I NEED THIS ASAP.
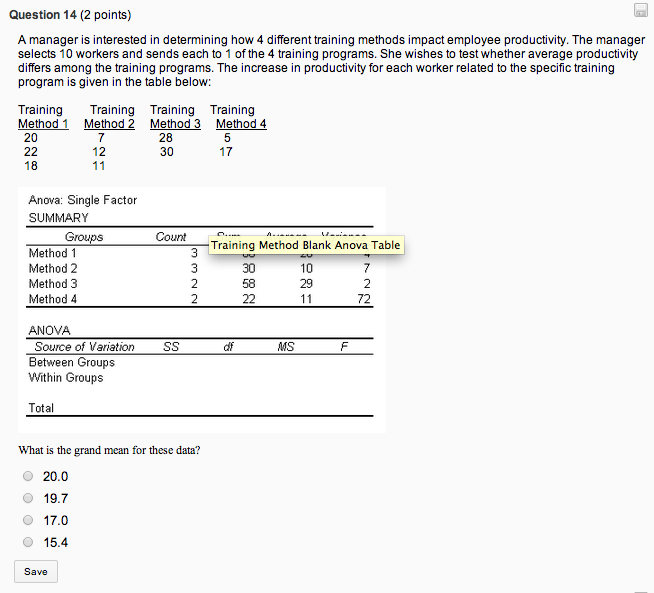
Question 1 (1 point) ANOVA models are set up such that the dependent (response) variable is quantitative and the explanatory variable is categorical. O True False Save Question 2 (1 point) Three assumptions are needed to meet the conditions for using one-way (single factor) ANOVA. They are normality of parent populations, independent random samples, and equal variances of parent population in each category level (homoscedasticity). True O False Save Question 3 (1 point) ANOVA can be used to test whether there are differences among three or more population means by using t-tests. True O False Save Question 4 (1 point) H When testing to see if o'1 > o-2, one would calculate the F-ratio as s'| divided by $ 2. O True FalseQuestion 14 (2 points) A manager is interested in determining how 4 different training methods impact employee productivity. The manager selects 10 workers and sends each to 1 of the 4 training programs. She wishes to test whether average productivity differs among the training programs. The increase in productivity for each worker related to the specific training program is given in the table below: Training Training Training Training Method 1 Method 2 Method 3 Method 4 20 28 5 22 12 30 17 18 11 Anova: Single Factor SUMMARY Groups Count Training Method Blank Anova Table Method 1 W W Method 2 10 Method 3 58 29 Method 4 NJ 22 11 72 ANOVA Source of Variation SS MS F Between Groups Within Groups Total What is the grand mean for these data? O 20.0 O 19.7 O 17.0 O 15.4 SaveQuestion 13 (1 point) A control factor may be added to an ANOVA model to help to isolate the variation in the dependent variable caused by experimental factors already included in the model. O True O False BABSQuestion 9 (1 point) The "Total Sum of Squares" in an ANOVA model is another name for the total variation in the dependent (response) variable. O True O False Save Question 10 (1 point) An experimental factor is something under examination in an experiment as a possible cause of variation in the response (dependent) variable. True O False Save Question 11 (1 point) As the F-ratio gets smaller, Ho is more easily rejected. True O False Save Question 12 (1 point) The Explained Sum of Squares is the variation in the dependent variable after the variation from all included explanatory factors is removed. True False SaveQuestion 5 (1 point) Analysis of variance assumes that each sample under study is drawn from a normally distributed population. True O False Save Question 6 (1 point) To find out if the averages on a management test were different for 4 class sections, the professor randomly sampled 7 seniors, 5 juniors, 6 sophomores, and 4 freshmen. The degrees of freedom for the F-statistic in the analysis of variance procedure would be 18 for the numerator and 3 for the denominator. True O False Save H Question 7 (1 point) The F-statistic, as used in the analysis of variance procedure, has as its numerator a value that is always a good estimator of the overall population variance. True O False Save Question 8 (1 point) Analysis of variance allows us to drop the assumption of equal variances in each category level if the sample sizes are large enough. True O False