i need to know how to complete the questions and fill in the blanks for the pictures provided
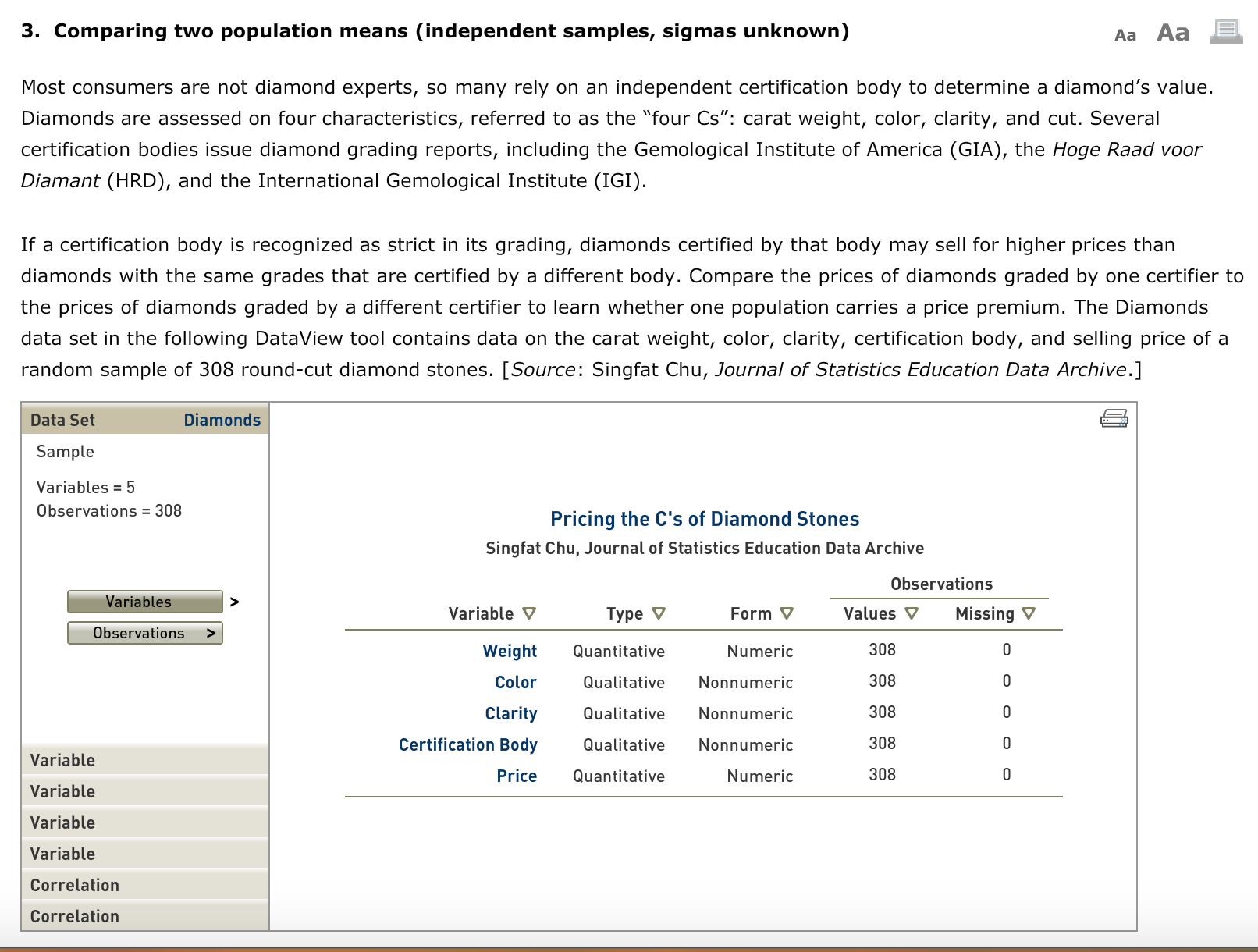
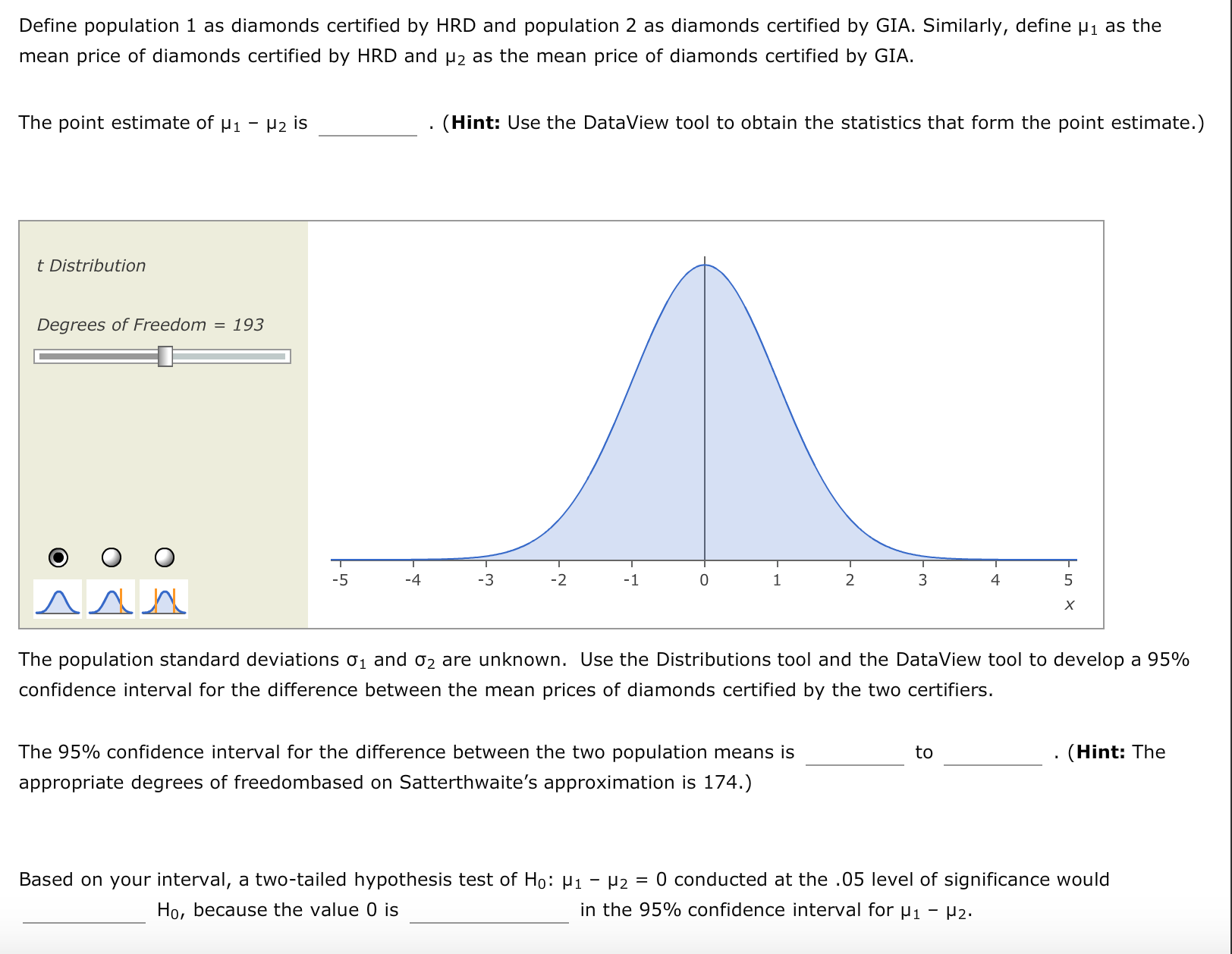
3. Comparing two population means (independent samples, sigmas unknown) Aa Aa E Most consumers are not diamond experts, so many rely on an independent certification body to determine a diamond's value. Diamonds are assessed on four characteristics, referred to as the \"four Cs": carat weight, color, clarity, and cut. Several certification bodies issue diamond grading reports, including the Gemological Institute of America (GIA), the Hoge Raad voor Diamant (HRD), and the International Gemological Institute (IGI). If a certification body is recognized as strict in its grading, diamonds certified by that body may sell for higher prices than diamonds with the same grades that are certified by a different body. Compare the prices of diamonds graded by one certifier to the prices of diamonds graded by a different certifier to learn whether one population carries a price premium. The Diamonds data set in the following DataView tool contains data on the carat weight, color, clarity, certification body, and selling price of a random sample of 308 roundcut diamond stones. [Source: Singfat Chu, Journal of Statistics Education Data Archive] Sample Variables = 5 Observatims = 308 Pricing the C's of Diamond Stones Singfat Chu. Journal of Statistics Education Data Archive Observations i > Variable V Type V Form V Values V Missing V Weight Quantitative Numeric 308 0 Color OuaLitative Nonnumeric 308 D Clarity QuaLitative Nonnumeric 308 0 Certification Body QuaLitative Nonnumeric 308 0 Variable _ Price Quantitative Numeric 308 0 Varlable Variable Variable Correlation Correlation Define population 1 as diamonds certified by HRD and population 2 as diamonds certified by GIA. Similarly, define m as the mean price of diamonds certified by HRD and [12 as the mean price of diamonds certified by GIA. The point estimate of [11 p; is . (Hint: Use the DataView tool to obtain the statistics that form the point estimate.) t Distribution Degrees of Freedom = 193 ll 0 O O 5 -4 -3 -2 -1 O 1 2 3 4 AAA x The population standard deviations 01 and 0'2 are unknown. Use the Distributions tool and the DataView tool to develop a 95% confidence interval for the difference between the mean prices of diamonds certified by the two certifiers. The 95% confidence interval for the difference between the two population means is to . (Hint: The appropriate degrees of freedombased on Satterthwaite's approximation is 174.) Based on your interval, a two-tailed hypothesis test of H0: p1 p2 = D conducted at the .05 level of significance would Ho, because the value 0 is in the 95% confidence interval for U1 p2. Maybe consumers don't perceive HRD to be stricter in its grading than GIA . It might be the case that prices of diamonds certified by the two certifiers are different because HRD certifies more large diamonds ( which sell for higher prices than small diamonds ) than GIA . Now redefine MI as the mean weight of diamonds certified by HRD and H2 as the mean weight of diamonds certified by GIA . Using a significance level of a = . 05 , conduct a hypothesis test to determine whether diamonds certified by HRD have a higher mean weight than diamonds certified by GIA . The appropriate degrees of freedom based on Satterthwaite's approximationis 201 . You conduct test with the null and alternate hypotheses formulated as :" O HO : HI - H2 = O ; HI: HI - H2 O O HO : HI - H 2 = O ; HI : HI - H 2 * O The value of the test statistic is The P- value is . Therefore , You conclude that diamonds certified by HRD have a higher mean weight than diamonds certified by GIA