Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
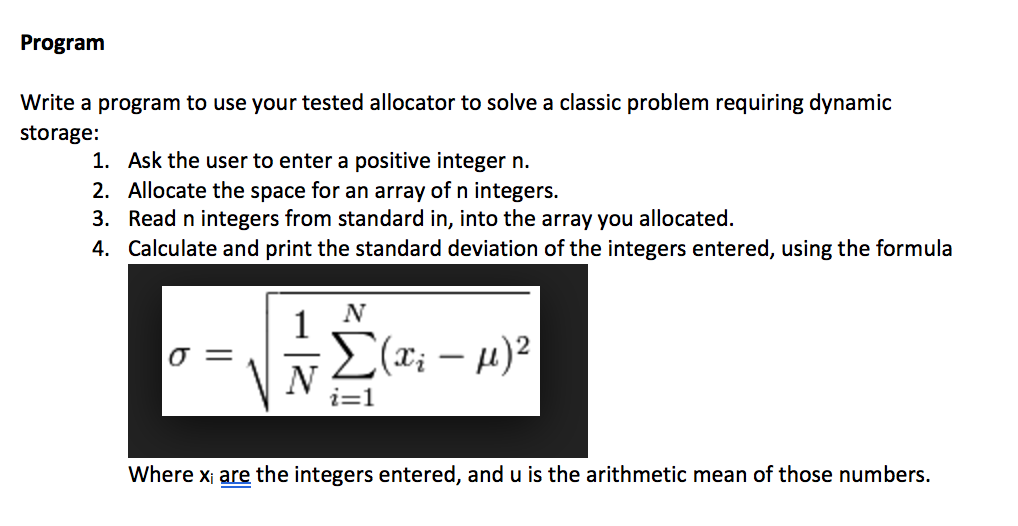
Question
1 Approved Answer
Implementation You must follow these implementation guidelines: 1. Define a struct to represent an allocation block: struct Block of bytes in the data section int



Implementation You must follow these implementation guidelines: 1. Define a struct to represent an allocation block: struct Block of bytes in the data section int block size struct Block next block //pointer to next block 2. Determine the size of a Block value using sizeof(struct Bock) and assign it to a global const variable. We refer to this value as the "overhead size 3. Determine the size of a void and save it in another const global 4. Create a global pointer struct Block free head, which will always point to the first block in the free list. 5. Create a function void my initialize heaplint size), which uses malloc to initialize a buffer of a given size to use in your custom allocator. (This is the only time you can use malloc in the entire program.) Your global free hand should point to this buffer, and you should initialize the head with appropriate values for block-size and next block. 6. Create a function void* my alloc (int size), which fills an allocation request of size bytes and returns a pointer to the data portion of the block used to satisfy the request. a. Walk the free list starting at free hand, looking for a block with a large enough size to fit the request. If no blocks can be found, return 0 (null). Use first fit heuristic b. size can be any positive integer value, but any blocks you use must have a data size that is a multiple of your void* size. So if a void s 4 bytes, and the function is told to allocate a 2 bytes block, you would actually find a block with 4 bytes of data and use that, with 2 bytes being fragmentation. c. Once you have found a block to fit the data size, decide whether you need to split that block i. f you do, then find the byte location of where the new block will start based on the size of the block you are splitting and the size of the allocation request. Initialize a new block at the at location by assigning its block size and setting its next block pointer to null. Reduce the size of the original block appropriately i. If you cannot split the block, then you need to redirect pointers to the block to point to the block that follows it, as if you are removing a node from a singly linked list
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


