Question: I really need help for this assignment. Please give me the answer in good handwriting! Thank you so much PLEASE GIVE ME THE ANSWER THAT
I really need help for this assignment. Please give me the answer in good handwriting! Thank you so much
PLEASE GIVE ME THE ANSWER THAT I CAN LOAD IT IN HASKELL

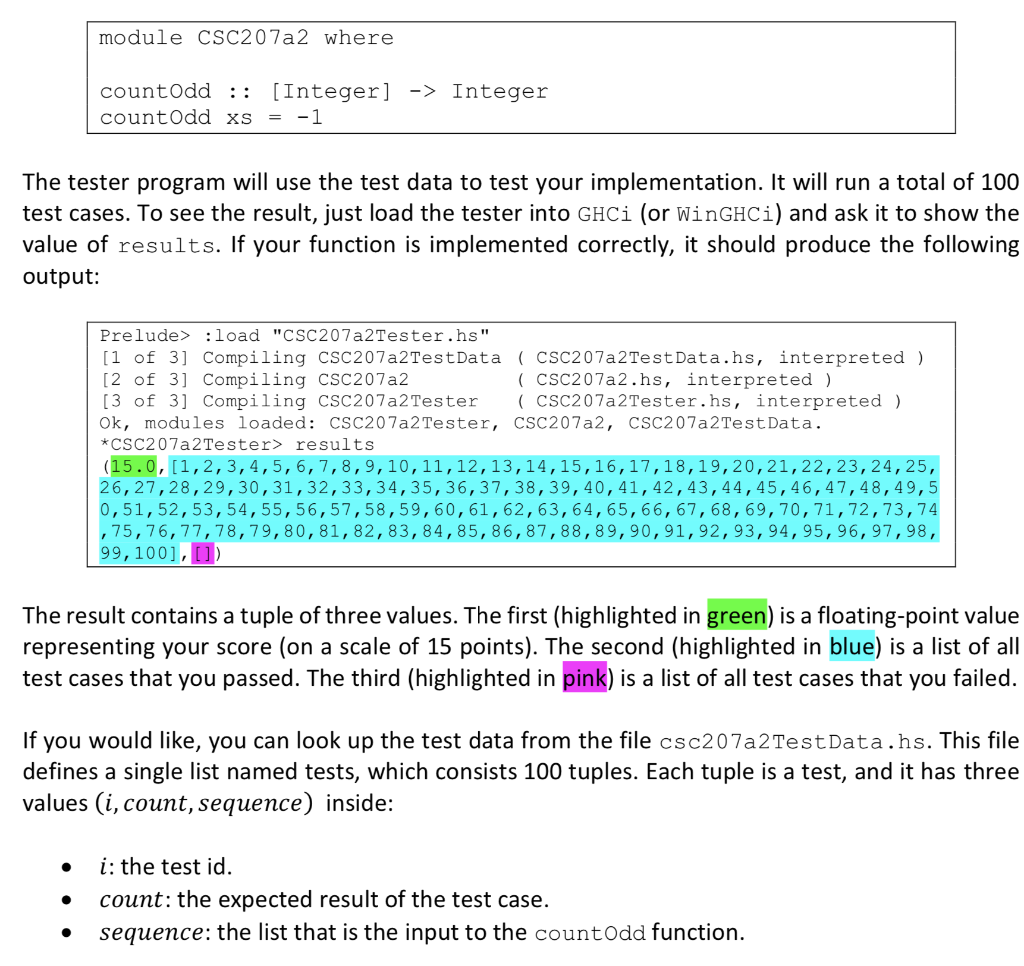

Below is the Template: the File CSC207A2.hs can be modified but the others.
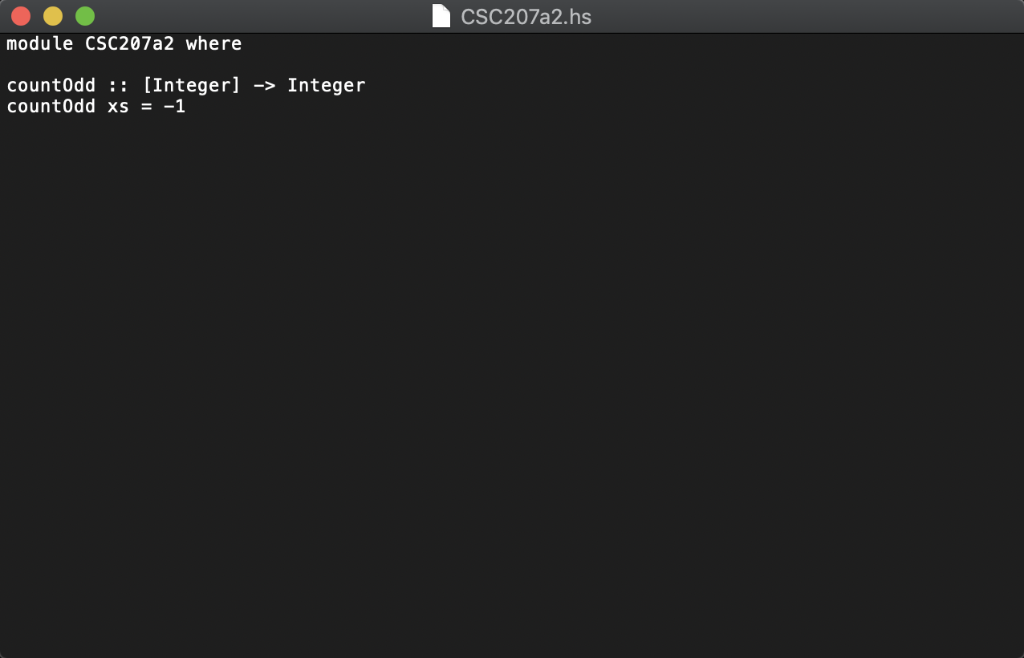
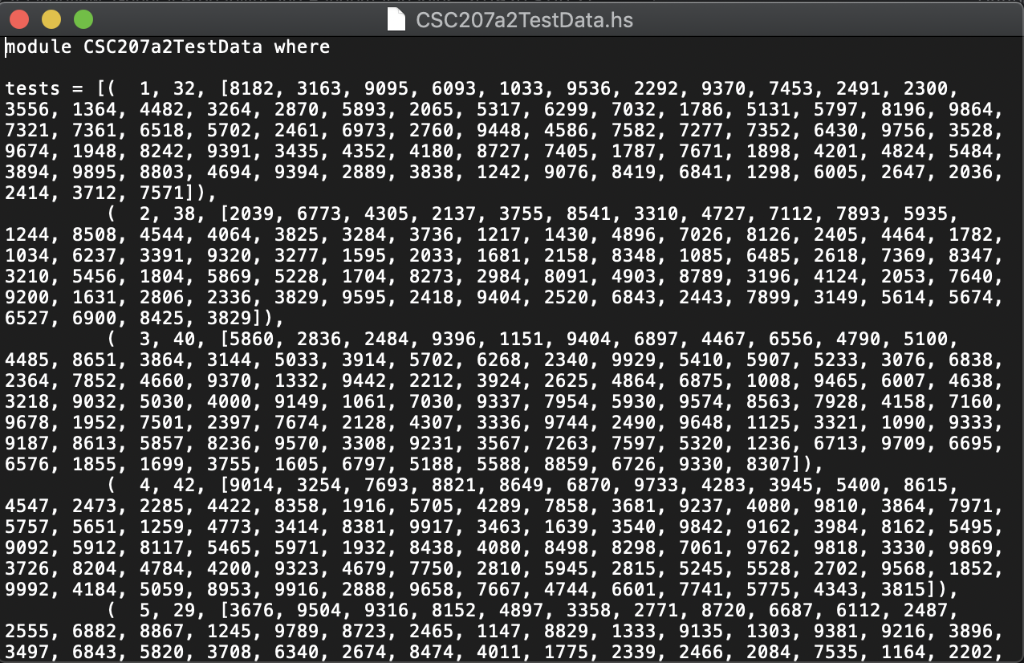
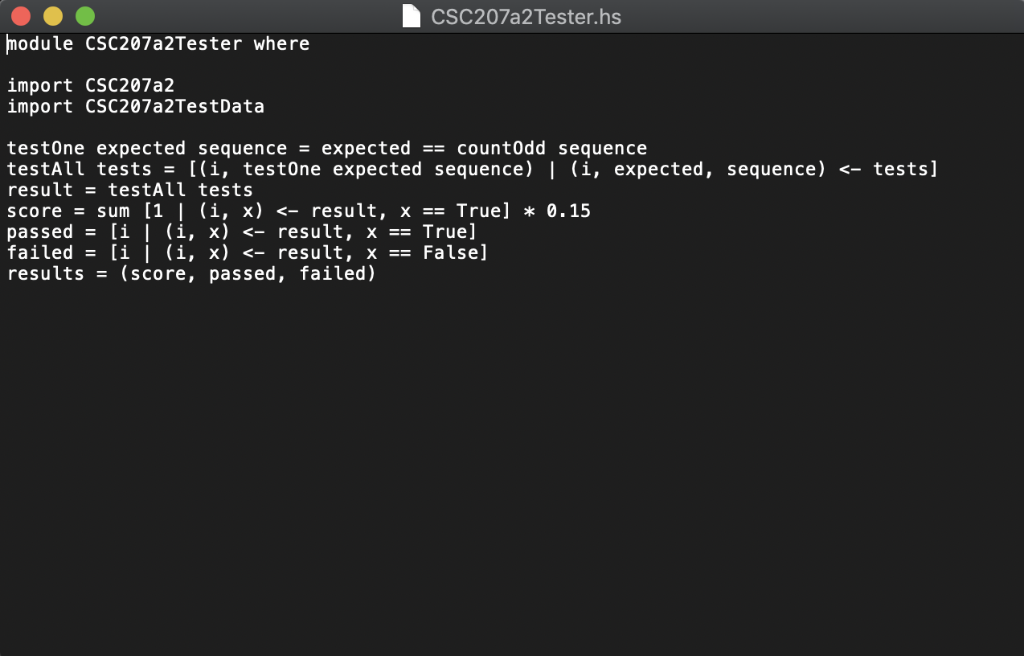
In this assignment, you are going to write a recursive function to count the number of odd elements in an Integer list. The signature of this function is: countOdd :: [Integer] -> Integer For example: countOdd [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] 3 countOdd [2, 4, 6, 8] > 0 countOdd [1, 3, 5, 1, 3, 5, 1, 3] > 8 Here is the algorithm to find the number of odd values recursively: There is no odd element in an empty list. If the list is not empty, let it be x: xs (that is, x is the head and xs is the tail), then countOdd xs 1+ countOdd xs if x is even ifx is odd coun todd (x:xs) Download the three files CSC207a2Tester.hs", "CSC207a2Te s t Data . hs", and "CSC207a2.hs" from Canvas and save them in the same folder. The first two files are the tester program and the testing data file, respectively. Do not modify these two files. The last file is the file you will work on. Note that you cannot rename this file and you cannot change the name of the function (otherwise the tester will not be able to pick up your implementation). However, you can change the names of the parameters if you like. Also note that the first line is required for the tester to locate your code so do not modify it. The file "cSC207a2.hs" contains, along with its signature, a dummy implementation of the function that returns an incorrect dummy value: module CSC207a2 where count The tester program will use the test data to test your implementation. It will run a total of 100 test cases. To see the result, just load the tester into GHCi (or WinGHC) and ask it to show the value of results. If your function is implemented correctly, it should produce the following output: Prelude> :load "CSC207a2Tester.hs" [1 of 3] Compiling CSC207 a2TestData CSC207a2TestData.hs, interpreted) [2 of 3] Compiling CSC207a2 [3 of 3] Compiling CSC207a2Tester CSC207a2Tester.hs, interpreted) Ok, modules loaded: CSC207a2Tester, CSC207a2, CSC207a2TestData. *CSC207a2Tester> results (15.0, [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25, 26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37, 38,39,40, 41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,5 0,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69, 70, 71,72,73,74 , 75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95, 96, 97,98 99,100],] CSC207a2.hs, interpreted ) The result contains a tuple of three values. The first (highlighted in green) is a floating-point value representing your score (on a scale of 15 points). The second (highlighted in blue) is a list of all test cases that you passed. The third (highlighted in pink) is a list of all test cases that you failed. If you would like, you can look up the test data from the file csc207a2TestData.hs. This file defines a single list named tests, which consists 100 tuples. Each tuple is a test, and it has three values (i, count, sequence) inside: i: the test id count: the expected result of the test case. * sequence: the list that is the input to the countOdd function. The following is the first few lines in the test data file: module CSC207a2TestData where tests-[1, 32, [8182, 3163, 9095, ..., 2414, 3712, 7571]) 2, 38, [2039, 6773, 4305, ...,6900, 8425, 3829]), 3, 40, [5860, 2836, 2484, ..,6726, 9330, 8307]), 4, 42, [9014, 3254, 7693, .,5775, 4343, 3815]), Notes: 1. Your function must be a recursive function (this is because there is no loop in Haskell) 2. Your program will be tested with similar but different data. The testing results will earn you up to 15 points (out of 20 points total) 3. The remaining 5 points will be awarded based on the structure, readability, and documentation of your implementation. Documentation should be in the form of Haskell 4. You cannot have any import statement in your program. And you can only use functions 5. The Prelude function odd (signature: odd : : Integral a => a-> Bool can be 6. There can be only one single function (the countodd function) defined in the comments, which start with --" and extend until the end of the line. in the Prelude module. use to test whether an integer is odd or not) "csc207a2.hs" file. No other helper function(s) is/are allowed. CSC207a2.hs module CSC207a2 where countOdd :: [Integer ->Integer countOdd xs =-1 CSC207a2TestData.hs module CSC207a2TestData where tests = [( 1, 32, [8182, 3163, 9095, 6093, 1033, 9536, 2292, 9370, 7453, 2491, 2300, 3556, 1364, 4482, 3264, 2870, 5893, 2065, 5317, 6299, 7032, 1786, 5131, 5797, 8196, 9864, 7321, 7361, 6518, 5702, 2461, 6973, 2760, 9448, 4586, 7582, 7277, 7352, 6430, 9756, 3528, 9674, 1948, 8242, 9391, 3435, 4352, 4180, 8727, 7405, 1787, 7671, 1898, 4201, 4824, 5484, 3894, 9895, 8803, 4694, 9394, 2889, 3838, 1242, 9076, 8419, 6841, 1298, 6005, 2647, 2036 2414, 3712, 7571]), (2, 38, [2039, 6773, 4305, 2137, 3755, 8541, 3310, 4727, 7112, 7893, 5935, 1244, 8508, 4544, 4064, 3825, 3284, 3736, 1217, 1430, 4896, 7026, 8126, 2405, 4464, 1782, 1034, 6237, 3391, 9320, 3277, 1595, 2033, 1681, 2158, 8348, 1085, 6485, 2618, 7369, 8347, 3210, 5456, 1804, 5869, 5228, 1704, 8273, 2984, 8091, 4903, 8789, 3196, 4124, 2053, 7640, 9200, 1631, 2806, 2336, 3829, 9595, 2418, 9404, 2520, 6843, 2443, 7899, 3149, 5614, 5674, 6527, 6900, 8425, 3829]), (3, 40, [5860, 2836, 2484, 9396, 1151, 9404, 6897, 4467, 6556, 4790, 5100, 4485, 8651, 3864, 3144, 5033, 3914, 5702, 6268, 2340, 9929, 5410, 5907, 5233, 3076, 6838, 2364, 7852, 4660, 9370, 1332, 9442, 2212, 3924, 2625, 4864, 6875, 1008, 9465, 6007, 4638, 3218, 9032, 5030, 4000, 9149, 1061, 7030, 9337, 7954, 5930, 9574, 8563, 7928, 4158, 7160, 9678, 1952, 7501, 2397, 7674, 2128, 4307, 3336, 9744, 2490, 9648, 1125, 3321, 1090, 9333, 9187, 8613, 5857, 8236, 9570, 3308, 9231, 3567, 7263, 7597, 5320, 1236, 6713, 9709, 6695, 6576, 1855, 1699, 3755, 1605, 6797, 5188, 5588, 8859, 6726, 9330, 8307]), (4, 42, [9014, 3254, 7693, 8821, 8649, 6870, 9733, 4283, 3945, 5400, 8615, 4547, 2473, 2285, 4422, 8358, 1916, 5705, 4289, 7858, 3681, 9237, 4080, 9810, 3864, 7971, 5757, 5651, 1259, 4773, 3414, 8381, 9917, 3463, 1639, 3540, 9842, 9162, 3984, 8162, 5495, 9092, 5912, 8117, 5465, 5971, 1932, 8438, 4080, 8498, 8298, 7061, 9762, 9818, 3330, 9869, 3726, 8204, 4784, 4200, 9323, 4679, 7750, 2810, 5945, 2815, 5245, 5528, 2702, 9568, 1852, 9992, 4184, 5059, 8953, 9916, 2888, 9658, 7667, 4744, 6601, 7741, 5775, 4343, 3815]), (5, 29, [3676, 9504, 9316, 8152, 4897, 3358, 2771, 8720, 6687, 6112, 2487, 2555, 6882, 8867, 1245, 9789, 8723, 2465, 1147, 8829, 1333, 9135, 1303, 9381, 9216, 3896, 3497, 6843, 5820, 3708, 6340, 2674, 8474, 4011, 1775, 2339, 2466, 2084, 7535, 1164, 2202, CSC207a2Tester.hs module CSC207a2Tester where import CSC207a2 import CSC207a2TestData testone expected sequence = expected =-countOdd sequence testAll tests[(i, testone expected sequence) | (i, expected, sequence)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


