Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
In C language I will upvote/ downvote the answer if it is correct or spam Functions int main(int argc, char** argv) Parameters Parameters: int argc,
In C language
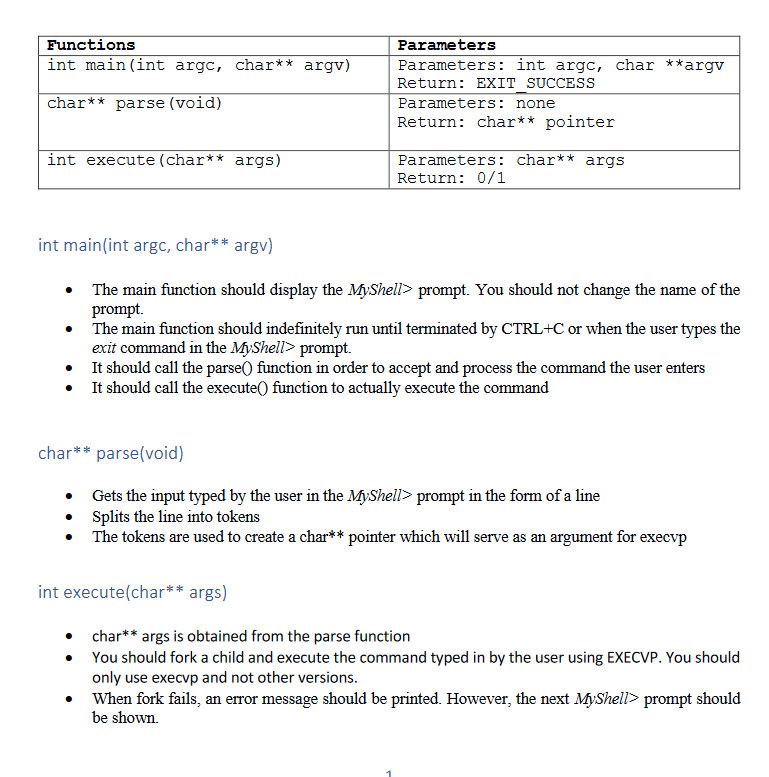

I will upvote/ downvote the answer if it is correct or spam
Functions int main(int argc, char** argv) Parameters Parameters: int argc, char **argv Return: EXIT_SUCCESS Parameters: none Return: char** pointer char** parse (void) int execute (char** args) Parameters: char** args Return: 0/1 int main(int argc, char** argv) The main function should display the MyShell> prompt. You should not change the name of the prompt. The main function should indefinitely run until terminated by CTRL+C or when the user types the exit command in the MyShell> prompt. It should call the parse() function in order to accept and process the command the user enters It should call the execute() function to actually execute the command char** parse(void) Gets the input typed by the user in the MyShell> prompt in the form of a line Splits the line into tokens The tokens are used to create a char** pointer which will serve as an argument for execvp int execute(char** args) char** args is obtained from the parse function You should fork a child and execute the command typed in by the user using EXECVP. You should only use execup and not other versions. When fork fails, an error message should be printed. However, the next MyShell> prompt should be shown. When execvp is not successful, an error message should be printed, and the child should terminate. However, the next MyShell> prompt should be shown. When an empty command is entered the next MyShell> prompt should be shown. When the command exit is entered by the user, the main program must exit [You may or may not fork in order to implement the exit command). The parent should wait for the child to terminate before it accepts another command. You can use wait or waitpid for this. Other guidelines or useful hints: User command plus arguments will not exceed 255 characters Each command may have different number of arguments Variables stored in Stack cannot be accessed outside of a function procedure, while data dynamically allocated in Heap can be accessed by any function within one program. Only one command should be typed at the MyShell> prompt, no pipelining of commands Commands run in MyShell> will assume the user's original path: Type "echo $PATH" to see the current path variable setting. Myshell is not responsible for finding the path for the commands or files. If the user makes a mistake typing a command and/or its arguments, execup should simply fail to run the command. A simple error should be shown, but next MyShell>prompt should be displayed. Please note that complicated commands like "cd may not work as shown in the sample output. If execvp was not successful (e.g., a wrong command), remember to exit(0) the child processStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


