Question
import java.io.*; import java.util.*; // Performs lookups and word completion using the WordTree class. // Also provides method to read from a file. public class

import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Performs lookups and word completion using the WordTree class. // Also provides method to read from a file.
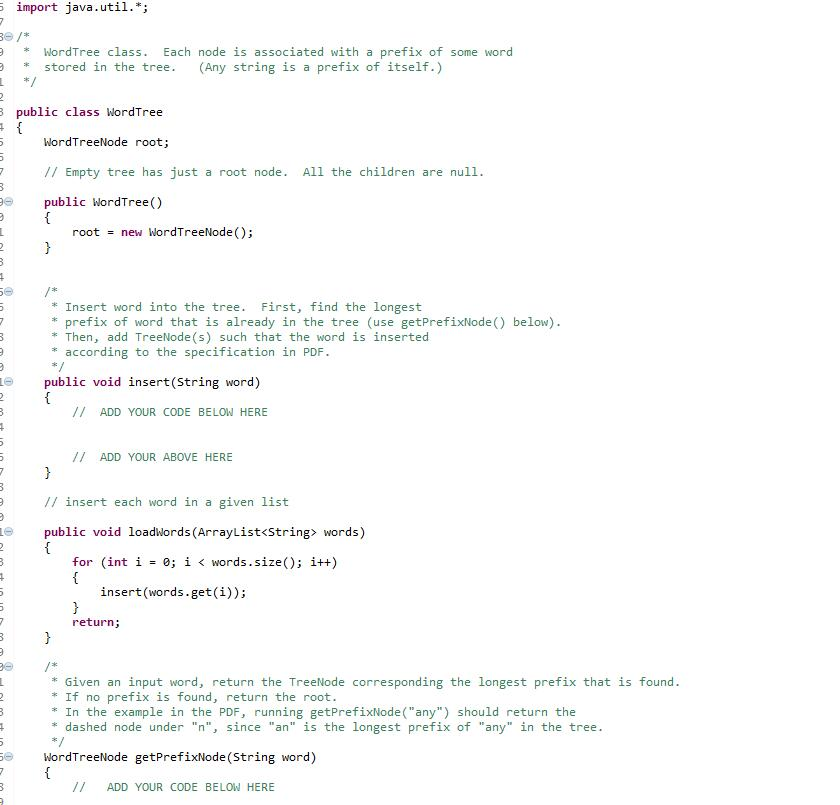
public class TesterA3starter { public static ArrayList readWordsFromFile(String filename) { ArrayList words = new ArrayList(); try { File file = new File(filename); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(file); /* Strip non-alphanumeric \\W characters * That is, remove any characters other than a to z, A to Z, and 0 to 9 * * See https://regexone.com/lesson/character_ranges * which lists the '\W' symbol in the right panel as any non alphanumeric character * and lists the '+' symbols as meaning any non-zero number of repetitions */ scanner.useDelimiter("\\W+"); while (scanner.hasNext()) { words.add(scanner.next()); } } catch(Exception e) { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); System.exit(1); } return words; }
public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
/* * You can test your code with the input file below. * For example, if you wish to share your outputs on the discussion board * that you obtained using the given text file, that's fine. * * You will need to put a different pathname in here. */ // String fileName = "C:\\Users\\Michael\\Dropbox\\Eclipse (Yoga)\\250\\src\\assignments2017\\a3\\bodybuilding.txt"; // list = readWordsFromFile(fileName); // String fileName = "//home//ramchalamkr//bodybuilding.txt"; // list = readWordsFromFile(fileName);
// For debugging, we suggest you use a smaller set of words such as the ones shown in the PDF. Collections.addAll(list, "a", "and", "ax", "dog", "door", "dot");
WordTree wordTree = new WordTree(); wordTree.loadWords(list);
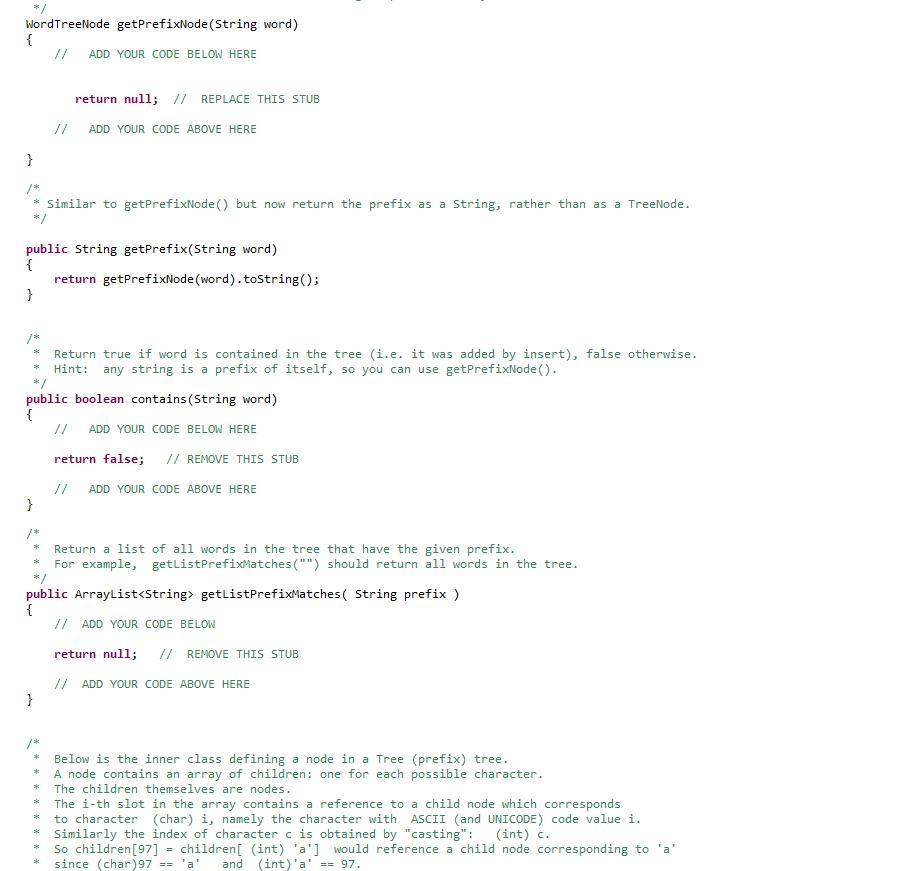
System.out.println("list contains " + list.size() + " words");
// Test if the contains() method works, print input and output // // e.g.: try door, an, cat (should return true, false, and false respectively)
System.out.println(); System.out.println("--- Test contains() method. Correct answer shown in brackets. -----" ); System.out.println("WordTree contains 'door' = " + wordTree.contains("door") + " (true)" ); System.out.println("WordTree contains 'and' = " + wordTree.contains("and") + " (true)"); System.out.println("WordTree contains 'cat' = " + wordTree.contains("cat") + " (false)"); System.out.println("WordTree contains 'dog' = " + wordTree.contains("dog") + " (true)"); System.out.println("WordTree contains 'ax' = " + wordTree.contains("ax") + " (true)"); System.out.println("WordTree contains 'dot' = " + wordTree.contains("dot") + " (true)"); System.out.println("WordTree contains 'a' = " + wordTree.contains("a") + " (true)"); System.out.println("WordTree contains 'an' = " + wordTree.contains("an") + " (false)");
/* Test if getPrefix works, print input and output * ex: "door", "any", "cat" should return "door", "an", and "" respectively * */ System.out.println(""); System.out.println("----- Test getPrefix()"); System.out.println("longest prefix of door = " + wordTree.getPrefix("door")); System.out.println("longest prefix of any = " + wordTree.getPrefix("any")); System.out.println("longest prefix of cat = " + wordTree.getPrefix("cat"));
/* Test getListPrefixMatches, print input and output * Try prefixes "a", "do", "c" (should return [a, and, ax], [dog, door, dot], [ ] respectively) */ System.out.println(""); System.out.println("----- Test getListPrefixMatches() i.e. autocomplete "); System.out.println("a = " + wordTree.getListPrefixMatches("a")); System.out.println("do = " + wordTree.getListPrefixMatches("do")); System.out.println("c = " + wordTree.getListPrefixMatches("c"));
} }
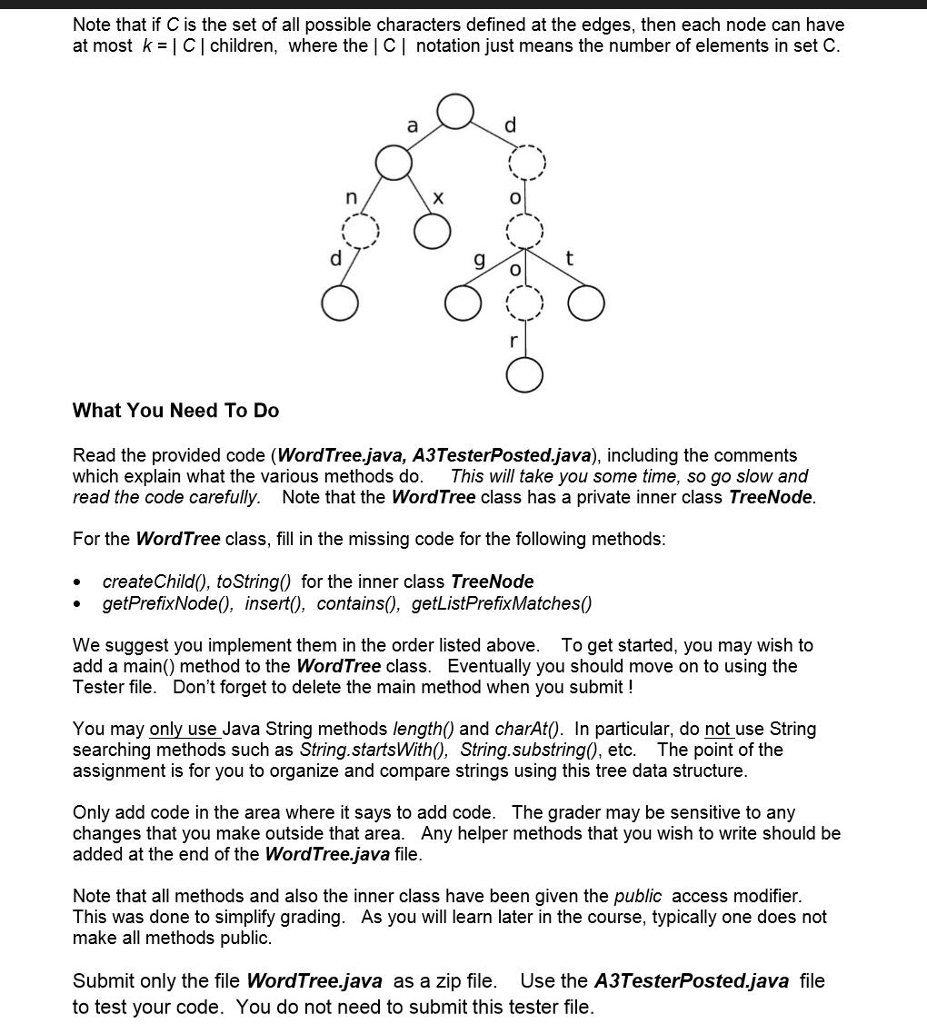
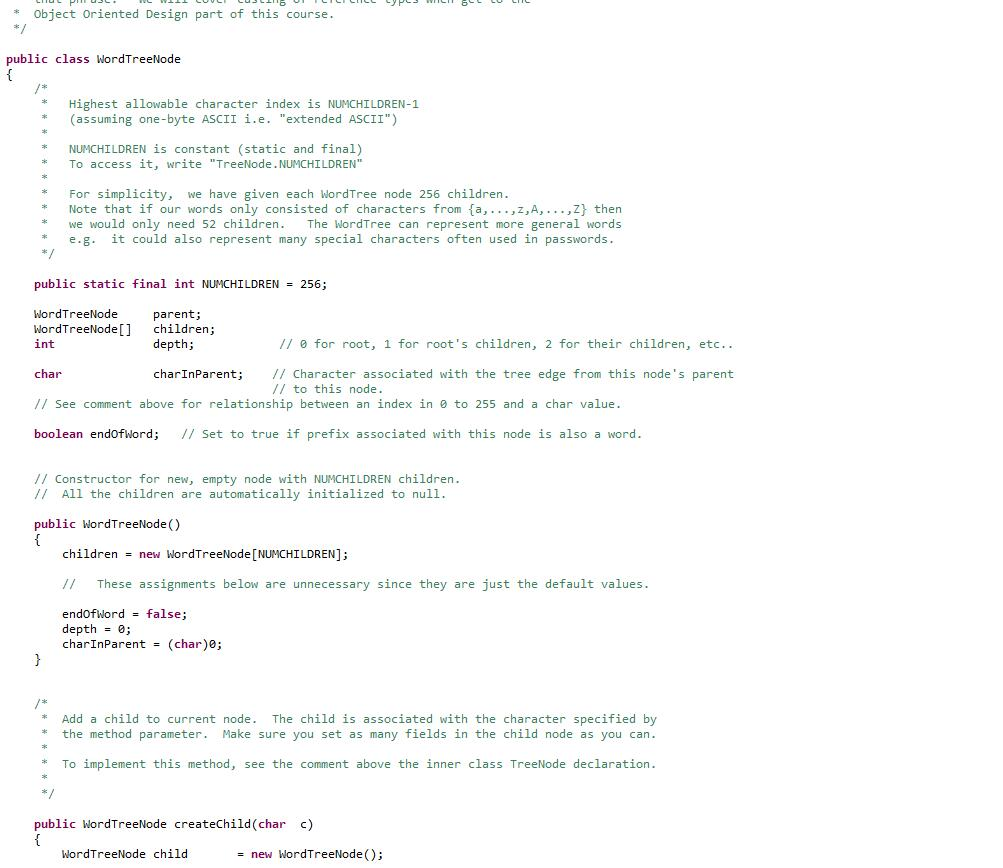
WordTree Data Structure Here we define a special kind of rooted tree that we use to efficiently index words by storing their prefixes. The main property of this tree is that each edge corresponds to a character. Thus the path from the root of the tree to any node in the tree defines a string. The string defined by each node is a prefix of all strings defined by the descendents of that node Below is an example tree. It contains the following words: a, and, ax, dog, door, dot. You will note that the dashed nodes correspond to prefixes in the tree (an, d, do, doo) that are not in our list of words. The tree must also keep track of this distinction by storing for each node whether it corresponds to a word or notStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


