. Assume the company uses the effect interest rate method. January 1, 2020: The bonds sold quickly so on the same day the company bought a state of the art computers along with a network system. The purchased all this with cash. The total cost of the computer system was $80,000 dollars. The useful life of the computer system is 5 years and the salvag value is $10,000 dollars. As noted before, the owners what you to make month adjusting entries for deprecation January 1, 2020: Still on the high created by selling the bonds quickly, the owners buy some amazing furniture to fit the office out. Because it's a law firm the furniture can only be the best. The company bought the furniture with cash in the amount of $300,000 dollars. The salvage value will be $20,000 dollars and the useful life will be 10 years. January 1, 2020: The Law Firm needs a place to set up all this nice computer equipment and office furniture. So they enter into a 2 year lease for some prime A commercial real estate. The company will a 00 (hp) HCC311 (1) - Compatibility Mode - Word Search ferences Mailings Review View Help LUOR GIULIE UNIE WHENE LU YE. January 1, 2020: The Law Firm needs a place to set up all this nice computer equipment and office furniture. So they enter into a 2 year lease for some prime A commercial real estate. The company will have to pay rent (including this month) on the first of each month in the amount of $60,000 dollars. January 1, 2020: What a busy day. The law firm decided to break ground on their second location. They are going to build this building on the land listed on the balance sheet. You will need to make journal entries for each stage of the building project and possibly make a journal entry at the end of the year for capitalization of interest. The company decided to take out a loan to build the building in the amount of $2,000,000 dollars. The interest rate on the building loan is 8%. The only other debt the company has is the bonds they issued earlier in the day. The law firm will use some cash to build the building as well. Assume the building loan was issued today. The payments to the builders when as followed: January 31, $900,000 dollars, March 31, $1,400,000, and June 30, $1,750,000. Make journal entries to record payments to the builders. Also make a journal entry to record the loan. No deprecation will be taken on the building this year. Assume interest was paid at year end. This is a self-constructed asset. January 15, 2020: The Law after two years finally has its first sale. The sale was on account and it was for representation of Rex Ryan. The law suit was over something to do with talking too much. The total sale was for $100,000 dollars. February 1, 2020: The Law firm entered into a contract situation with the NHL. Our firm will provide legal services for 2 years for a set amount of $2,400,000 dollars. This amount was paid upfront and should be reported as unearned revenue. We will work equally over the next 24 months to earn this contract. We should make an adjusting entry each month accordingly, March 1, 2020: The Law firm received a bill from the National Grid for $10,000. The terms are 2/10, net 30. March 4, 2020: The Law firm received a bill from Charter Cable for internet service in the amount of $5,000 dollars. The terms were 3/10, net 30. March 8, 2020: The Law Firm paid the National Grid bill March 12, 2020: The Law firm paid Charter Cable. o 2 roo hp 0311(1) - Compatibility Mode - Word Search erences Mailings Review View Help 4 March 12, 2020: The Law firm paid Charter Cable. April 1, 2020: The Law firm received a check from Rex Ryan for payment in full. May 1, 2020: The Law firm bought a 4 year prepaid insurance policy. This is an umbrella policy which will cover the firm in regards to any possible situations. The firm paid cash in the amount of $720,000. Please make an adjusting entry to record the use of the insurance at the end of each month going forward. May 15, 2020: The Law firm bought a patent in the amount of $300,000 dollars. This patent has a limited life of 10 years. Please amortize the patent at the end of each month. Please use the direct method. June 1, 20120: The Law Firm was hired to represent Ray Lewis. It is alleged that he killed someone. The amount of the sale is $1,400,000 dollars which Ray paid in cash. June 15, 2020: The Law Firm was hired to sue a pharmsutical company. It was proven that a drug they produced makes people say accounting over and over again without stopping for days. The Law firm won this case and takes a 30% fee from the case verdict. The verdict was $30,000,000. June 28, 2020: The Law Firm has a sale in the amount of $500,000 dollars to a local gas station that may have polluted a river. This sale was on account Focus a (hp) rences Mailings Review View Help July 14, 2020: The law firm received a bill from National Grid for $20,000 dollars. The terms were 2/10 and net 30. July 9 2020: The law firm paid National Grid September 1, 2020: The Law Firm decides that it might be a good idea to set up an allowance account. The law firm decided to use the A/R approach. Based on historical and industry analysis the law firm sets the rate at 1% of accounts receivable. Make the adjusting entry as of September 1st. December 1, 2020: The Law Firm finally decides to pay salaries. This will be a monthly journal entry made at the end of each month. Total salaries paid each month will be $300,000 dollars. Assume no caps will be met by the end of the year. Federal Income tax will be at 20%, State Income Tax at 5%, FICA and Medicare at normal rates. Health Insurance will be paid by the Law Firm in the amount of $5,000 a month. 401K will only be paid by the Law Firm in the amount of $20,000 month. Unemployment taxes are at the maximum rates for state and federal governments. Remember that there must be an employee and employer entry each month. Instructions: Each month make sure you make all the necessary journal entries along with all the necessary adjusting entries. You must hand in the following: 1) You must submit through blackboard the following: A journal entry and adjusting entry sheet labeled so I know what the entry goes too.....this must be in excel 2) Year end income statement and balance sheet. Please do this in one excel file so you can upload it to blackboard. You can use the different worksheets to get all the material into the file...but honestly you can do whatever works for you in excel. Have fun! Focus O BI a hop