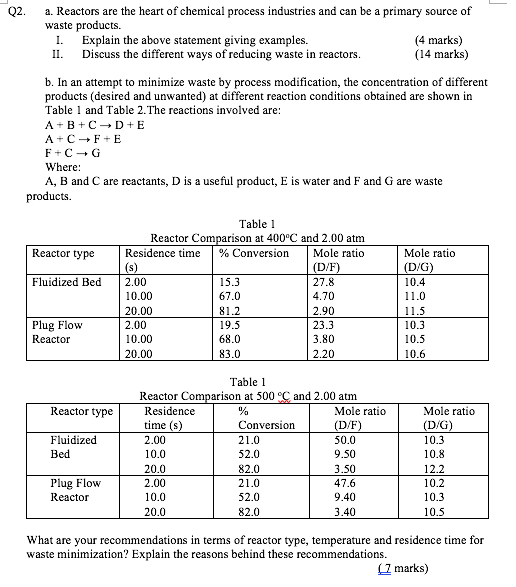
II. Q2 a. Reactors are the heart of chemical process industries and can be a primary source of waste products. 1. Explain the above statement giving examples. (4 marks) Discuss the different ways of reducing waste in reactors. (14 marks) b. In an attempt to minimize waste by process modification, the concentration of different products (desired and unwanted) at different reaction conditions obtained are shown in Table 1 and Table 2. The reactions involved are: A+B+ CD+E A+ C + F + E F+C+G Where: A, B and C are reactants, D is a useful product, E is water and F and G are waste products. Reactor type Fluidized Bed Table 1 Reactor Comparison at 400C and 2.00 atm Residence time % Conversion Mole ratio (s) (D/F) 2.00 15.3 27.8 10.00 67.0 4.70 20.00 81.2 2.90 2.00 19.5 23.3 10.00 68.0 3.80 20.00 83.0 2.20 Mole ratio (D/G) 10.4 11.0 11.5 10.3 10.5 10.6 Plug Flow Reactor Reactor type Fluidized Bed Table 1 Reactor Comparison at 500 C and 2.00 atm Residence % Mole ratio time (s) Conversion (D/F) 2.00 21.0 50.0 10.0 52.0 9.50 20.0 82.0 3.50 2.00 21.0 47.6 10.0 52.0 9.40 20.0 82.0 3.40 Mole ratio (D/G) 10.3 10.8 12.2 10.2 10.3 10.5 Plug Flow Reactor What are your recommendations in terms of reactor type, temperature and residence time for waste minimization? Explain the reasons behind these recommendations. (1 marks) II. Q2 a. Reactors are the heart of chemical process industries and can be a primary source of waste products. 1. Explain the above statement giving examples. (4 marks) Discuss the different ways of reducing waste in reactors. (14 marks) b. In an attempt to minimize waste by process modification, the concentration of different products (desired and unwanted) at different reaction conditions obtained are shown in Table 1 and Table 2. The reactions involved are: A+B+ CD+E A+ C + F + E F+C+G Where: A, B and C are reactants, D is a useful product, E is water and F and G are waste products. Reactor type Fluidized Bed Table 1 Reactor Comparison at 400C and 2.00 atm Residence time % Conversion Mole ratio (s) (D/F) 2.00 15.3 27.8 10.00 67.0 4.70 20.00 81.2 2.90 2.00 19.5 23.3 10.00 68.0 3.80 20.00 83.0 2.20 Mole ratio (D/G) 10.4 11.0 11.5 10.3 10.5 10.6 Plug Flow Reactor Reactor type Fluidized Bed Table 1 Reactor Comparison at 500 C and 2.00 atm Residence % Mole ratio time (s) Conversion (D/F) 2.00 21.0 50.0 10.0 52.0 9.50 20.0 82.0 3.50 2.00 21.0 47.6 10.0 52.0 9.40 20.0 82.0 3.40 Mole ratio (D/G) 10.3 10.8 12.2 10.2 10.3 10.5 Plug Flow Reactor What are your recommendations in terms of reactor type, temperature and residence time for waste minimization? Explain the reasons behind these recommendations. (1 marks)







