Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
I only need help with the post lab questions please. Data And Report Submission - Determination Of An Equilibrium Constant (2pts) Determination of an Equilibrium
I only need help with the post lab questions please. 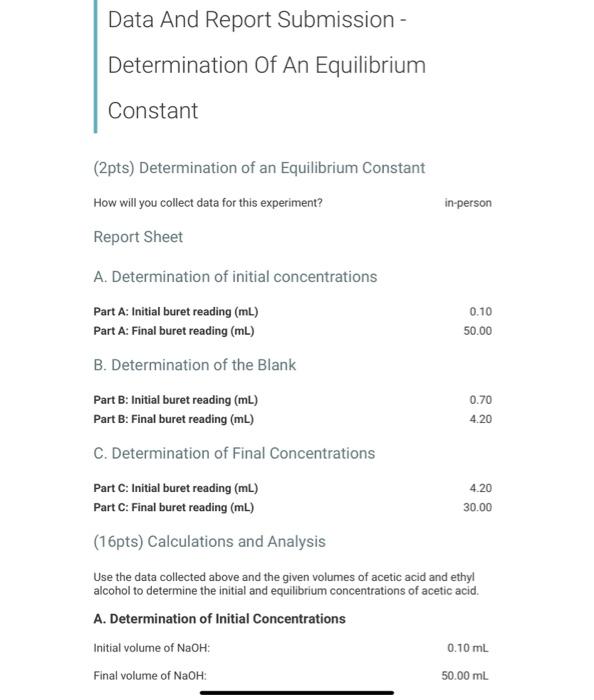

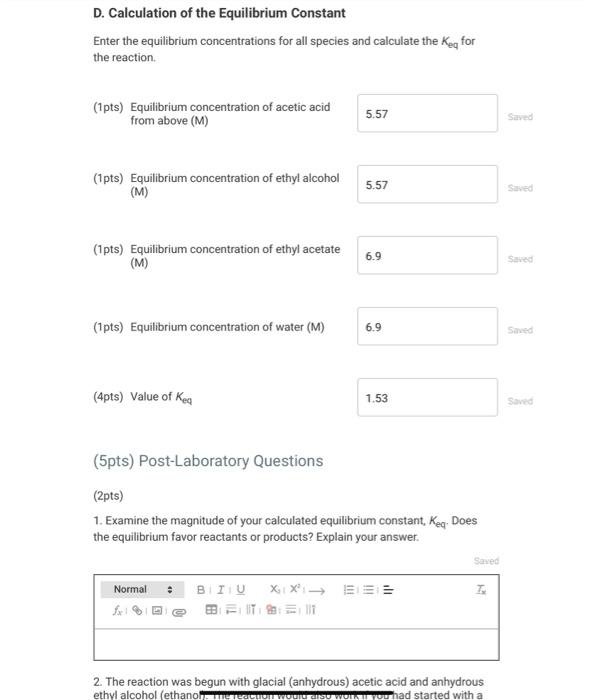


Data And Report Submission - Determination Of An Equilibrium Constant (2pts) Determination of an Equilibrium Constant How will you collect data for this experiment? Report Sheet in-person A. Determination of initial concentrations Part A: Initial buret reading (mL) Part A: Final buret reading (mL) B. Determination of the Blank 0.10 50.00 0.70 4.20 Part B: Initial buret reading (mL) Part B: Final buret reading (mL) C. Determination of Final Concentrations Part C. Initial buret reading (mL) 4.20 Part C: Final buret reading (mL) 30.00 (16pts) Calculations and Analysis Use the data collected above and the given volumes of acetic acid and ethyl alcohol to determine the initial and equilibrium concentrations of acetic acid. A. Determination of Initial Concentrations Initial volume of NaOH: Final volume of NaOH: 0.10 ml 50.00 ml (1pts) Volume of 0.25 M NaOH added (mL) 49.9 Saved (2pts) Initial concentration of acetic acid (M) 12.48 Saved B. Determination of the Blank Initial volume of NaOH: Final volume of NaOH: 0.70 ml 4.20 ml (1 pts) Volume of 0.25 M NaOH added (mL) 3.50 Saved C. Determination of Final Concentrations Initial volume of NaOH Final volume of NaOH 4.20 mL 30.00 mL (1pts) Volume of 0.25 M NaOH added (mL) 25.8 Saved (1pts) Volume of 0.25 M NaOH required to neutralize acetic acid (corrected volume, 22.3 Saved mL) (2pts) Final concentration of acetic acid (M) 5.58 Saved D. Calculation of the Equilibrium Constant Enter the equilibrium concentrations for all species and calculate the Keq for the reaction. D. Calculation of the Equilibrium Constant Enter the equilibrium concentrations for all species and calculate the Kig for the reaction (1pts) Equilibrium concentration of acetic acid from above (M) 5.57 Saved (1pts) Equilibrium concentration of ethyl alcohol (M) 5.57 Saved (1pts) Equilibrium concentration of ethyl acetate (M) 6.9 Saved (1pts) Equilibrium concentration of water (M) 6.9 Saved (4pts) Value of Ken 1.53 saved (5pts) Post-Laboratory Questions (2pts) 1. Examine the magnitude of your calculated equilibrium constant. Keg. Does the equilibrium favor reactants or products? Explain your answer. Saved Normal BIU XIX ill 2. The reaction was begun with glacial (anhydrous) acetic acid and anhydrous ethyl alcohol (ethanol TACTION WOU SO WON You had started with a (5pts) Post-Laboratory Questions (2pts) 1. Examine the magnitude of your calculated equilibrium constant, Keq. Does the equilibrium favor reactants or products? Explain your answer. Saved Normal BIUXX Tx 2. The reaction was begun with glacial (anhydrous) acetic acid and anhydrous ethyl alcohol (ethanol). The reaction would also work if you had started with a lower grade of acetic acid (80% m/m acetic acid in water) and 95% m/m ethanol, which are commonly available in chemistry stockrooms. What changes would you need to make in your calculation for Keq if the reaction had been carried out with a lower grade of acetic acid and 95% ethanol, and therefore has some amount of water in the initial set-up of the reaction? (1 pts) A. Water must be eliminated from the equation for Keq because the reaction is now happening in a dilute aqueous solution B. The equilibrium concentration of water increases; you must add the initial concentration of water to the concentration of water produced by the reaction. C. No change is needed because the small amount of water in these reagents will have no effect on the Choose... reaction. D. The term (H20), must be moved to the denominator because water is available at the start of the reaction and is now a reactant E. The equilibrium concentration of water decreases; you must subtract the initial concentration of water from the concentration of water produced by the reaction. E 3. Students wanted to test ways of improving the amount of ethyl acetate produced. One student added 20 ml of water to the cauilibrium mixture at A D Saved B 3. Students wanted to test ways of improving the amount of ethyl acetate produced. One student added 30 mL of De water to the equilibrium mixture at the end of the activity. How will the addition of water effect the concentration of ethyl acetate? (1pts) A. The reaction is at equilibrium so there will be no effect on the concentration of ethyl acetate. B. According to the Le Chtelier principle, the addition of water shifts the reaction to the left and decreases the concentration of ethyl acetate. C. According to the Le Chtelier principle, the addition of water shifts the reaction to the right and decreases the concentration of ethyl A acetate. D. According to the Le Chatelier Choose... principle, the addition of water shifts the reaction to the left and increases VA the concentration of ethyl acetate, E. According to the Le Chtelier principle, the addition of water shifts the reaction to the right and increases the concentration of ethyl acetate. D 4. Another student added a drying agent (anhydrous absorbs water removing it mixture) to the equilibrium E activity. How will the addition of a drying agent effect the concentrator ethyl acetate? (1pts) A. The reaction is at equilibrium so there will be no effect on the concentration of ethyl acetate. B. According to the Le Chtelier principle, the addition of a drying agent shifts the reaction to the left and decreases the concentration of ethyl acetate C. According to the Le Chtelier principle, the addition of a drying agent shifts the reaction to the right and decreases the concentration of ethyl acetate. D. According to the Le Chtelier principle, the addition of a drying agent shit there B Saved to the Data And Report Submission - Determination Of An Equilibrium Constant (2pts) Determination of an Equilibrium Constant How will you collect data for this experiment? Report Sheet in-person A. Determination of initial concentrations Part A: Initial buret reading (mL) Part A: Final buret reading (mL) B. Determination of the Blank 0.10 50.00 0.70 4.20 Part B: Initial buret reading (mL) Part B: Final buret reading (mL) C. Determination of Final Concentrations Part C. Initial buret reading (mL) 4.20 Part C: Final buret reading (mL) 30.00 (16pts) Calculations and Analysis Use the data collected above and the given volumes of acetic acid and ethyl alcohol to determine the initial and equilibrium concentrations of acetic acid. A. Determination of Initial Concentrations Initial volume of NaOH: Final volume of NaOH: 0.10 ml 50.00 ml (1pts) Volume of 0.25 M NaOH added (mL) 49.9 Saved (2pts) Initial concentration of acetic acid (M) 12.48 Saved B. Determination of the Blank Initial volume of NaOH: Final volume of NaOH: 0.70 ml 4.20 ml (1 pts) Volume of 0.25 M NaOH added (mL) 3.50 Saved C. Determination of Final Concentrations Initial volume of NaOH Final volume of NaOH 4.20 mL 30.00 mL (1pts) Volume of 0.25 M NaOH added (mL) 25.8 Saved (1pts) Volume of 0.25 M NaOH required to neutralize acetic acid (corrected volume, 22.3 Saved mL) (2pts) Final concentration of acetic acid (M) 5.58 Saved D. Calculation of the Equilibrium Constant Enter the equilibrium concentrations for all species and calculate the Keq for the reaction. D. Calculation of the Equilibrium Constant Enter the equilibrium concentrations for all species and calculate the Kig for the reaction (1pts) Equilibrium concentration of acetic acid from above (M) 5.57 Saved (1pts) Equilibrium concentration of ethyl alcohol (M) 5.57 Saved (1pts) Equilibrium concentration of ethyl acetate (M) 6.9 Saved (1pts) Equilibrium concentration of water (M) 6.9 Saved (4pts) Value of Ken 1.53 saved (5pts) Post-Laboratory Questions (2pts) 1. Examine the magnitude of your calculated equilibrium constant. Keg. Does the equilibrium favor reactants or products? Explain your answer. Saved Normal BIU XIX ill 2. The reaction was begun with glacial (anhydrous) acetic acid and anhydrous ethyl alcohol (ethanol TACTION WOU SO WON You had started with a (5pts) Post-Laboratory Questions (2pts) 1. Examine the magnitude of your calculated equilibrium constant, Keq. Does the equilibrium favor reactants or products? Explain your answer. Saved Normal BIUXX Tx 2. The reaction was begun with glacial (anhydrous) acetic acid and anhydrous ethyl alcohol (ethanol). The reaction would also work if you had started with a lower grade of acetic acid (80% m/m acetic acid in water) and 95% m/m ethanol, which are commonly available in chemistry stockrooms. What changes would you need to make in your calculation for Keq if the reaction had been carried out with a lower grade of acetic acid and 95% ethanol, and therefore has some amount of water in the initial set-up of the reaction? (1 pts) A. Water must be eliminated from the equation for Keq because the reaction is now happening in a dilute aqueous solution B. The equilibrium concentration of water increases; you must add the initial concentration of water to the concentration of water produced by the reaction. C. No change is needed because the small amount of water in these reagents will have no effect on the Choose... reaction. D. The term (H20), must be moved to the denominator because water is available at the start of the reaction and is now a reactant E. The equilibrium concentration of water decreases; you must subtract the initial concentration of water from the concentration of water produced by the reaction. E 3. Students wanted to test ways of improving the amount of ethyl acetate produced. One student added 20 ml of water to the cauilibrium mixture at A D Saved B 3. Students wanted to test ways of improving the amount of ethyl acetate produced. One student added 30 mL of De water to the equilibrium mixture at the end of the activity. How will the addition of water effect the concentration of ethyl acetate? (1pts) A. The reaction is at equilibrium so there will be no effect on the concentration of ethyl acetate. B. According to the Le Chtelier principle, the addition of water shifts the reaction to the left and decreases the concentration of ethyl acetate. C. According to the Le Chtelier principle, the addition of water shifts the reaction to the right and decreases the concentration of ethyl A acetate. D. According to the Le Chatelier Choose... principle, the addition of water shifts the reaction to the left and increases VA the concentration of ethyl acetate, E. According to the Le Chtelier principle, the addition of water shifts the reaction to the right and increases the concentration of ethyl acetate. D 4. Another student added a drying agent (anhydrous absorbs water removing it mixture) to the equilibrium E activity. How will the addition of a drying agent effect the concentrator ethyl acetate? (1pts) A. The reaction is at equilibrium so there will be no effect on the concentration of ethyl acetate. B. According to the Le Chtelier principle, the addition of a drying agent shifts the reaction to the left and decreases the concentration of ethyl acetate C. According to the Le Chtelier principle, the addition of a drying agent shifts the reaction to the right and decreases the concentration of ethyl acetate. D. According to the Le Chtelier principle, the addition of a drying agent shit there B Saved to the 




Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


