Question
In a Java AVL tree class, some functions below are given. Question : how to compile // copy constructor public AVLTree(AVLTree tree) ? // searches
In a Java AVL tree class, some functions below are given.
Question : how to compile // copy constructor public AVLTree(AVLTree tree) ?
// searches the tree for a key public Boolean Contains(Comparable item)
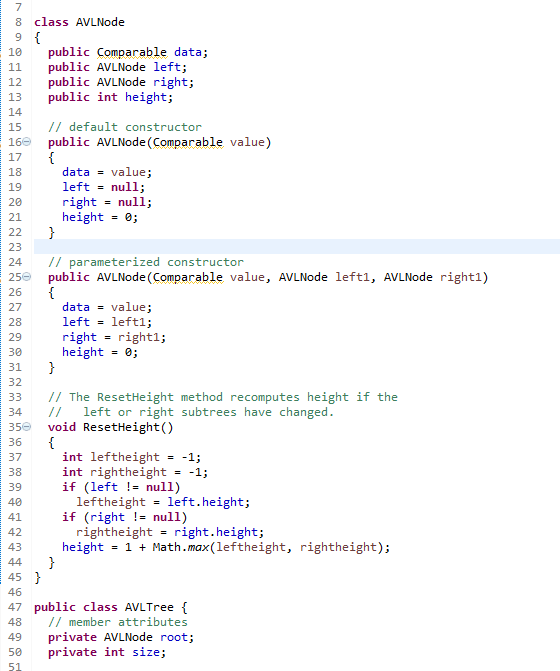
class AVLNode { public Comparable data; public AVLNode left; public AVLNode right; public int height; // default constructor public AVLNode(Comparable value) { data = value; left = null; right = null; height = 0; } // parameterized constructor public AVLNode(Comparable value, AVLNode left1, AVLNode right1) { data = value; left = left1; right = right1; height = 0; } // The ResetHeight method recomputes height if the // left or right subtrees have changed. void ResetHeight() { int leftheight = -1; int rightheight = -1; if (left != null) leftheight = left.height; if (right != null) rightheight = right.height; height = 1 + Math.max(leftheight, rightheight); } }
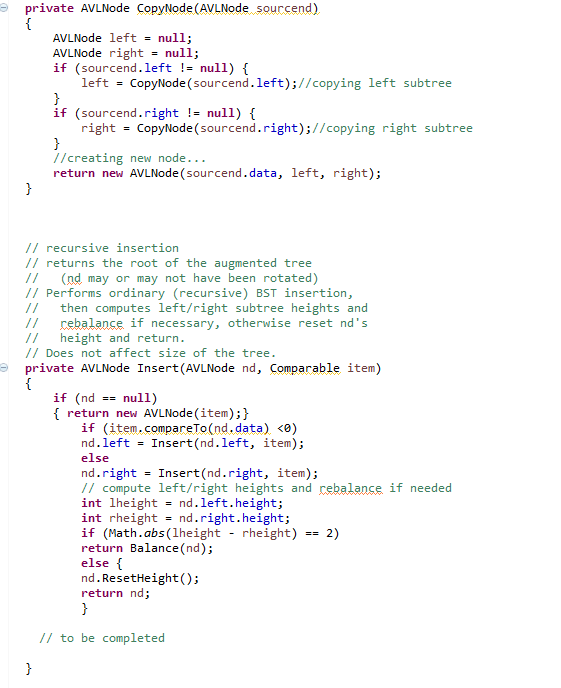
public class AVLTree { // member attributes private AVLNode root; private int size; // private methods // recursive helper function for deep copy // creates a new node based on sourcend's contents, // recurses to create left and right children. // returns a reference to the newly created node. // The new tree should have the same structure as the source tree private AVLNode CopyNode(AVLNode sourcend) { AVLNode left = null; AVLNode right = null; if (sourcend.left != null) { left = CopyNode(sourcend.left);//copying left subtree } if (sourcend.right != null) { right = CopyNode(sourcend.right);//copying right subtree } //creating new node... return new AVLNode(sourcend.data, left, right); } // recursive insertion // returns the root of the augmented tree // (nd may or may not have been rotated) // Performs ordinary (recursive) BST insertion, // then computes left/right subtree heights and // rebalance if necessary, otherwise reset nd's // height and return. // Does not affect size of the tree. private AVLNode Insert(AVLNode nd, Comparable item) { if (nd == null) { return new AVLNode(item);} if (item.compareTo(nd.data)
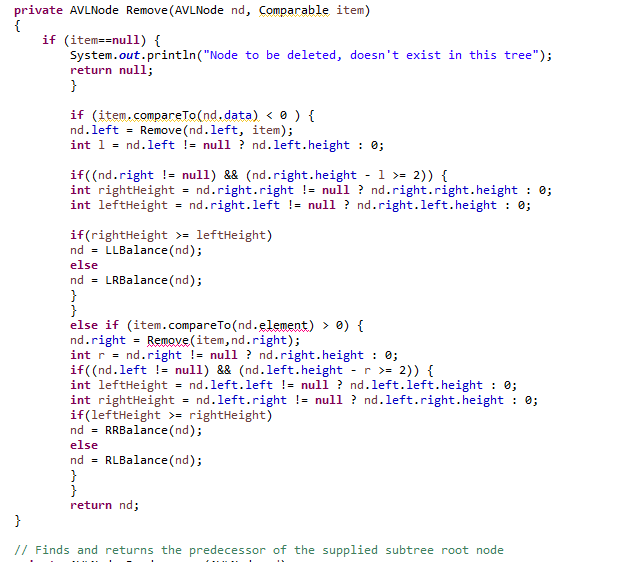
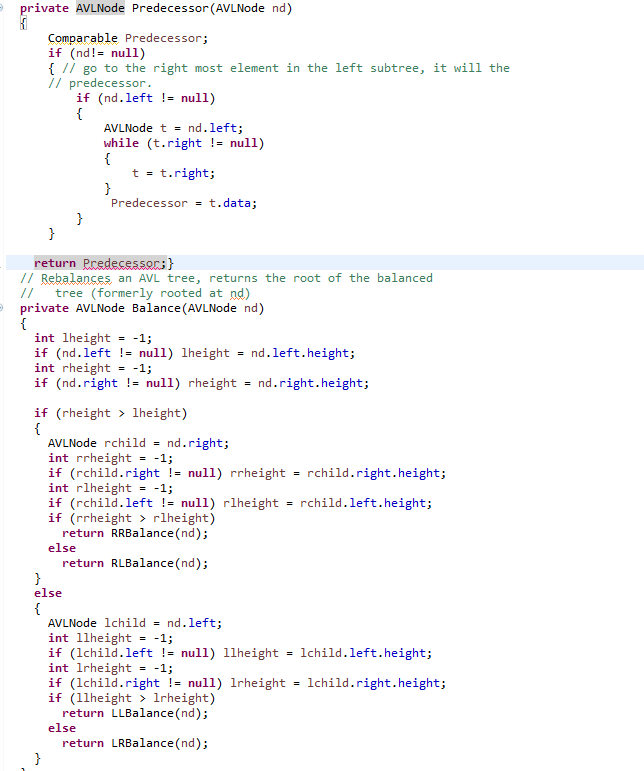
// to be completed } // recursive remove // returns root of the supplied (possibly rebalanced) tree // with the key value removed (if found) // return null if not found private AVLNode Remove(AVLNode nd, Comparable item) { if (item==null) { System.out.println("Node to be deleted, doesn't exist in this tree"); return null; } if (item.compareTo(nd.data) = 2)) { int rightHeight = nd.right.right != null ? nd.right.right.height : 0; int leftHeight = nd.right.left != null ? nd.right.left.height : 0; if(rightHeight >= leftHeight) nd = LLBalance(nd); else nd = LRBalance(nd); } } else if (item.compareTo(nd.element) > 0) { nd.right = Remove(item,nd.right); int r = nd.right != null ? nd.right.height : 0; if((nd.left != null) && (nd.left.height - r >= 2)) { int leftHeight = nd.left.left != null ? nd.left.left.height : 0; int rightHeight = nd.left.right != null ? nd.left.right.height : 0; if(leftHeight >= rightHeight) nd = RRBalance(nd); else nd = RLBalance(nd); } } return nd; } // Finds and returns the predecessor of the supplied subtree root node private AVLNode Predecessor(AVLNode nd) { Comparable Predecessor; if (nd!= null) { // go to the right most element in the left subtree, it will the // predecessor. if (nd.left != null) { AVLNode t = nd.left; while (t.right != null) { t = t.right; } Predecessor = t.data; } }
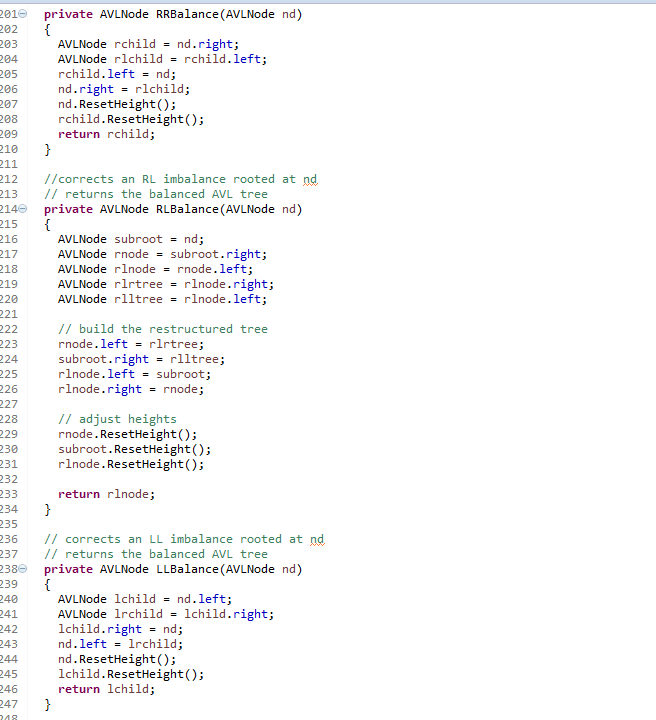
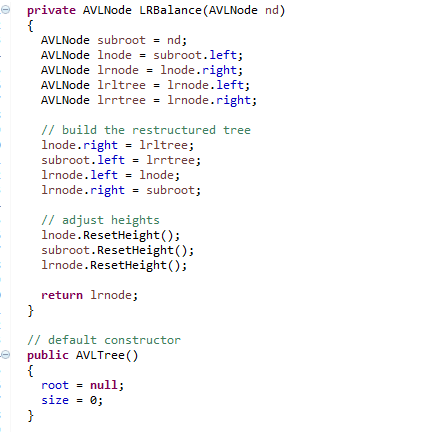
return Predecessor;} // Rebalances an AVL tree, returns the root of the balanced // tree (formerly rooted at nd) private AVLNode Balance(AVLNode nd) { int lheight = -1; if (nd.left != null) lheight = nd.left.height; int rheight = -1; if (nd.right != null) rheight = nd.right.height; if (rheight > lheight) { AVLNode rchild = nd.right; int rrheight = -1; if (rchild.right != null) rrheight = rchild.right.height; int rlheight = -1; if (rchild.left != null) rlheight = rchild.left.height; if (rrheight > rlheight) return RRBalance(nd); else return RLBalance(nd); } else { AVLNode lchild = nd.left; int llheight = -1; if (lchild.left != null) llheight = lchild.left.height; int lrheight = -1; if (lchild.right != null) lrheight = lchild.right.height; if (llheight > lrheight) return LLBalance(nd); else return LRBalance(nd); } } // corrects an RR imbalance rooted at nd // returns the balanced AVL tree private AVLNode RRBalance(AVLNode nd) { AVLNode rchild = nd.right; AVLNode rlchild = rchild.left; rchild.left = nd; nd.right = rlchild; nd.ResetHeight(); rchild.ResetHeight(); return rchild; } //corrects an RL imbalance rooted at nd // returns the balanced AVL tree private AVLNode RLBalance(AVLNode nd) { AVLNode subroot = nd; AVLNode rnode = subroot.right; AVLNode rlnode = rnode.left; AVLNode rlrtree = rlnode.right; AVLNode rlltree = rlnode.left; // build the restructured tree rnode.left = rlrtree; subroot.right = rlltree; rlnode.left = subroot; rlnode.right = rnode; // adjust heights rnode.ResetHeight(); subroot.ResetHeight(); rlnode.ResetHeight(); return rlnode; } // corrects an LL imbalance rooted at nd // returns the balanced AVL tree private AVLNode LLBalance(AVLNode nd) { AVLNode lchild = nd.left; AVLNode lrchild = lchild.right; lchild.right = nd; nd.left = lrchild; nd.ResetHeight(); lchild.ResetHeight(); return lchild; } //corrects an LR imbalance rooted at nd // returns the balanced AVL tree private AVLNode LRBalance(AVLNode nd) { AVLNode subroot = nd; AVLNode lnode = subroot.left; AVLNode lrnode = lnode.right; AVLNode lrltree = lrnode.left; AVLNode lrrtree = lrnode.right; // build the restructured tree lnode.right = lrltree; subroot.left = lrrtree; lrnode.left = lnode; lrnode.right = subroot; // adjust heights lnode.ResetHeight(); subroot.ResetHeight(); lrnode.ResetHeight(); return lrnode; } // default constructor public AVLTree() { root = null; size = 0; } // copy constructor public AVLTree(AVLTree tree) { // to be completed // should set member attributes and perform deep copy } // gets the number of items in the tree public int Size() { return size; } // gets the height of the tree (root) public int Height() { if (root == null) return -1; return root.height; } // searches the tree for a key public Boolean Contains(Comparable item) { // to be completed return false; } // Inserts an item into the tree. public boolean Insert(Comparable item) { boolean result = false; if(Insert(root.left, item) != null) { result = true; } return result;
} // Removes an item from the tree. // Returns true if the item is successfully removed // Returns false if the item cannot be removed (i.e. not found) public boolean Remove(Comparable item) { // to be completed return false; } // removes all items in the tree public void RemoveAll() { // to be completed } // returns a formatted string, reverse in-order traversal // (as done in lab 5) public String PrintTree() { return PrintTree(root, 0, new StringBuilder()).toString(); } // recursive helper for PrintTree private StringBuilder PrintTree(AVLNode nd, int level, StringBuilder tree) { if (nd == null) { return tree; } else { PrintTree(nd.right, 1+level, tree); for (int i = 0; i 8 class AVLNo de 10 public comparable data; 11 public de left 12 public de right 13 public int height; 14 15 default constructor 16e public AVLNode (Comparable value) 17 data value 18 left null 19 20 righ null 21 heigh 22 23 24 parameterized constructor 25 public AVLNode parable value AVLNode left1. AVLNo right 1) de 26 data value 27 left left1. 28 29 right right1 30 heigh 0; 31 32 The ResetHeight method recomputes height if the 33 34 left or right subtrees have changed. 35 void ResetHeight() 36 37 int lefth eight -1; int rightheight -1; 38 89 if (left null) leftheight left. height 41 if (right null) rightheight righ heigh 42 43 heigh ath. max (left height rightheight) 45 46 47 public class Tree 48 member attributes 49 private de root 50 private int size 51
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


