Question
i need only solution of QS 3 part which is Explain any difference between the cost per equivalent unit in the assembly department under
 i need only solution of QS 3 part which is " Explain any difference between the cost per equivalent unit in the assembly department under the WEIGHTED AVERAGE METHOD and the FIFO method.". i posted the question before but they didn't provide WEIGHTED AVERAGE METHOD and doesn't explain the "difference between the cost per equivalent unit in the assembly department under the weighted average method and the FIFO method". kindly answer this as soon as possible., i'll give u thumbs up. if u need solution of qs 1 then mention in comment. URGENT HELP REQUIRED. i'll surely give u thumbs up
i need only solution of QS 3 part which is " Explain any difference between the cost per equivalent unit in the assembly department under the WEIGHTED AVERAGE METHOD and the FIFO method.". i posted the question before but they didn't provide WEIGHTED AVERAGE METHOD and doesn't explain the "difference between the cost per equivalent unit in the assembly department under the weighted average method and the FIFO method". kindly answer this as soon as possible., i'll give u thumbs up. if u need solution of qs 1 then mention in comment. URGENT HELP REQUIRED. i'll surely give u thumbs up 
this is the solution provided by chegg of qs 1. i attach pics of Qs 1 solution. kindly take help from this and solve qs 3 with " WEIGHTED AVERAGE METHOD and DIFFERENCE between the cost per equivalent unit in the assembly department under the weighted average method and the FIFO method."
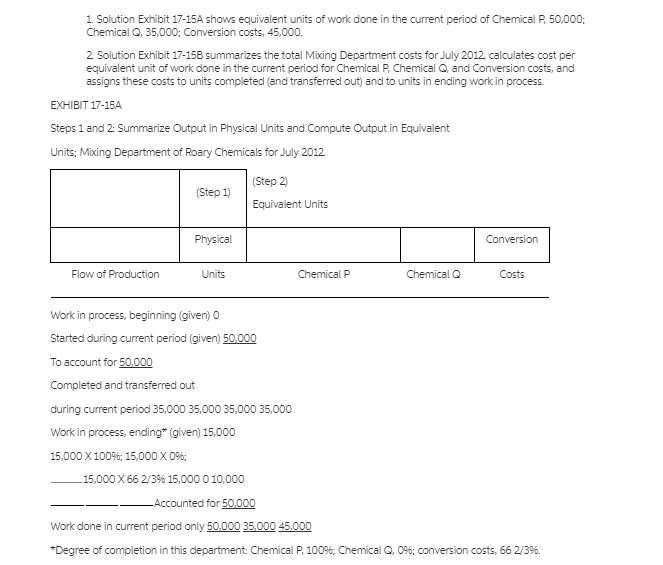
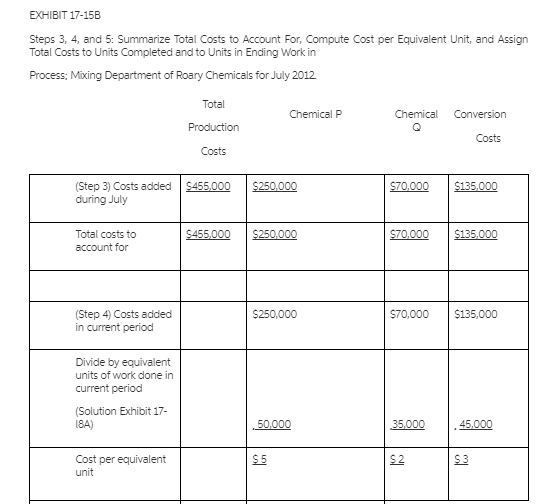
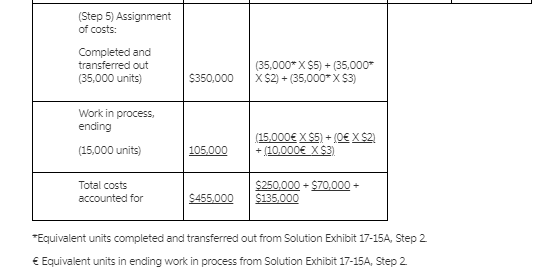
1. Solution Exhibit 17-15A shows equivalent units of work done in the current period of Chemical P. 50,000: Chemical Q, 35,000: Conversion costs, 45,000. 2 Solution Exhibit 17-158 summarizes the total Mixing Department costs for July 2012 calculates cost per equivalent unit of work done in the current period for Chemical P, Chemical and Conversion costs, and assigns these costs to units completed (and transferred out) and to units in ending work in process. EXHIBIT 17-154 Steps 1 and 2. Summarize Output in Physical Units and Compute Output in Equivalent Units: Mixing Department of Roary Chemicals for July 2012 (Step 1) (Step 2) Equivalent Units Physical Conversion Flow of Production Units Chemical P Chemical Costs Work in process, beginning (given) Started during current period (given) 50,000 To account for 50,000 Completed and transferred out during current period 35,000 35,000 35,000 35,000 Work in process, ending* (given) 15,000 15,000 X 100%: 15,000 X 0% 15,000 X 66 2/39 15,000 0 10,000 Accounted for 50,000 Work done in current period only 50,000 35,000 45,000 *Degree of completion in this department Chemical P. 100%: Chemical Q,0%; conversion costs, 66 2/3%. EXHIBIT 17-15B Steps 3, 4, and 5: Summarize Total Costs to Account For, Compute Cost per Equivalent Unit, and Assign Total Costs to Units Completed and to Units in Ending Work in Process: Mixing Department of Roary Chemicals for July 2012 Total Chemical P Chemical Conversion Production Costs Costs $250,000 $70,000 $135,000 (Step 3) Costs added $455,000 during July Total costs to account for $455,000 $250,000 $70,000 $135,000 $250,000 $70,000 $135,000 (Step 4) Costs added in current period Divide by equivalent units of work done in current period (Solution Exhibit 17- 18A) 50,000 35,000 45,000 $ 5 $2 $ 3 Cost per equivalent unit (Step 5) Assignment of costs: Completed and transferred out (35,000 units) $350,000 (35,000*X $5) + (35,000* X $2) + (35,000*X $3) Work in process ending (15,000 units) 105,000 (15,000 X $5) + (0 X $2 + (10,000 X $3) Total costs accounted for $250,000 - $70,000 + $135,000 $455,000 *Equivalent units completed and transferred out from Solution Exhibit 17-15A, Step 2 Equivalent units in ending work in process from Solution Exhibit 17-15A, Step 2 Q.3 FIFO method (continuation of question 1). Do question 1, using the FIFO method of process costing. Explain any difference between the cost per equivalent unit in the assembly department under the weighted average method and the FIFO method. Q.1 Zero beginning inventory, materials introduced in middle of process. Roary Chemicals has a mixing department and a refining department. Its process-costing system in the mixing department has two direct materials cost categories (chemical and chemical Q) and one conversion costs pool. The following data pertain to the mixing department for July 2012: 0 50,000 35,000 Units Work in process, July 1 Units started Completed and transferred to refining department Costs Chemical P Chemical Conversion costs $250,000 70,000 135,000 Chemical P is introduced at the start of operations in the mixing department, and chemical Q is added when the product is three-fourths completed in the mixing department. Conversion costs are added evenly during the process. The ending work in process in the mixing department is two-thirds complete. Required: a. Compute the equivalent units in the mixing department for July 2012 for each cost category. b. Compute (i) the cost of goods completed and transferred to the refining department during July and (ii) the cost of work in process as of July 31, 2012Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


![For Heintz/parrys College Accounting, Chapters 1-15, 22nd Edition, [instant Access]](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/book_images/2022/04/6257c8d15b633_2096257c8d10b1d2.jpg)