Question
Identify which question you are answering. Round all decimals. On January 1, Year 4 A purchased 80% of the outstanding common shares of B. The
Identify which question you are answering. Round all decimals.
On January 1, Year 4 A purchased 80% of the outstanding common shares of B.
The acquisition differential of $20,000 was allocated as follows:
Equipment with a remaining useful life of 5 years $10,000
Goodwill to the parent company only $10,000
On this date B had a balance of common shares of $100,000 and retained earnings of $180, 000. Accumulated depreciation on Bs equipment on this date was $20,000.
On July 1, Year 5 B purchased 60% of the outstanding common shares of C. The acquisition differential of $5,000 was allocated to equipment with a remaining useful life of 5 years. On this date C had a balance of common shares of $100,000 and retained earnings of $90, 000. Accumulated depreciation on Cs equipment on this date was $8,000.
A and B use the cost method to account for their investments. All companies have a 40% tax rate and a December 31 fiscal year-end.
During Year 6 intercompany sales were as follows:
A selling to B $40,000
C selling to B $20,000
Beginning Inventory Profits:
A selling to B $5,000
C selling to B $3,000
Ending Inventory Profits:
A selling to B $8,000
C selling to B $4,000
On June 30, Year 4 A sold land to C and recorded a gain on sale of $10,000. This land was sold by C in Year 6.
On June 30, Year 5 A sold equipment to B and recorded a gain on sale of $5,000. The equipment had a remaining useful life at the time of the sale of 5 years.
B charged C $2,000 for management fees in Year 6. B records this as Sales and C records it as General expenses.
The recoverable amount of goodwill as of December 31, Year 6 was determined to be $7,000. The impairment was charged in Year 6. C declared dividends but has not paid them yet. All other dividends have been paid.
The separate income statements, statements of retained earnings and balance sheets for each company for Year 6 are:
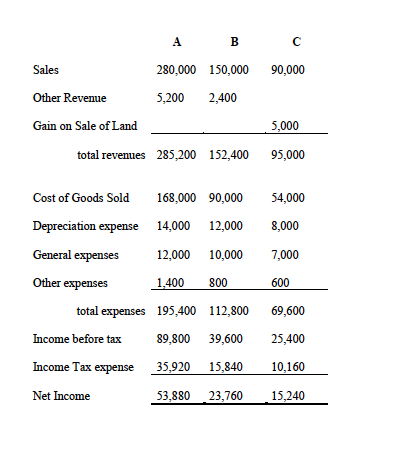
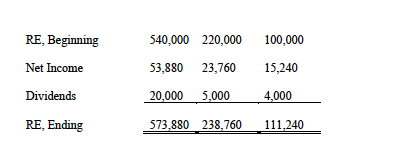
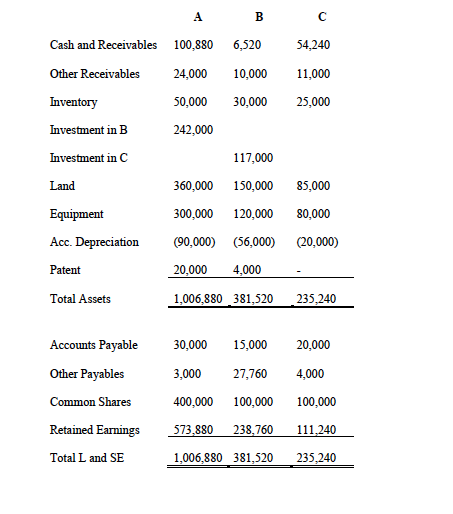
1) Calculate consolidated net income attributable to A and NCI (13 marks)
2) Calculate consolidated retained earnings for January 1, Year 6 (10 marks)
3) Calculate consolidated retained earnings for December 31, Year 6 (do NOT simply use a statement of retained earnings, you must calculate it). (10 marks)
4) Calculate NCI for December 31, Year 6 (9 marks)
5) Prepare a consolidated income statement for year ended December 31, Year 6 (18 marks)
6) Prepare a consolidated balance sheet for December 31, Year 6 (23 marks)
Sales A 280,000 5,200 B 150,000 2,400 90,000 Other Revenue Gain on Sale of Land 5,000 total revenues 285,200 152,400 95,000 168,000 54,000 Cost of Goods Sold Depreciation expense General expenses 8,000 14,000 12,000 90,000 12,000 10,000 800 7,000 Other expenses 1,400 600 total expenses Income before tax Income Tax expense 195,400 112,800 89,800 39,600 35,920 15,840 69,600 25,400 10,160 Net Income 53,880 23,760 15,240 RE, Beginning 540,000 220,000 100,000 Net Income 53,880 23,760 15,240 Dividends 20,000 5,000 4,000 RE, Ending 573,880 238,760 111,240 Cash and Receivables 100,880 6,520 54,240 Other Receivables 24,000 50,000 10,000 30,000 11,000 25,000 Inventory Investment in B 242,000 Investment in C 117,000 Land 150,000 120,000 $5,000 80,000 Equipment 360,000 300,000 (90,000) 20,000 Acc. Depreciation (20,000) (56,000) 4,000 Patent Total Assets 1,006,880 381,520 235,240 Accounts Payable 30,000 3,000 400,000 Other Payables 15,000 27,760 100.000 20,000 4,000 Common Shares 100.000 Retained Earnings 573,880 238,760 111,240 Total L and SE 1,006,880 381,520 235,240 Sales A 280,000 5,200 B 150,000 2,400 90,000 Other Revenue Gain on Sale of Land 5,000 total revenues 285,200 152,400 95,000 168,000 54,000 Cost of Goods Sold Depreciation expense General expenses 8,000 14,000 12,000 90,000 12,000 10,000 800 7,000 Other expenses 1,400 600 total expenses Income before tax Income Tax expense 195,400 112,800 89,800 39,600 35,920 15,840 69,600 25,400 10,160 Net Income 53,880 23,760 15,240 RE, Beginning 540,000 220,000 100,000 Net Income 53,880 23,760 15,240 Dividends 20,000 5,000 4,000 RE, Ending 573,880 238,760 111,240 Cash and Receivables 100,880 6,520 54,240 Other Receivables 24,000 50,000 10,000 30,000 11,000 25,000 Inventory Investment in B 242,000 Investment in C 117,000 Land 150,000 120,000 $5,000 80,000 Equipment 360,000 300,000 (90,000) 20,000 Acc. Depreciation (20,000) (56,000) 4,000 Patent Total Assets 1,006,880 381,520 235,240 Accounts Payable 30,000 3,000 400,000 Other Payables 15,000 27,760 100.000 20,000 4,000 Common Shares 100.000 Retained Earnings 573,880 238,760 111,240 Total L and SE 1,006,880 381,520 235,240Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


