Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
I would like you to make an effort to calculate the WACC for Marriott overall which requires following a couple of steps: First, we need
I would like you to make an effort to calculate the WACC for Marriott overall which requires following a couple of steps:
- First, we need to unlever Marriott's Equity Beta with the actual debt ratio and relever the unlevered asset beta with the target debt ratio.
- Second, calculate the cost of equity using CAPM.
- Third estimate the firm's cost of debt using the yield data in the case.
- Finally, estimate their WACC.
- After that is done, go through the same steps to calculate the WACC for the lodging and restaurant divisions using their respective comparable firms to estimate an average asset beta.
- Since there are no comparable firms for the contract services, consider how you might estimate their WACC using what you know about the other two divisions.
Case:

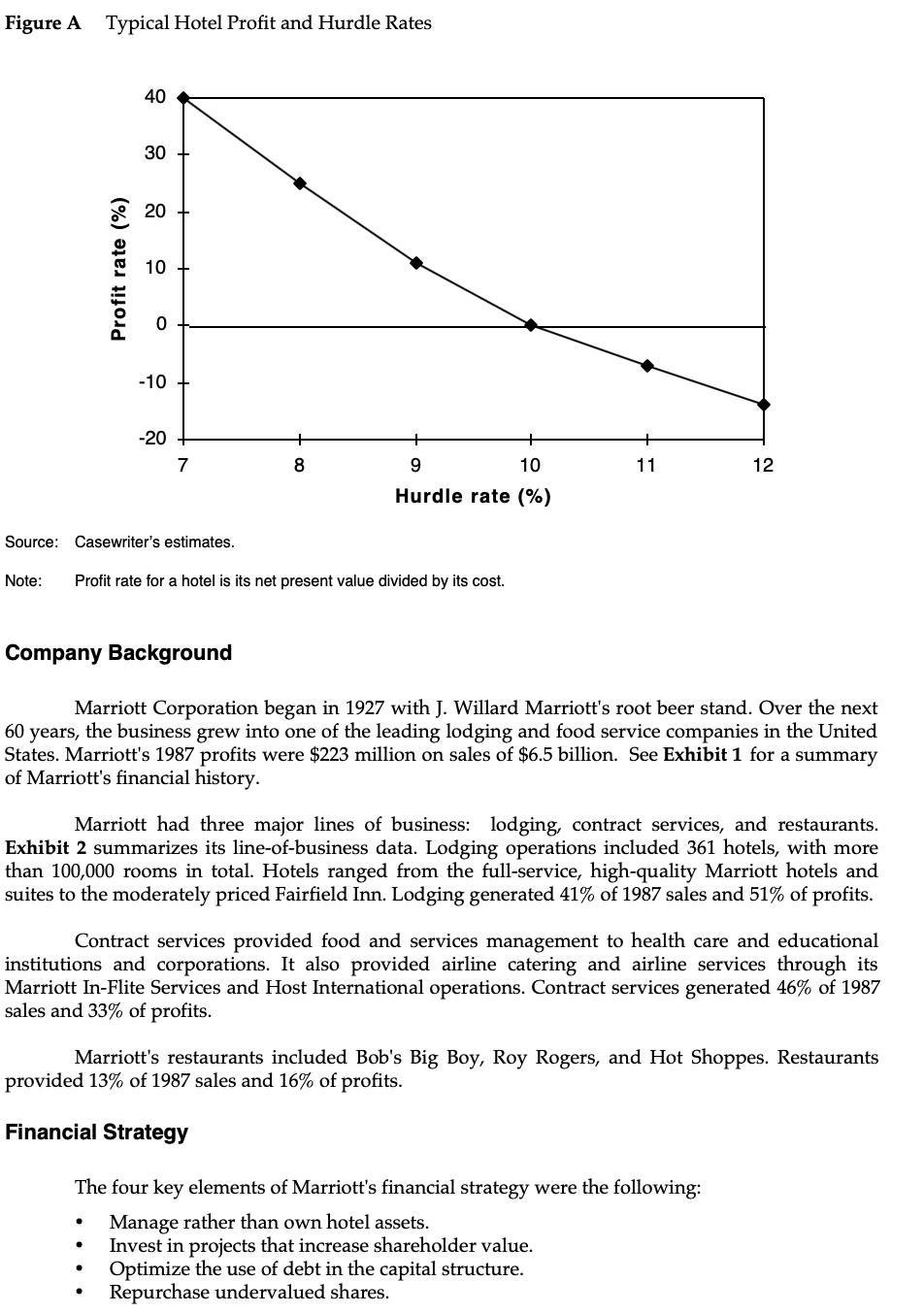

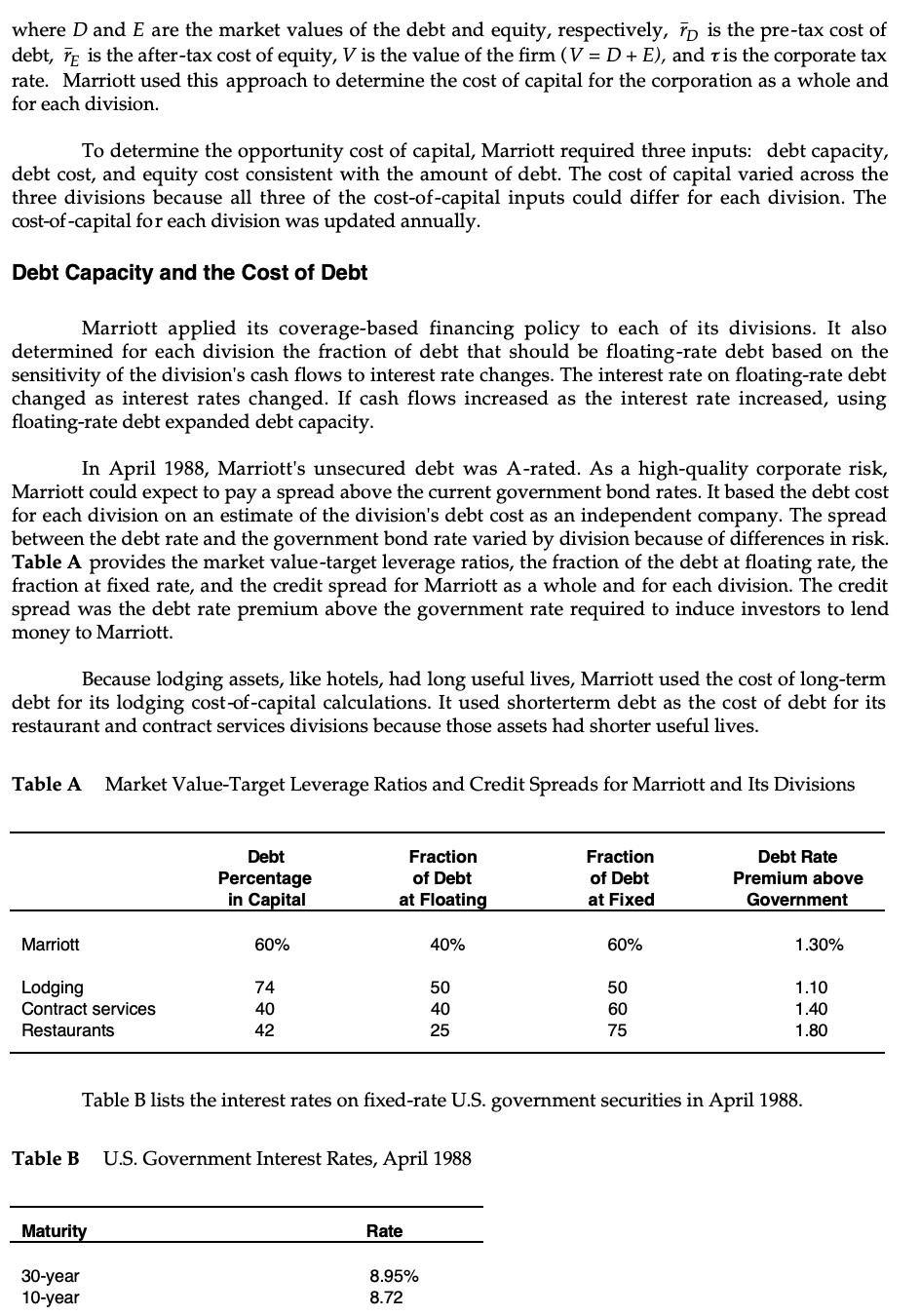

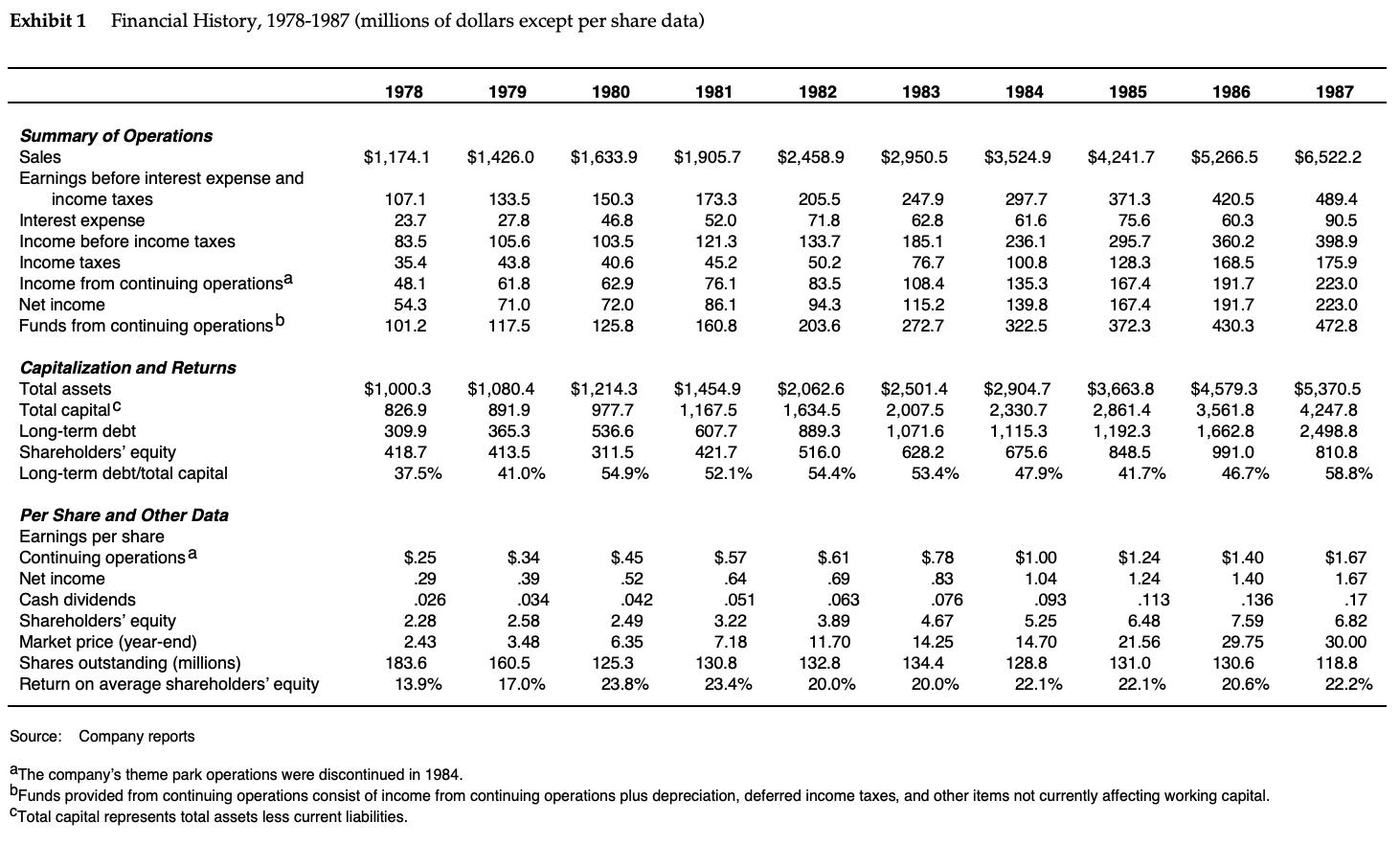
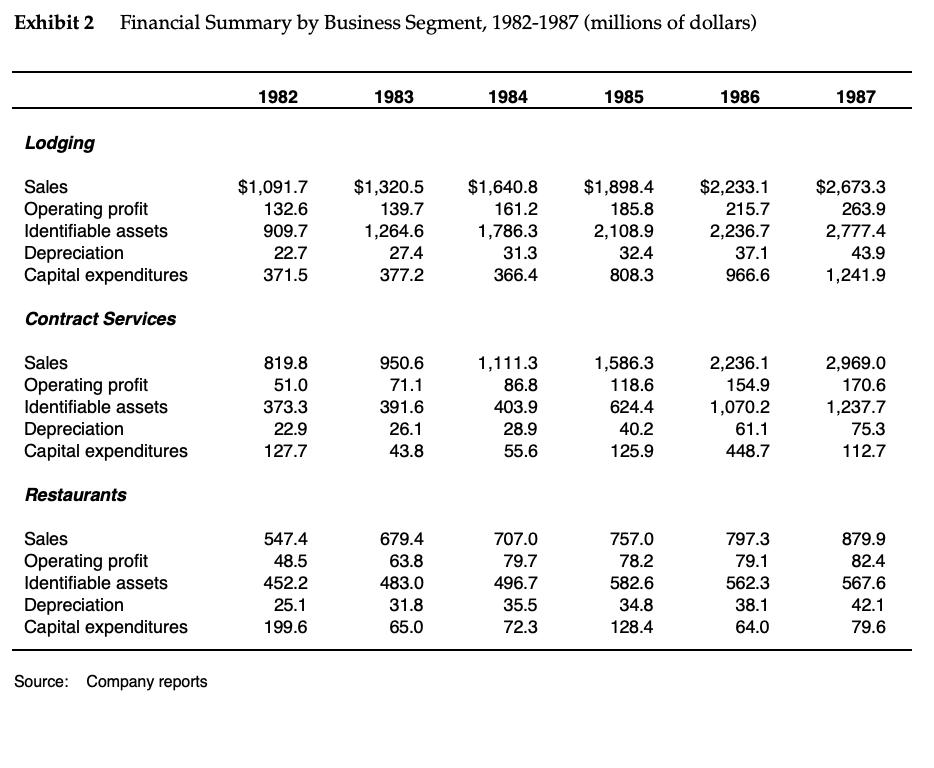
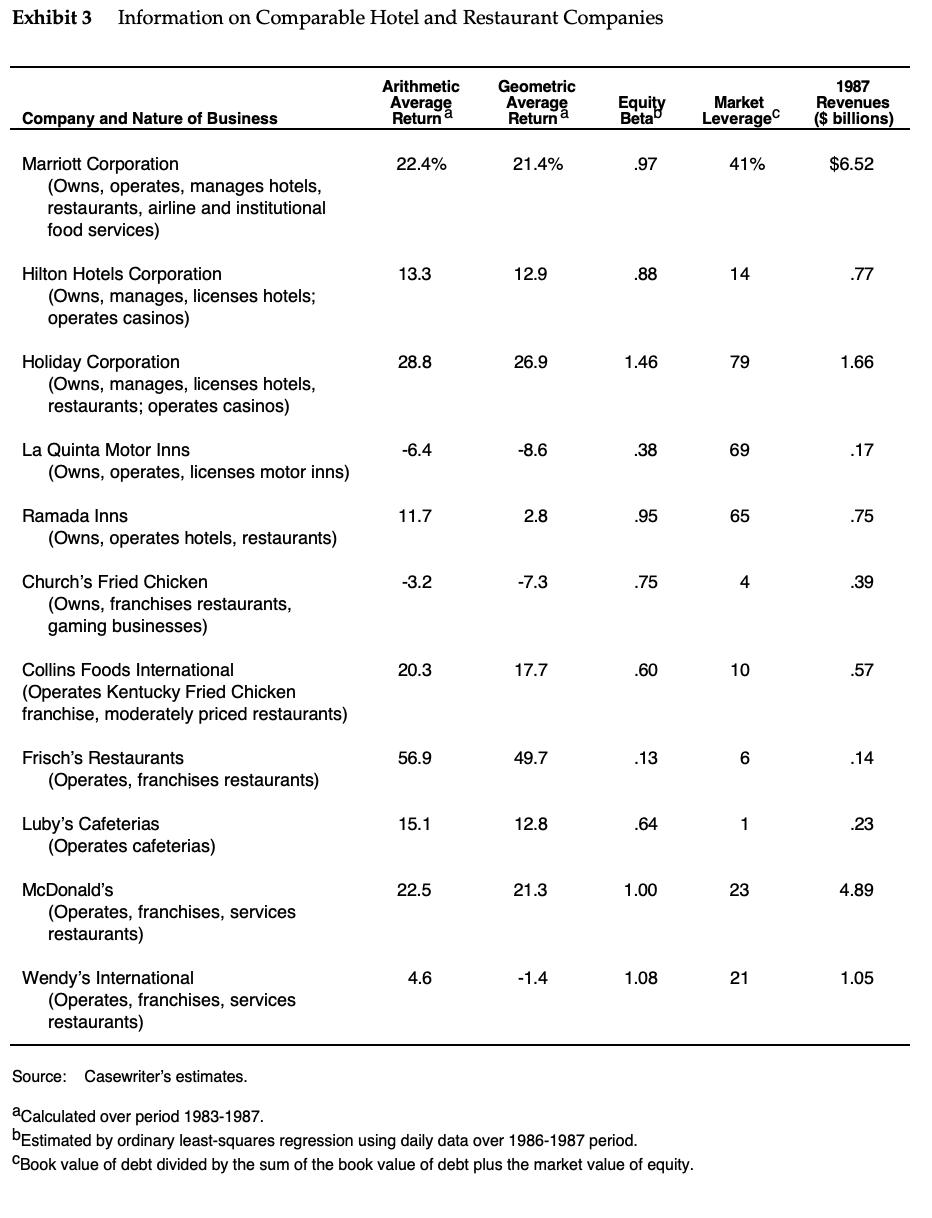
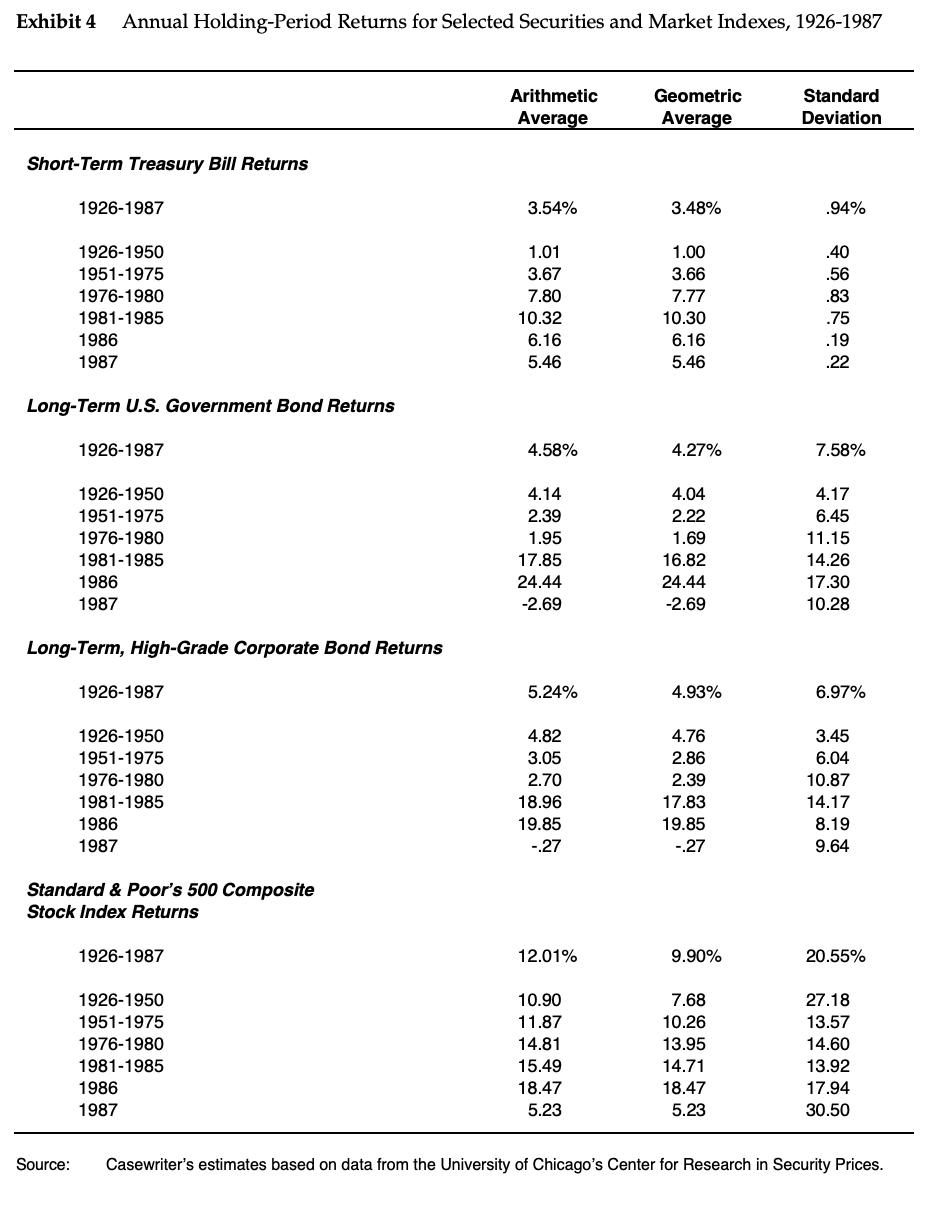
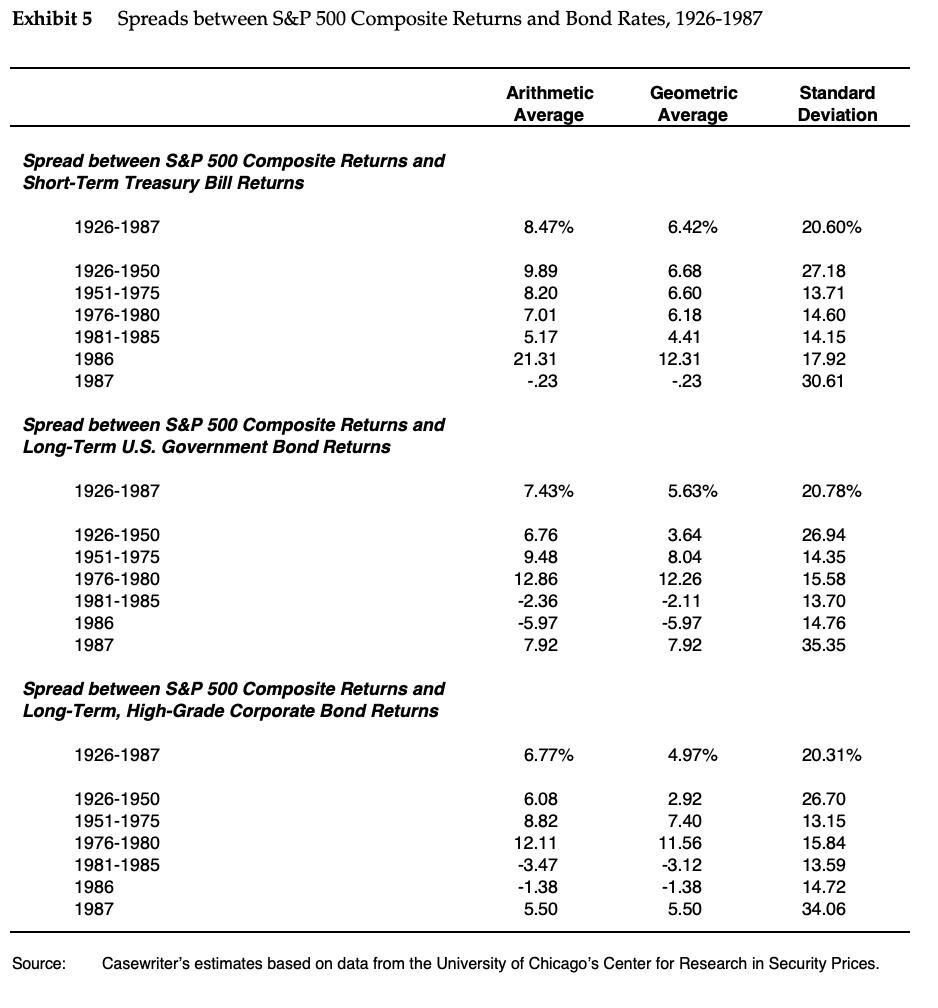
Marriott Corporation: The Cost of Capital In April 1988, Dan Cohrs, vice president of project finance at the Marriott Corporation, was preparing his annual recommendations for the hurdle rates at each of the firm's three divisions. Investment projects at Marriott were selected by discounting the appropriate cash flows by the appropriate hurdle rate for each division. In 1987, Marriott's sales grew by 24% and its return on equity stood at 22%. Sales and earnings per share had doubled over the previous four years, and the operating strategy was aimed at continuing this trend. Marriott's 1987 annual report stated: We intend to remain a premier growth company. This means aggressively developing appropriate opportunities within our chosen lines of business-lodging, contract services, and related businesses. In each of these areas our goal is to be the preferred employer, the preferred provider, and the most profitable company. Mr. Cohrs recognized that the divisional hurdle rates at Marriott would have a significant effect on the firm's financial and operating strategies. As a rule of thumb, increasing the hurdle rate by 1% (for example, from 12% to 12.12%), decreases the present value of project inflows by 1%. Because costs remained roughly fixed, these changes in the value of inflows translated into changes in the net present value of projects. Figure A shows the substantial effect of hurdle rates on the anticipated net present value of projects. If hurdle rates were to increase, Marriott's growth would be reduced as once profitable projects no longer met the hurdle rates. Alternatively, if hurdle rates decreased, Marriott's growth would accelerate. Marriott also considered using the hurdle rates to determine incentive compensation. Annual incentive compensation constituted a significant portion of total compensation, ranging from 30% to 50% of base pay. Criteria for bonus awards depended on specific job responsibilities but often included the earnings level, the ability of managers to meet budgets, and overall corporate performance. There was some interest, however, in basing the incentive compensation, in part, on a comparison of the divisional return on net assets and the market-based divisional hurdle rate. The compensation plan would then reflect hurdle rates, making managers more sensitive to Marriott's financial strategy and capital market conditions.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
The case youve provided discusses Marriott Corporations approach to determining hurdle rates for its divisions The hurdle rate is the minimum rate of return required by the company on its investments ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


