Question
(i) Using the information from the Friday, October 26, 1996 Wall Street Journal, calculate the implied volatility from the S&P 100 index (put only). In
(i) Using the information from the Friday, October 26, 1996 Wall Street Journal, calculate
the implied volatility from the S&P 100 index (put only). In particular, calculate for all
strike/exercise prices between 660 and 680 for options expiring in December and January
only. Note that by design index options expire on the 3rd Friday of each month so
calculate the time to maturity accordingly (assume 365 day year). In addition, use the
risk-free rate (T-Bills) closest to expiration date of the option. Remember that the RF rate
is quoted in annualized terms.
! 2
Graph the implied volatility against the strike price on a separate graph for December and
January.
Is the volatility constant?
To solve for the implied volatility you may use trial and error by equating the theoretical
price from B-S (which you must compute) to the actual market (closing price) by trial
and error, i.e. varying , but I recommend using either the Solver or Goal Seek function
in Excel.
(ii) Use the above data to estimate delta. Create graph in excel.
(iii) Use the above data to estimate gamma. Create graph in excel.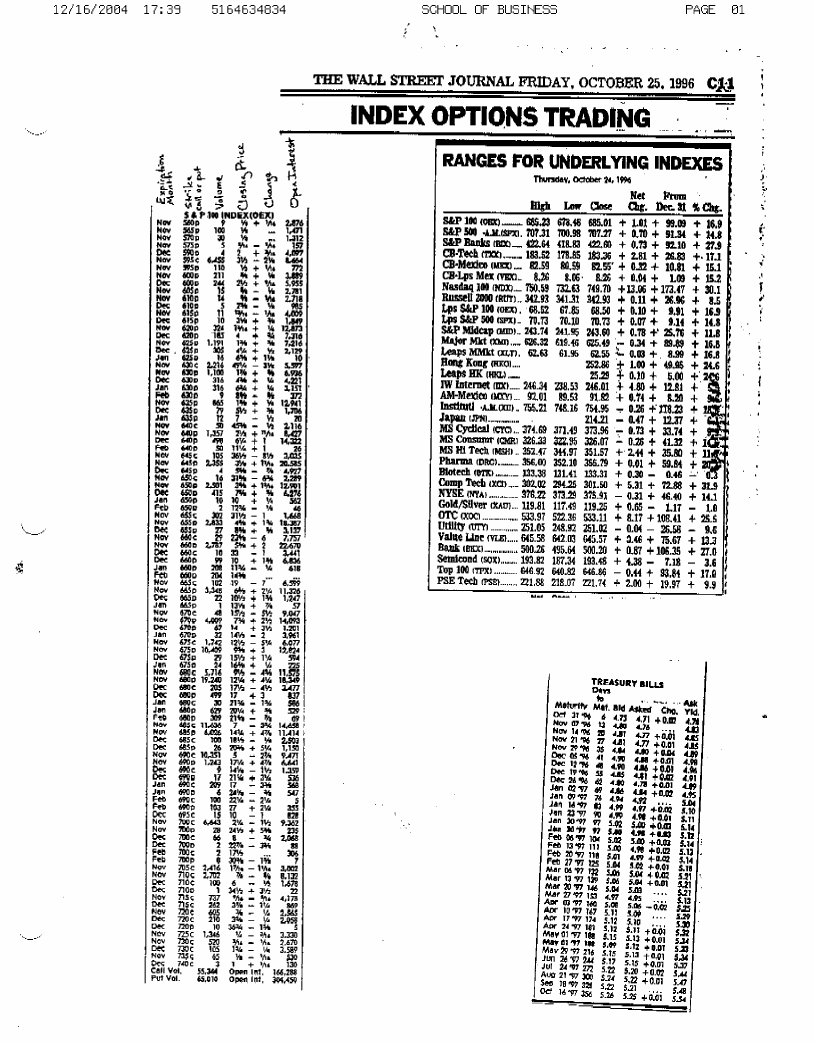

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


