Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
I need the solution urgently please I have an exam right now please solve it fast.i'll gave you vote up Canada Semiconductor Inc (CSCI) makes


I need the solution urgently please
I have an exam right now please solve it fast.i'll gave you vote up
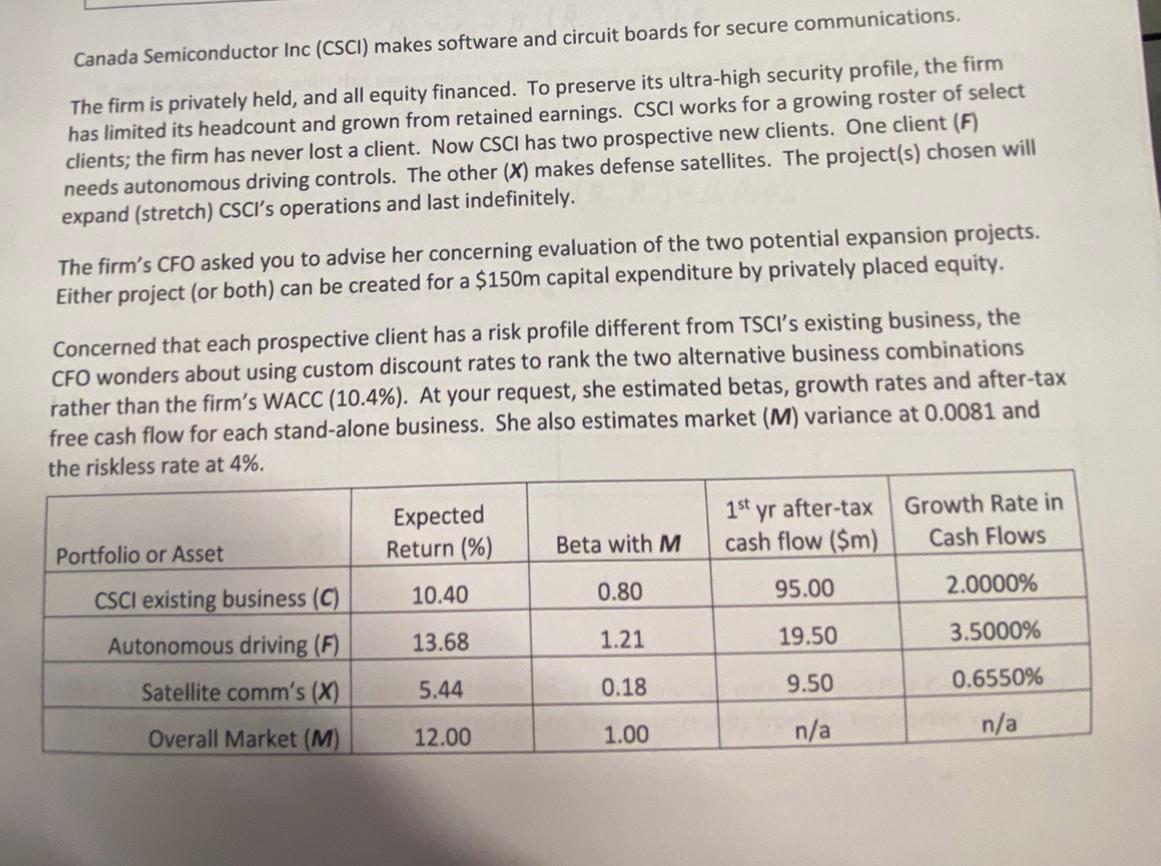
Canada Semiconductor Inc (CSCI) makes software and circuit boards for secure communications. The firm is privately held, and all equity financed. To preserve its ultra-high security profile, the firm has limited its headcount and grown from retained earnings. CSCI works for a growing roster of select clients; the firm has never lost a client. Now CSCI has two prospective new clients. One client (F) needs autonomous driving controls. The other (X) makes defense satellites. The project(s) chosen will expand (stretch) CSCI's operations and last indefinitely. The firm's CFO asked you to advise her concerning evaluation of the two potential expansion projects. Either project (or both) can be created for a $150m capital expenditure by privately placed equity. Concerned that each prospective client has a risk profile different from TSCI's existing business, the CFO wonders about using custom discount rates to rank the two alternative business combinations rather than the firm's WACC (10.4\%). At your request, she estimated betas, growth rates and after-tax free cash flow for each stand-alone business. She also estimates market (M) variance at 0.0081 and the riskless rate at 4%. a) ( 21 mark) If CSCI compares expected returns (IRRs) of the two alternative projects to its WACC which of the projects will it accept or reject? b) (31 mark) Use the CFO's data to estimate the stand-alone market value of each of the three ongoing businesses (C,F, and X). c) (60.5 mark) If the Security Market Line truly describes returns on any risky investment A, so that stock returns obey this time-series regression, with uncorrelated errors (t) across time or across assets, normally distributed with zero expected values. R~At=rft+At(R~Mtrft)+t It can be shown that, with this assumption, variances and covariances for C,F and X may be written as follows (HINT: use the definitions of variance and covariance): var(RC)=T2M2var(RF)=F2M2var(RX)=X2M2cov(RC,RX)=CXM2cov(RC,RF)=CFM2 Use the results above and the CFO's data. Calculate return variances and covariances for each possible pair of the new projects and the existing business. Here is a table for your results: d) (40.5 mark) For each new project alternative, in combination with C(C and F or C and X ), find the (portfolio) beta and (portfolio) required return. Use your results from (b) for market value weights. (31 mark) Use your discount rates from (d) to compute the market value of the two combinations, ( C and F or C and X ). If it must pick only one of the two new projects without increasing its number of employees with high security clearance, which project is the better match for CSCI,F or X ? Why? ( 21 mark) Last, using the means and standard deviations of the two combinations ( C and F or C and X ), estimate the probability (assume normality) that the enlarged company has a negative return in any given year. These two results may also be useful input in choosing whether to invest in F or X because it suggests which will bring with it higher risk of financial distressStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


