Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
i need questions 10-15 please! I've provided the previous work and answers for 1-9 to refer to if needed. The Foundational 15 LO6-1, L06-2, L06-3,
i need questions 10-15 please! I've provided the previous work and answers for 1-9 to refer to if needed. 
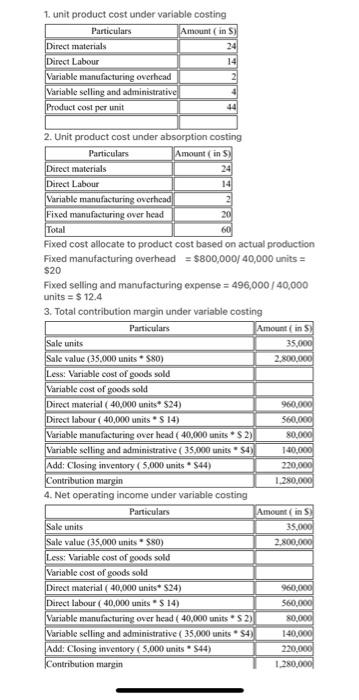
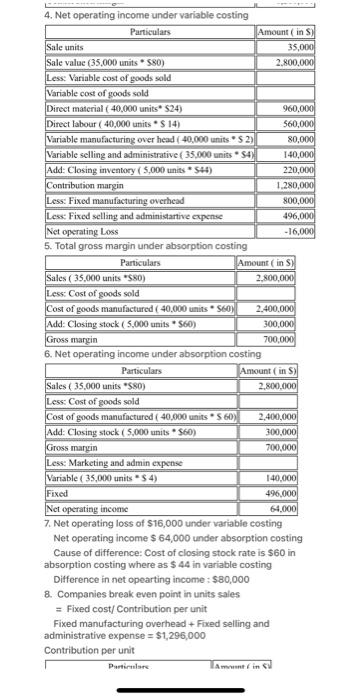
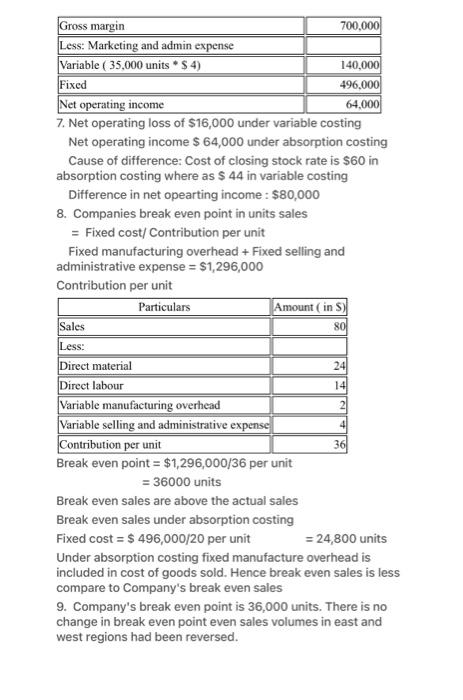
The Foundational 15 LO6-1, L06-2, L06-3, LO6-4, LO6-5 Diego Company manufactures one product that is sold for $80 per unit in two geographic regions--the East and West regions. The following information pertains to the company's first year of operations in which it produced 40,000 units and sold 35,000 units. Variable costs per unit: Manufacturing: Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Variable selling and administrative Fixed costs per year: $24 $14 $2 $4 Fixed manufacturing overhead $800,000 Fixed selling and administrative expense $496,000 The company sold 25,000 units in the East region and 10,000 units in the West region. It determined that $250,000 of its fixed selling and administrative expense is traceable to the West region, $150,000 is traceable to the East region, and the remaining $96,000 is a common fixed expense. The company will continue to incur the total amount of its fixed manufacturing overhead costs as long as it continues to produce any amount of its only product. Required: Answer each question independently based on the original data unless instructed otherwise. You do not need to prepare a segmented income statement until question 13. 1. What is the unit product cost under variable costing? 2. What is the unit product cost under absorption costing? 3. What is the company's total contribution margin under variable costing? 4. What is the company's net operating income under variable costing? 5. What is the company's total gross margin under absorption costing? 6. What is the company's net operating income under absorption costing? 7. What is the amount of the difference between the variable costing and absorption costing net operating incomes? What is the cause of this difference? 8. What is the company's break-even point in unit sales? Is it above or below the actual unit sales? Compare the break-even point in unit sales to your answer for question 6 and comment. 9. If the sales volumes in the East and West regions had been reversed, what would be the company's overall break-even point in unit sales? Format Tools Table Window Help Design 18 Layout obe X X A- A- Chapter 6 The Foundational 15 Handout References Mailings Review View 10. What would have been the company's variable costing net operating income if it had produced and sold 35,000 units? You do not need to perform any calculations to answer this question. 11. What would have been the company's absorption costing net operating income if it had produced and sold 35,000 units? You do not need to perform any calculations to answer this question. 12. If the company produces 5,000 fewer units than it sells in its second year of operations, will absorption costing net operating income be higher or lower than variable costing net operating income in Year 2? Why? No calculations are necessary. 13. Prepare a contribution format segmented income statement that includes a Total column and columns for the East and West regions. 14. Diego is considering eliminating the West region because an internally generated report suggests the region's total gross margin in the first year of operations was $50,000 less than its traceable fixed selling and administrative expenses. Diego believes that if it drops the West region, the East region's sales will grow by 5% in Year 2. Using the contribution approach for analyzing segment profitability and assuming all else remains constant in Year 2, what would be the profit impact of dropping the West region in Year 27 15. Assume the West region invests $30,000 in a new advertising campaign in Year 2 that increases its unit sales by 20%. If all else remains constant, what would be the profit impact of pursuing the advertising campaign? English (United States) Accessibility: Investigate 30 AubCcDdie Normal tv S Focus TE 97 A Q- Search in Docume AabCcOdle No Spacing Aa AaBbCcDe Heading 1 J 1. unit product cost under variable costing Particulars Amount (in S) 24 Direct materials Direct Labour Variable manufacturing overhead Variable selling and administrative Product cost per unit 14 2 44 2. Unit product cost under absorption costing Particulars Amount (in S) 24 14 Direct materials Direct Labour Variable manufacturing overhead 20 Fixed manufacturing over head Total 60 Fixed cost allocate to product cost based on actual production Fixed manufacturing overhead = $800,000/ 40,000 units = $20 Sale units Sale value (35,000 units $80) Less: Variable cost of goods sold Variable cost of goods sold Direct material (40,000 units $24) Fixed selling and manufacturing expense = 496,000/40,000 units = $12.4 3. Total contribution margin under variable costing Particulars Direct labour (40,000 units * $ 14) Variable manufacturing over head ( 40,000 units $2) Variable selling and administrative ( 35,000 units $4)) Add: Closing inventory (5,000 units $44) Contribution margin 4. Net operating income under variable costing Particulars Sale units Sale value (35,000 units $80) Less: Variable cost of goods sold Variable cost of goods sold Direct material (40,000 units* $24) Direct labour (40,000 units $14) Variable manufacturing over head (40,000 units S2) Variable selling and administrative (35,000 units $4) Add: Closing inventory (5,000 units. $44) Contribution margin Amount ( in S) 35,000 2,800,000 960,000 560,000 80,000 140,000 220,000 1,280,000 Amount (in S) 35,000 2,800,000 960,000 560,000 80,000 140,000 220,000 1,280,000 4. Net operating income under variable costing Particulars Sale units Sale value (35,000 units 580) Less: Variable cost of goods sold Variable cost of goods sold Direct material (40,000 units* $24) Direct labour (40,000 units * $ 14) Variable manufacturing over head (40,000 units* $ 2) Variable selling and administrative (35,000 units 54) Add: Closing inventory (5,000 units 544) Contribution margin Less: Fixed manufacturing overhead Less: Fixed selling and administartive expense Net operating Loss 5. Total gross margin under absorption costing Particulars Amount ( in S) 35,000 2,800,000 Sales (35,000 units *$80) Less: Cost of goods sold Cost of goods manufactured (40,000 units $60) Add: Closing stock (5,000 units * $60) Gross margin 6. Net operating income under absorption costing Particulars Particulare 960,000 560,000 80,000 140,000 220,000 Amount (in S) 2,800,000 1,280,000 800,000 496,000 -16,000 2,400,000 300,000 700,000 Amount (in S) 2,800,000 Sales (35,000 units *$80) Less: Cost of goods sold Cost of goods manufactured (40,000 units S60) Add: Closing stock (5,000 units $60) Gross margin Less: Marketing and admin expense Variable (35,000 units *$ 4) Fixed Net operating income 7. Net operating loss of $16,000 under variable costing Net operating income $ 64,000 under absorption costing Cause of difference: Cost of closing stock rate is $60 in absorption costing where as $44 in variable costing Difference in net opearting income: $80,000 8. Companies break even point in units sales = Fixed cost/ Contribution per unit Fixed manufacturing overhead + Fixed selling and administrative expense = $1,296,000 Contribution per unit Amontin 2,400,000 300,000 700,000 140,000 496,000 64,000 Gross margin Less: Marketing and admin expense Variable (35,000 units * $ 4) Fixed Sales Less: Net operating income 7. Net operating loss of $16,000 under variable costing Net operating income $ 64,000 under absorption costing Cause of difference: Cost of closing stock rate is $60 in absorption costing where as $ 44 in variable costing Difference in net opearting income: $80,000 8. Companies break even point in units sales = Fixed cost/ Contribution per unit Fixed manufacturing overhead + Fixed selling and administrative expense = $1,296,000 Contribution per unit Direct material Direct labour Particulars 700,000 140,000 496,000 64,000 Variable manufacturing overhead Variable selling and administrative expense Contribution per unit Break even point = $1,296,000/36 per unit = 36000 units Amount (in S) 80 24 14 4 36 Break even sales are above the actual sales Break even sales under absorption costing Fixed cost = $ 496,000/20 per unit = 24,800 units Under absorption costing fixed manufacture overhead is included in cost of goods sold. Hence break even sales is less compare to Company's break even sales 9. Company's break even point is 36,000 units. There is no change in break even point even sales volumes in east and west regions had been reversed 




Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


