Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
I'm having difficulty with this question. Please Help M. Anthony, LLP, produces music in a studio in London. The cost of producing one typical song
I'm having difficulty with this question. Please Help 
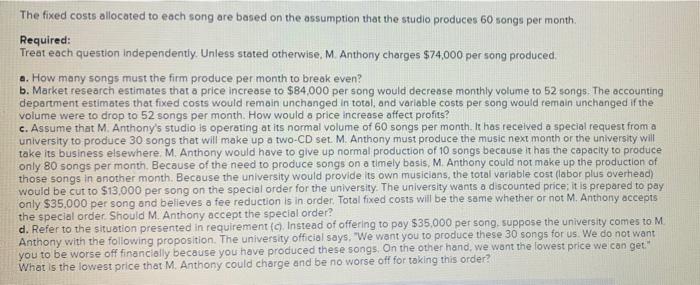
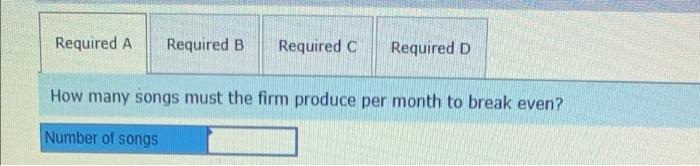
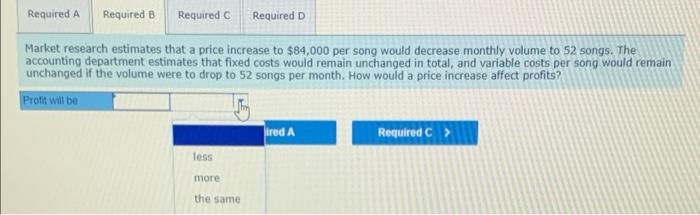
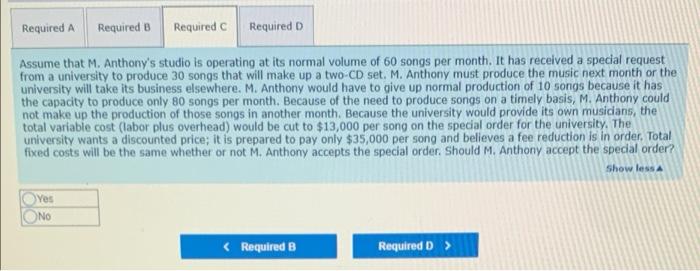
M. Anthony, LLP, produces music in a studio in London. The cost of producing one typical song follows Average cost per Song: Labor, including musicians and technicians Variable overhead, including clerical support Fixed overhead Marketing and administrative costs (all fixed) Total cost per song $16,400 2,480 20,400 16,400 $55,600 The fixed costs allocated to each song are based on the assumption that the studio produces 60 songs per month Required: The fixed costs allocated to each song are based on the assumption that the studio produces 60 songs per month Required: Treat each question Independently. Unless stated otherwise, M. Anthony charges $74,000 per song produced a. How many songs must the firm produce per month to break even? b. Market research estimates that a price increase to $84,000 per song would decrease monthly volume to 52 songs. The accounting department estimates that fixed costs would remain unchanged in total, and variable costs per song would remain unchanged if the volume were to drop to 52 songs per month. How would a price increase affect profits? c. Assume that M. Anthony's studio is operating at its normal volume of 60 songs per month. It has received a special request from a university to produce 30 songs that will make up a two-CD set M. Anthony must produce the music next month or the university will take its business elsewhere. M. Anthony would have to give up normal production of 10 songs because it has the capacity to produce only 80 songs per month. Because of the need to produce songs on a timely basis, M. Anthony could not make up the production of those songs in another month Because the university would provide its own musicians, the total variable cost (labor plus overhead) would be cut to $13,000 per song on the special order for the university. The university wants a discounted price; it is prepared to pay only $35.000 per song and believes a fee reduction is in order. Total fixed costs will be the same whether or not M. Anthony accepts the special order . Should M. Anthony accept the special order? d. Refer to the situation presented in requirement (Instead of offering to pay $35,000 per song, suppose the university comes to M Anthony with the following proposition. The university official says. "We want you to produce these 30 songs for us. We do not want you to be worse off financially because you have produced these songs. On the other hand, we want the lowest price we can get." What is the lowest price that M. Anthony could charge and be no worse off for taking this order? Required A Required B Required c Required D How many songs must the firm produce per month to break even? Number of songs Required A Required B Required Required Market research estimates that a price increase to $84,000 per song would decrease monthly volume to S2 songs. The accounting department estimates that fixed costs would remain unchanged in total, and variable costs per song would remain unchanged if the volume were to drop to 52 songs per month. How would a price increase affect profits? Profit will be ired A Required c > less more the same Required a Required B Required Required D Assume that M. Anthony's studio is operating at its normal volume of 60 songs per month. It has received a special request from a university to produce 30 songs that will make up a two-CD set. M. Anthony must produce the music next month or the university will take its business elsewhere. M. Anthony would have to give up normal production of 10 songs because it has the capacity to produce only 80 songs per month. Because of the need to produce songs on a timely basis, M. Anthony could not make up the production of those songs in another month. Because the university would provide its own musicians, the total variable cost (labor plus overhead) would be cut to $13,000 per song on the special order for the university. The university wants a discounted price; it is prepared to pay only $35,000 per song and believes a fee reduction is in order. Total fixed costs will be the same whether or not M. Anthony accepts the special order. Should M. Anthony accept the special order? Show less Yes NO Required A Required B Required Required D Refer to the situation presented in requirement (c). Instead of offering to pay $35,000 per song, suppose the university comes to M. Anthony with the following proposition. The university official says, "We want you to produce these 30 songs for us. We do not want you to be worse off financially because you have produced these songs. On the other hand, we want the lowest price we can get." What is the lowest price that M. Anthony could charge and be no worse off for taking this order? (Round your final answer to the nearest whole dollar.) Show less Lowest price 





Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


